* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Weathering and Erosion
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Crop rotation wikipedia , lookup
Terra preta wikipedia , lookup
Soil horizon wikipedia , lookup
Soil food web wikipedia , lookup
Soil compaction (agriculture) wikipedia , lookup
No-till farming wikipedia , lookup
Soil salinity control wikipedia , lookup
Soil microbiology wikipedia , lookup
Surface runoff wikipedia , lookup
Canadian system of soil classification wikipedia , lookup
Soil erosion wikipedia , lookup
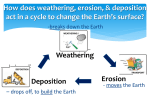
Name _______________________________ Period _________ Weathering, Erosion Deposition & Landscapes NOTES I. A. Weathering __________________________________ The breakdown of rocks without changing the composition (only changes size and shape) ______________ Picture: _______________ Picture: _________________________________ The breakdown of rocks through reactions that change the composition (and size and shape) _____________ Picture: _____________ Picture: Water (Hydrolysis) “universal solvent” – can dissolve most rocks given enough time Biologic Activity Physical ____________________________ Picture: Chemical ____________________________ Picture: Differential Weathering Examples: (Label more and less resistant layers) Factors Affecting the Rate of Weathering Exposure ___________ ___________ ___________ ___________ ___________ ___________ ___________ ___________ Particle Size ______________ ______________ ______________ ______________ ______________ ______________ ______________ ______________ Mineral Composition ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ Climate _____________ _____________ _____________ _____________ _____________ _____________ _____________ _____________ B. Soil Types of soil 1. Residual Soil 2. Comes from: __________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ 3. Transported Soil 1. Comes from: __________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 2. It is transported 3. By what process does soil get transported? __________________________ Soil Formation • Types of weathering involved: ________________________ ________________________ • Soils develop over time – It takes _____________of years for just one _______ of soil to form. • Fully developed soils consist of distinct horizons (layers) • Many thousands of years are necessary to form soils Soil Horizons (in residual soils or mature transported soils) • A horizon – Formed by:__________________________________ ___________________________________________ – Contains the most living things • B horizon – Is also called/contains:_________________________ ___________________________________________ • Minerals are leached by the action of water moving through a layer of soil • C horizon – Formed by:__________________________________ ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ New York State Soils • Most are young (Less than 10,000 years old) Why?______________________ Human Factors that Affect Soil (we will do this together) • Growing plants protect soil from being washed away (eroded) • Many agricultural practices leave large areas of soil exposed to wind and rain. – __________________________________________________________ • _____________________________________________________ • _____________________________________________________ Soil Building Practices • _______________________________________________________________ • _______________________________________________________________ II. EROSION & DEPOSITION (Sedimentation) A . Sediments are ___________________________ ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ B. Erosion is _______________________________ ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ C. Deposition is _____________________________ ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ Sediment Factors that Affect Deposition Size:________ ____________ ____________ ____________ Shape :_______________ _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ Density:_______ _____________ _____________ _____________ REMEMBER: ______________,________________, _______________, ________________!!!! D. Erosion & Deposition by Mass Wasting (Mass Movement) _____________________________________________________________________________ 1. Defined by: -_________________________________________________________________ -_________________________________________________________________ -_________________________________________________________________ 2. Types (of Mass Wasting/Movement) E. Erosion & Deposition by Rivers 1. How do rivers transport sediment? _________ _________ __ _________ Stream Velocity 2.Velocity of streams is controlled by: – ___________________ • ______________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ – __________________________________________________________________ – Stream velocity is a balance between______________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ – Friction is exerted by the sides of a stream – Friction is even exerted by the air above a stream Gradient • _____________________________________________________ 3. PRACTICE: How much energy is required to move sediments in water? See ESRT page 6 A. What must the stream velocity be to transport a particle that is 0.006 cm? B. What is the largest sediment that a stream with a velocity of 300cm/sec can carry? C. What is the largest sediment that can be transported by a stream that has