factors influencing the adoption of land conserving technologies
... Group Discussions (FGD) and taking field measurements. Of the total 672 households for the study area, a total of 60 farmers were then randomly selected and interviewed of which half were selected from the farmers that had hill slope gardens. The study revealed that farmers perceived that soil ferti ...
... Group Discussions (FGD) and taking field measurements. Of the total 672 households for the study area, a total of 60 farmers were then randomly selected and interviewed of which half were selected from the farmers that had hill slope gardens. The study revealed that farmers perceived that soil ferti ...
Weathering and Soil Formation
... water that sinks through air pockets in the soil. The result is a weak acid called carbonic acid. Carbonic acid easily weathers rocks such as marble and limestone. ...
... water that sinks through air pockets in the soil. The result is a weak acid called carbonic acid. Carbonic acid easily weathers rocks such as marble and limestone. ...
Nylex Cordrain Geocomposite Drainage Layer
... Typically eliminates the need for aggregate or sand backfill. Lightweight and flexible Easy to handle and quick to install. ...
... Typically eliminates the need for aggregate or sand backfill. Lightweight and flexible Easy to handle and quick to install. ...
Weathering: breakdown of rocks into sediments The difference
... A settles first (shortest time), B settles second, C third, and D settles last (longest time) ...
... A settles first (shortest time), B settles second, C third, and D settles last (longest time) ...
silicate agrominerals as nutrient sources and as soil conditioners for
... After the initial success of this approach, the challenges nowadays are dedicated on the efficient supply of nutrients for agriculture. The efficiency of the management of these soluble sources must improve to ensure the best use of the nutrients that are derived from finite mineral resources and hi ...
... After the initial success of this approach, the challenges nowadays are dedicated on the efficient supply of nutrients for agriculture. The efficiency of the management of these soluble sources must improve to ensure the best use of the nutrients that are derived from finite mineral resources and hi ...
SOILS.
... colloidal state. This includes water retaining capacity as well. The texture of the soil (Particle) depends upon the relative proportions of particles of different sizes. Thus, the soil can be classified as sandy, loamy and clayey depending upon the amount of sand silt, clay and humus in it. A loamy ...
... colloidal state. This includes water retaining capacity as well. The texture of the soil (Particle) depends upon the relative proportions of particles of different sizes. Thus, the soil can be classified as sandy, loamy and clayey depending upon the amount of sand silt, clay and humus in it. A loamy ...
File
... Classification of Metamorphic Rocks Classified by __________________________________________ Classified by Texture Foliated Metamorphic Rock ...
... Classification of Metamorphic Rocks Classified by __________________________________________ Classified by Texture Foliated Metamorphic Rock ...
FERTILITY CAPABILITY CLASSIFICATION Problem soils have been
... within 50 cm, except in organic soils where pH must be less than 4.7; h = (acid): 10-60% AI-saturation of the effective CEC within 50 cm of soil surface, or pH in 1:1 H20 between 5.0 and 6.0%; i = (high p-fixation by iron): % free Fe2 03/% clay> 0.15 and more than 35% clay, or hues of 7.5 YR or redd ...
... within 50 cm, except in organic soils where pH must be less than 4.7; h = (acid): 10-60% AI-saturation of the effective CEC within 50 cm of soil surface, or pH in 1:1 H20 between 5.0 and 6.0%; i = (high p-fixation by iron): % free Fe2 03/% clay> 0.15 and more than 35% clay, or hues of 7.5 YR or redd ...
Earth*s External Processes
... water percolating through decaying organic matter and into the soil ...
... water percolating through decaying organic matter and into the soil ...
“Distribution of tetraether lipids in agricultural soils – differentiation
... Management practices exert a major control on the duration and frequency of anoxic-oxic cycles, dependent one whether 1, 2, or 3 rice growth period per annum occurred. The question whether natural or human-induced variation in ecosystem properties dominate the microbial community association was add ...
... Management practices exert a major control on the duration and frequency of anoxic-oxic cycles, dependent one whether 1, 2, or 3 rice growth period per annum occurred. The question whether natural or human-induced variation in ecosystem properties dominate the microbial community association was add ...
Study on carbon in Midwest Soil
... more of it and store it (via photosynthesis) in their root systems — a net gain of carbon to the soil. However, as temperatures simultaneously increase, the microbes in soil become increasingly active, eating up more soil matter and releasing more carbon. Whatever small benefit higher atmospheric CO ...
... more of it and store it (via photosynthesis) in their root systems — a net gain of carbon to the soil. However, as temperatures simultaneously increase, the microbes in soil become increasingly active, eating up more soil matter and releasing more carbon. Whatever small benefit higher atmospheric CO ...
The Eco-Hydrological Role of Physical Surface Sealing in Dry
... between vegetation patches. The low hydraulic conductivity that characterizes the seal layer reduces both infiltration and evaporation fluxes from the soil, and thus has the potential to affect local vegetation water availability and consequently transpiration rates. This effect is investigated here ...
... between vegetation patches. The low hydraulic conductivity that characterizes the seal layer reduces both infiltration and evaporation fluxes from the soil, and thus has the potential to affect local vegetation water availability and consequently transpiration rates. This effect is investigated here ...
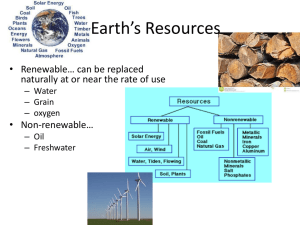
Earth`s Resources
... Service has set many restrictions of size, amount, and season to help sustain this valuable resource – Aquaculture… fish hatcheries • Raises fish for human consumption – Causes coastal pollution and eutrophication is not wisely managed ...
