The Impact of Growing Cover Crops in Vineyards on Soil Health
... The Impact of Growing Cover Crops in Vineyards on Soil Health Kathryn Carter, Anne Verhallen, and Deanna Nemeth (OMAFRA), Mehdi Sharifi (AAFC) ...
... The Impact of Growing Cover Crops in Vineyards on Soil Health Kathryn Carter, Anne Verhallen, and Deanna Nemeth (OMAFRA), Mehdi Sharifi (AAFC) ...
soil makeup
... • Earthworms, ants, crawfish, moles, and other organisms improve the soil tilth (the ease with which soil can be worked). ▫ create openings in the soil as they tunnel ▫ enhances drainage and improves air exchange ...
... • Earthworms, ants, crawfish, moles, and other organisms improve the soil tilth (the ease with which soil can be worked). ▫ create openings in the soil as they tunnel ▫ enhances drainage and improves air exchange ...
Tabela 5.2 Course specification Methods of soil Analysis OK
... Chemical methods of soil testing: The absorption method (colorimetry, spectrophotometry, atomic absorption spectrophotometry) Emission methods (flame photometry, inductively coupled plasma) potentiometric method (EUF method). Microbial methods for soil investigation: Microorganisms as indicators of ...
... Chemical methods of soil testing: The absorption method (colorimetry, spectrophotometry, atomic absorption spectrophotometry) Emission methods (flame photometry, inductively coupled plasma) potentiometric method (EUF method). Microbial methods for soil investigation: Microorganisms as indicators of ...
Weathering - NewPath Learning
... burning of fossil fuels. Here is a list of some forms of chemical weathering. 1. Limestone is dissolved by acid rain. Sulfur is released into the atmosphere when fossil fuels are burned. The sulfur combines with water to form sulfuric acid. These acids slowly dissolve some types of rock. 2. Sulfur r ...
... burning of fossil fuels. Here is a list of some forms of chemical weathering. 1. Limestone is dissolved by acid rain. Sulfur is released into the atmosphere when fossil fuels are burned. The sulfur combines with water to form sulfuric acid. These acids slowly dissolve some types of rock. 2. Sulfur r ...
Which of the following was most likely caused by tectonic plates
... 7. Above a hot spot under an oceanic plate, large quantities of lava continually erupt through the seafloor. If the lava builds up to an elevation greater than sea level, what type of landform will result? A Barrier island B Volcanic island C Peninsula D Continent 8. A group of students found metamo ...
... 7. Above a hot spot under an oceanic plate, large quantities of lava continually erupt through the seafloor. If the lava builds up to an elevation greater than sea level, what type of landform will result? A Barrier island B Volcanic island C Peninsula D Continent 8. A group of students found metamo ...
Teacher Background on Erosion, Weathering, Soil
... weather. Lichens growing on rocks produce organic acids that slowly weather the host rock. Oxidation can cause rust. Scientists study rock strata for signs of oxidation to determine the amounts of oxygen in Earth’s atmosphere at a particular time. So, in chemical weathering, new minerals might be ad ...
... weather. Lichens growing on rocks produce organic acids that slowly weather the host rock. Oxidation can cause rust. Scientists study rock strata for signs of oxidation to determine the amounts of oxygen in Earth’s atmosphere at a particular time. So, in chemical weathering, new minerals might be ad ...
Unit 1, Lesson 2- Spheres of the earth
... growing together-Eww!) form on rock surfaces 2) Acids start weathering the rock’s surface 3) Plants grow on the weathering rock 4) The plants die and their remains mix with the rock sediments 5) Soil is formed!! ...
... growing together-Eww!) form on rock surfaces 2) Acids start weathering the rock’s surface 3) Plants grow on the weathering rock 4) The plants die and their remains mix with the rock sediments 5) Soil is formed!! ...
Carbon-14 and Tritium as tracers of soil movement in earth hummocks
... Department of Geography, University of Ottawa K1N 6N5 ...
... Department of Geography, University of Ottawa K1N 6N5 ...
IP004 - Institute of Safety Management
... The “Fill” or "Made up Ground” describes all refuse, added materials (eg. brick paving & its base materials), excavated ground used for filling a depression or raising the level of the ground and it overlies or is dug into the transported soils The “Transported soil” (gravels, sand, silts & clays) a ...
... The “Fill” or "Made up Ground” describes all refuse, added materials (eg. brick paving & its base materials), excavated ground used for filling a depression or raising the level of the ground and it overlies or is dug into the transported soils The “Transported soil” (gravels, sand, silts & clays) a ...
Roberts Soil - Clydebank High School
... Involve the action of vegetation and organisms. They interact, influenced by climate to produce humus. This may lie below the L and F layers of the Ao horizon or mixed through the whole A horizon ...
... Involve the action of vegetation and organisms. They interact, influenced by climate to produce humus. This may lie below the L and F layers of the Ao horizon or mixed through the whole A horizon ...
