Learning About Soil
... This layer keeps the ground damp by preventing too much water from evaporating ...
... This layer keeps the ground damp by preventing too much water from evaporating ...
Chapter 14 Final Review Weathering and Erosion
... What is Weathering? • Weathering is a process that occurs in nature that disintegrates and decomposes rocks • This happens when the temperature changes or atmospheric and environmental agents change. • Weathering can change the physical or chemical composition of rock materials. ...
... What is Weathering? • Weathering is a process that occurs in nature that disintegrates and decomposes rocks • This happens when the temperature changes or atmospheric and environmental agents change. • Weathering can change the physical or chemical composition of rock materials. ...
2974b719ed02e1d05b6180accf6894840a8bcccc
... 1. This is also known as the “parent rock” underneath the soil horizon bedrock 2. This is a wind deposit (there are 4 types of these that we studied) dunes 3. This is the movement of weathered material erosion 4. This is a flowing river of ice glacier 5. This is organic matter that provides nutrient ...
... 1. This is also known as the “parent rock” underneath the soil horizon bedrock 2. This is a wind deposit (there are 4 types of these that we studied) dunes 3. This is the movement of weathered material erosion 4. This is a flowing river of ice glacier 5. This is organic matter that provides nutrient ...
Chapter 5 Test - Bloomsburg Area School District
... weathered rock deposited at the edge of a glacier? ...
... weathered rock deposited at the edge of a glacier? ...
Soil Student Notes
... Important in vigor and vitality of plant - Carries ________________________________________________________ - Improves ______________________________________________________ - Improves ______________________________________________________ - Promotes _________________________________________________ ...
... Important in vigor and vitality of plant - Carries ________________________________________________________ - Improves ______________________________________________________ - Improves ______________________________________________________ - Promotes _________________________________________________ ...
WeatheringandErosion
... • Expanding water causes rock to break apart • Ice melts and processes repeat. ...
... • Expanding water causes rock to break apart • Ice melts and processes repeat. ...
Back To Organic Farming
... by cutting down trees and clearing the forest for growing crops. The soil microbes were deprived of shade and leaves and their activity started going down. As their activity declined, plant nutrition suffered and the soil became infertile. Fortunately, our farmers’ forefathers were using cow dung ma ...
... by cutting down trees and clearing the forest for growing crops. The soil microbes were deprived of shade and leaves and their activity started going down. As their activity declined, plant nutrition suffered and the soil became infertile. Fortunately, our farmers’ forefathers were using cow dung ma ...
Non-permeable rocks haves no spaces between the particles, so
... will tell you how much water a rock will absorb ...
... will tell you how much water a rock will absorb ...
Glossary for the Lithosphere
... millipedes and woodlice. They break down dead organic matter that can be further digested by decomposers. the natural nutrient enrichment of a water body. It can be accelerated by human actions such as the release of sewage effluent or the use of fertilisers that are leached into water bodies. a the ...
... millipedes and woodlice. They break down dead organic matter that can be further digested by decomposers. the natural nutrient enrichment of a water body. It can be accelerated by human actions such as the release of sewage effluent or the use of fertilisers that are leached into water bodies. a the ...
Summative Assessment Questions on Soils (LCA Ag,Hort Basic Hort
... 3. Name the three main soil types. 4. Soils can have different pH. What does pH mean when referring to soils? 5. Which type of soil is good for crops? 6. Where would you find acid soils? 7. Why is lime added to soil? 8. What is humus and why is it good for soil? 9. What test would a horticulturalist ...
... 3. Name the three main soil types. 4. Soils can have different pH. What does pH mean when referring to soils? 5. Which type of soil is good for crops? 6. Where would you find acid soils? 7. Why is lime added to soil? 8. What is humus and why is it good for soil? 9. What test would a horticulturalist ...
Soil Study Guide
... Moist slippery earth usually red in color. Clay is often found in Georgia. Plants do not generally grow well in clay. ...
... Moist slippery earth usually red in color. Clay is often found in Georgia. Plants do not generally grow well in clay. ...
Influence of different water saturation levels for mobility of Antimony
... Shooting range soil is potentially contaminated by Sb, copper (Cu), lead (Pb) and zinc (Zn). These elements are released due to weathering of spent bullets. The bullet core consists of 2-5 wt% Sb for getting hard lead alloys. A potential soil remediation method is to add Febased sorbents, which are ...
... Shooting range soil is potentially contaminated by Sb, copper (Cu), lead (Pb) and zinc (Zn). These elements are released due to weathering of spent bullets. The bullet core consists of 2-5 wt% Sb for getting hard lead alloys. A potential soil remediation method is to add Febased sorbents, which are ...
Soil Study Guide
... The test will be given on _____________. 1. Plants need nutrients from soil to grow. 2. Topsoil is a natural product of subsoil and bedrock. It is rich with a lot of humus. It is the top layer of soil made up of the smallest grains with the most humus. 3. Soil is formed by broken down rocks, moving ...
... The test will be given on _____________. 1. Plants need nutrients from soil to grow. 2. Topsoil is a natural product of subsoil and bedrock. It is rich with a lot of humus. It is the top layer of soil made up of the smallest grains with the most humus. 3. Soil is formed by broken down rocks, moving ...