a velocity of 125 cm/sec? D. Which stream velocity carried only clay particles to the depositional environment where the shale formed? (1) 0.02 cm/s (2) 0.05 cm/s (3) 10 cm/s (4) 20 cm/s E. The largest sediment particles that can be transported by a stream traveling at a velocity of 200 centimeters per second are (1) boulders (2) cobbles (3) pebbles (4) sand 4. Erosional Features of Rivers Rounded sediment Depositional Features of Rivers Horizontal sorting - ________________________ _________________________________________ The farther a river carries sediment – the rounder it becomes because of abrasion. V- shaped valleys Deltas - _________________________________ Top view Side View Floodplains - ______________________________ __________________________________________ _________________________________ _________ Meanders (erode outside of curve – deposit inside of curve) • _________________________________ _________________________________ _________________________________ – ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ F. Erosion & Deposition by Waves and Currents 1. Turbidity Current ________________________________________________________________ When sediments settle afterward, they are ____________________________________ 2. Sandy shoreline features Rounded Sediment Beaches Sandbars Barrier Islands Spits/Baymouth Bars 3. Longshore Current __________________________________ __________________________________ ____________________________ 4. Rocky shoreline features Sea Caves Sea Arch Sea Stack G. Erosion & Deposition by Wind: • ________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ • ________________________________________________________________________ _____________________ • _______________________________ • So a sandstorm is like a huge sandblaster Causes pits and frosted sediments Dune Formation H. Erosion & Deposition by Ice (Glaciers) • _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ • Glacial movement is similar to streams: _____________________________________________ – Ice can be thousands of feet thick and thus very powerful. – Surface materials (like soil) are easily removed. Glaciers in North America over the past 2.0 x 106 years • Ice covered most of New York several times in the “recent” past • Most recently about 11,000 – 15,000 ybp. 2 Types of Glaciers • Continental – _______________________________________ – _______________________________________ • Alpine (Valley) – _______________________________________ – _______________________________________ Erosional Features of Glaciers Angular sediment with parallel scratches Depositional Features of Glaciers • Till_________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ • ________________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ • Erratic_______________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ – _______________________ _______________________ • U-shaped Valleys • Drumlin- ______________________ Finger lakes – deep, narrow, U-shaped lakes Kettle Lake formation Moraine – pile of glacial till • Layered and sorted sediment:________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ III. Landscapes A. Landscape Regions of New York State (ESRT p. 2) Plains (Lowlands) – ___________________________ _________________________________________ _________________________________________ Plateaus – _________________________________ _________________________________________ _________________________________________ _________________________________________ Mountains - ________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ ________________________________________ Escarpment – cliff (usually between plains and plateaus) B. Vocabulary 1. Watershed: ________________________________________________________________ 2. Relief: ______________________________________________________________________ C. Factors that affect the shape of the landscape: 1. Climate 2. People 3. Geology (see table below) a. b. Water Drainage Patterns ________________________________________________ Dendritic Radial _________________________________ Example: Canisteo, NY Trellis (Rectangular) _________________________________ Example: The rim of the Adirondacks Annular _________________________________ Example: Finger Lakes (inlcluding York) _________________________________ _________________________________ Example: Esopus Creek, Phoenicia, NY IV. Sedimentary Rocks Rock Type: How type of rock is formed: Generally how rock type is identified How to specifically identify Using ESRT Sedimentary __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ Three types __________________________________________________ o Composed of different sized particles o Pebbles, sand, silt __________________________________________________ o Composed of decomposed plant and animal remains __________________________________________________ o Form by minerals precipitating out of water Page 7 1. Shade Clastic rocks yellow 2. Shade Crystalline (chemical) rocks green 3. Shade Bioclasic rocks orange 4. What clastic rock has a grain size of .0005cm? 5. What is the difference between conglomerate and Breccia? 6. Draw the map symbol for Limestone. 7. Why is limestone classified as both crystalline and bioclastic? 8. How is bituminous coal formed? 9. How does Rock Gypsum form? 10.What is the name of the rock that will bubble with acid? Depositional Environments - ________________________________________________________________________