... Service has set many restrictions of size, amount, and season to help sustain this valuable resource – Aquaculture… fish hatcheries • Raises fish for human consumption – Causes coastal pollution and eutrophication is not wisely managed ...
10. 1 Directed Reading A
... _____ 2. Mechanical weathering is the breakdown of rock into smaller pieces by a. warm weather. b. cold weather. c. chemical processes. d. physical means. _____ 3. Ice, wind, water, gravity, plants, and animals can all be agents of a. mechanical weathering. b. chemical weathering. c. chemical proces ...
... _____ 2. Mechanical weathering is the breakdown of rock into smaller pieces by a. warm weather. b. cold weather. c. chemical processes. d. physical means. _____ 3. Ice, wind, water, gravity, plants, and animals can all be agents of a. mechanical weathering. b. chemical weathering. c. chemical proces ...
Soils and Global Warming: A Positive or Negative Feedback?
... •Climate change may change inputs •Will climate change loss rates? (k) –Virtually all studies show it will (at least on short term)\ –Microbes increase rates, decompose the most readily accessable C materials (and therefore increase CO2 losses) •Some recent discussions have confused soil respiration ...
... •Climate change may change inputs •Will climate change loss rates? (k) –Virtually all studies show it will (at least on short term)\ –Microbes increase rates, decompose the most readily accessable C materials (and therefore increase CO2 losses) •Some recent discussions have confused soil respiration ...
Weathering Erosion and Deposition
... • Sinkholes ! form when the roof of a cave collapses (2) • Stalactites ! when water with dissolved minerals drips down and solidifies before falling all the way to ground. Looks like an icicle (3) • Stalagmites ! when the dissolved calcite that drips down from the ceiling of the cave falls to the fl ...
... • Sinkholes ! form when the roof of a cave collapses (2) • Stalactites ! when water with dissolved minerals drips down and solidifies before falling all the way to ground. Looks like an icicle (3) • Stalagmites ! when the dissolved calcite that drips down from the ceiling of the cave falls to the fl ...
Agricultural Science Past Exam Questions Soil Science
... Agricultural Science Past Exam Questions Soil Science Higher Level ...
... Agricultural Science Past Exam Questions Soil Science Higher Level ...
Organic Matter
... Sandy soils have good aeration but dry out quickly. Sandy soils increase water holding capacity and have less erosion as O.M. is added? ...
... Sandy soils have good aeration but dry out quickly. Sandy soils increase water holding capacity and have less erosion as O.M. is added? ...
Engineering Properties of Soils
... Type of water found in soil Free water or gravitational water – found below groundwater – free to flow under the laws of gravity Capillary water – brought up through the soil pores – above the groundwater table Attached water or held water – moisture film around soil grains The rate of wat ...
... Type of water found in soil Free water or gravitational water – found below groundwater – free to flow under the laws of gravity Capillary water – brought up through the soil pores – above the groundwater table Attached water or held water – moisture film around soil grains The rate of wat ...
Soil Forming Processes
... Soil Forming Processes Introduction Soil forming processes are determined by climate and organisms (both plants and animals) acting on the local geological surface materials over time under the influence of the slope of the land and human activities. The interaction between these factors initiates a ...
... Soil Forming Processes Introduction Soil forming processes are determined by climate and organisms (both plants and animals) acting on the local geological surface materials over time under the influence of the slope of the land and human activities. The interaction between these factors initiates a ...
File
... Release of pressure-erosion moving material from the outside of a rock releases pressure on rocks below causing the rock’s surface to crack and flake off. ...
... Release of pressure-erosion moving material from the outside of a rock releases pressure on rocks below causing the rock’s surface to crack and flake off. ...
Weathering Overview
... reduced c. bedrock surface that was buried expands d. long, curved cracks form (AKA joints) ...
... reduced c. bedrock surface that was buried expands d. long, curved cracks form (AKA joints) ...
Higher Geography Biosphere For this unit you should be able to
... The term Biosphere refers to the biotic response to specific climatic and other environmental conditions such as relief and soils, which results in a variety of different types of vegetation. The various plants which exist on the earth’s surface inter-react within a system called an ecosystem. ...
... The term Biosphere refers to the biotic response to specific climatic and other environmental conditions such as relief and soils, which results in a variety of different types of vegetation. The various plants which exist on the earth’s surface inter-react within a system called an ecosystem. ...
Talking points for classroom discussion
... Erosion – the physical wearing away of the earth’s surface; surface soil material is removed in the process. (Surface water) runoff – water from precipitation that is not absorbed into the ground and instead flows along the surface Organic matter – material from anything that once lived, inclu ...
... Erosion – the physical wearing away of the earth’s surface; surface soil material is removed in the process. (Surface water) runoff – water from precipitation that is not absorbed into the ground and instead flows along the surface Organic matter – material from anything that once lived, inclu ...
Chapter 10 Chapter Review Answer Key
... 11. Describe the two major types of weathering. Mechanical weathering is the breaking down of rock by physical means. Chemical weathering is the process by which rocks break down as a result of a chemical reaction. 12. Why is Devil’s Tower higher than the surrounding area? Devil’s tower is higher th ...
... 11. Describe the two major types of weathering. Mechanical weathering is the breaking down of rock by physical means. Chemical weathering is the process by which rocks break down as a result of a chemical reaction. 12. Why is Devil’s Tower higher than the surrounding area? Devil’s tower is higher th ...