APES 10 Things-Weathering and Erosion
... Rock Cycle- weathering and erosion are important to creation of sedimentary rock 4. Weathering- breaks down rocks into loose material, aka sediments. 5. Erosion- moves the sediment to a location conducive to creation of sedimentary rocks 6. Material cycling- long term loops of every cycle- Phosphoru ...
... Rock Cycle- weathering and erosion are important to creation of sedimentary rock 4. Weathering- breaks down rocks into loose material, aka sediments. 5. Erosion- moves the sediment to a location conducive to creation of sedimentary rocks 6. Material cycling- long term loops of every cycle- Phosphoru ...
GLACIAL EROSIONAL FEATURES
... a) Pedology - study of the origin, classification, distribution & description of soil b) Edaphology - study of soil as a medium for sustaining plants Soil Components 1) inorganic materials - consist of O, Si, Al, Fe, Ca, Na, K & Mg, primarily. They combine to form quartz, alumina oxide & calcium car ...
... a) Pedology - study of the origin, classification, distribution & description of soil b) Edaphology - study of soil as a medium for sustaining plants Soil Components 1) inorganic materials - consist of O, Si, Al, Fe, Ca, Na, K & Mg, primarily. They combine to form quartz, alumina oxide & calcium car ...
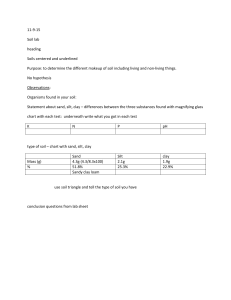
11-9-15 Soils Lab
... Purpose: to determine the different makeup of soil including living and non-living things. No hypothesis Observations: Organisms found in your soil: Statement about sand, silt, clay – differences between the three substances found with magnifying glass chart with each test: underneath write what you ...
... Purpose: to determine the different makeup of soil including living and non-living things. No hypothesis Observations: Organisms found in your soil: Statement about sand, silt, clay – differences between the three substances found with magnifying glass chart with each test: underneath write what you ...
ROCKS, FOSSILS AND SOILS GLOSSARY
... A segmented worm that aerates the soil, adding space and air pockets as it eats the organic materials, breaking them down to basic minerals that are returned to the soil for plants to use. They are hermaphrodites, meaning they have both sperm and egg. Earthworms have 4 hearts and 150 segments. Earth ...
... A segmented worm that aerates the soil, adding space and air pockets as it eats the organic materials, breaking them down to basic minerals that are returned to the soil for plants to use. They are hermaphrodites, meaning they have both sperm and egg. Earthworms have 4 hearts and 150 segments. Earth ...
Soil formation
... inorganic (minerals and rocks) and organic compounds (plants and dead animals or substances produced by them, like leaves and faeces) that are present in the area, their deposit and the subsequent formation of new minerals and organic ...
... inorganic (minerals and rocks) and organic compounds (plants and dead animals or substances produced by them, like leaves and faeces) that are present in the area, their deposit and the subsequent formation of new minerals and organic ...
TYPES OF SOIL Mansi Jain B.Ed VDIT SOIL
... Residual soils are those that remain at the place of their formation as result of the weathering of the parent rocks. The depth of residual soils depends primarily on climatic conditions and the time of espouser. In temperate zones residual soils are commonly stiff and stable. An important charact ...
... Residual soils are those that remain at the place of their formation as result of the weathering of the parent rocks. The depth of residual soils depends primarily on climatic conditions and the time of espouser. In temperate zones residual soils are commonly stiff and stable. An important charact ...
Catastrophic Event
... of air that is in contact with both the surface of the earth and a cumulonimbus cloud ...
... of air that is in contact with both the surface of the earth and a cumulonimbus cloud ...
Erosion Notes and Fill in the Blank HW
... ___________________ crust is covered by soil. The ingredients in soils can vary from _____________ to place and around the Earth. Different soils have many properties such as texture, _______________size, pH, fertility and ability to hold moisture. Depending upon the combination of _________________ ...
... ___________________ crust is covered by soil. The ingredients in soils can vary from _____________ to place and around the Earth. Different soils have many properties such as texture, _______________size, pH, fertility and ability to hold moisture. Depending upon the combination of _________________ ...
Lindsey`s Basic Guide to the Soil Orders of Canada Disclaimer: This
... order can be found in the Canadian System of Soil Classification and the Soil Management Guide. However, I have found that these resources can be difficult to understand especially for people with little experience in soil classification. Hopefully this will start you off on the right track! 1. Cryo ...
... order can be found in the Canadian System of Soil Classification and the Soil Management Guide. However, I have found that these resources can be difficult to understand especially for people with little experience in soil classification. Hopefully this will start you off on the right track! 1. Cryo ...
Soil science facts
... generally begins at the surface of rocks and progresses in depth over the course of time, whereby layers are formed with ...
... generally begins at the surface of rocks and progresses in depth over the course of time, whereby layers are formed with ...
Soil Stories
... Soil: A complex mixture of minerals, air, water, and microorganisms that supports life on Earth. Soils modify the atmosphere by emitting and absorbing dust and gases. They process and recycle nutrients, including carbon, so that living things can use them over and over again. ...
... Soil: A complex mixture of minerals, air, water, and microorganisms that supports life on Earth. Soils modify the atmosphere by emitting and absorbing dust and gases. They process and recycle nutrients, including carbon, so that living things can use them over and over again. ...