Weathering and Erosion
... Glaciers in North America over the past 2.0 x 106 years • Ice covered most of New York several times in the ...
... Glaciers in North America over the past 2.0 x 106 years • Ice covered most of New York several times in the ...
AG-GH-PS-01.461
... Note: fresh mud and sand that will someday be sedimentary rock. • Igneous rock• like basalt,formed from molten rock as in volcano. Most of the earth’s crust is igneous rock overlain by sedimentary rock August 2008 ...
... Note: fresh mud and sand that will someday be sedimentary rock. • Igneous rock• like basalt,formed from molten rock as in volcano. Most of the earth’s crust is igneous rock overlain by sedimentary rock August 2008 ...
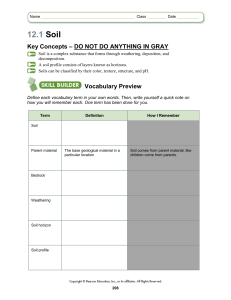
12.1 Soil - Union High School
... For Questions 2−4, write True if the statement is true. If the statement is false, replace the underlined word or words to make the statement true. Write your changes on the line. 2. Parent material is the base geological material from which soil is formed. 3. Weathering is often the last process in ...
... For Questions 2−4, write True if the statement is true. If the statement is false, replace the underlined word or words to make the statement true. Write your changes on the line. 2. Parent material is the base geological material from which soil is formed. 3. Weathering is often the last process in ...
Soil Matrix Cleanup The Soil Matrix cleanup level is the allowable
... n Most sites in the Portland area have a cleanup level of 500 ppm and removing impacted to less than 500 ppm is considered a “Soil Matrix Cleanup.” n The DEQ requires the removal of any free-‐p ...
... n Most sites in the Portland area have a cleanup level of 500 ppm and removing impacted to less than 500 ppm is considered a “Soil Matrix Cleanup.” n The DEQ requires the removal of any free-‐p ...
Soil
... What is the work of soil? • Soil helps hold the roots of all plants in place. The roots of plants take in water from the soil. They also take in nutrients from the soil. ...
... What is the work of soil? • Soil helps hold the roots of all plants in place. The roots of plants take in water from the soil. They also take in nutrients from the soil. ...
AG-NR-03.411-04.1
... Glacial Ice– Carried parent materials all over the northern part of the North America during the four separate periods of glaciations – What is glacial drift? • It is the melting and the shrunk between the glacial periods and transported materials remained in deposits. This is how we got the most be ...
... Glacial Ice– Carried parent materials all over the northern part of the North America during the four separate periods of glaciations – What is glacial drift? • It is the melting and the shrunk between the glacial periods and transported materials remained in deposits. This is how we got the most be ...
The influence of SiO3 2- on the reductive reactivity of Fe(II) adsorbed
... Pollution Integrated Control, Guangdong Institute of EcoEnvironmental and Soil Sciences, Guangzhou 510650, P. R. China (*correspondence: [email protected]) ...
... Pollution Integrated Control, Guangdong Institute of EcoEnvironmental and Soil Sciences, Guangzhou 510650, P. R. China (*correspondence: [email protected]) ...
5 th Grade Essentials Guide: Rocks, Soil, and Minerals Unit 6
... Know the difference between organic and inorganic matter. Explain how soil layers form. Be able to identify soil horizons based on their composition. Explain how soil varies in structure based on its geographic location. (i.e., desert soil does not have much humus, but it is rich in minerals because ...
... Know the difference between organic and inorganic matter. Explain how soil layers form. Be able to identify soil horizons based on their composition. Explain how soil varies in structure based on its geographic location. (i.e., desert soil does not have much humus, but it is rich in minerals because ...
1 Weathering and Soils 10-9-06 Weathering is the process that
... Weathering is the process that converts rock into soils and sediment, providing the raw materials for creation of sedimentary rocks and redistributing chemical compounds and elements throughout the biosphere. The effects of weathering vary depending upon the types of rocks, the environmental conditi ...
... Weathering is the process that converts rock into soils and sediment, providing the raw materials for creation of sedimentary rocks and redistributing chemical compounds and elements throughout the biosphere. The effects of weathering vary depending upon the types of rocks, the environmental conditi ...
1887–1893 Sir Arthur Conan Doyle wrote about scientific ideas and
... The study of pollen and spores Important to know: What is produced in a given area The dispersal pattern ...
... The study of pollen and spores Important to know: What is produced in a given area The dispersal pattern ...
webinar presentation
... Rainfall 25” (when not in drought!!) Sandy Loam – CEC 4-5 Low calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, zinc, copper, boron & sulphur High potassium ...
... Rainfall 25” (when not in drought!!) Sandy Loam – CEC 4-5 Low calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, zinc, copper, boron & sulphur High potassium ...
013368718X_CH03_029
... G. the portion of Earth and its atmosphere that contains organisms H. a process in which producers use light energy to make carbohydrates ...
... G. the portion of Earth and its atmosphere that contains organisms H. a process in which producers use light energy to make carbohydrates ...