main forms of energy governing soil formation
... acids through the biological decomposition of litter at the soil surface and of roots within the soil, or the delivering of photosynthates to root mycorrhizas, which acts at the weathering front by exponentially increasing of the rooting surface, delivering exudates and other organic forms of proton ...
... acids through the biological decomposition of litter at the soil surface and of roots within the soil, or the delivering of photosynthates to root mycorrhizas, which acts at the weathering front by exponentially increasing of the rooting surface, delivering exudates and other organic forms of proton ...
Chapter 2 Section 2 Review PAGE 38 Questions 1
... • 1. Water evaporates into the atmosphere and ...
... • 1. Water evaporates into the atmosphere and ...
Doc 7
... from millions of species Total weight of living organisms in the top six inches of an acre of soil can range from 5,000 pounds to as much as 20,000 pounds. Soil from one spot may house a very different community from soil just a meter away, because of variations in the availability of water or n ...
... from millions of species Total weight of living organisms in the top six inches of an acre of soil can range from 5,000 pounds to as much as 20,000 pounds. Soil from one spot may house a very different community from soil just a meter away, because of variations in the availability of water or n ...
Revealing Patterns of Soil Organic Carbon on
... In recent years, the costs of both Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) and multi-spectral cameras have fallen dramatically, opening up the possibility for more widespread use of these tools in precision agriculture. There is already interest in using this remote sensing technology to help assess crop yi ...
... In recent years, the costs of both Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) and multi-spectral cameras have fallen dramatically, opening up the possibility for more widespread use of these tools in precision agriculture. There is already interest in using this remote sensing technology to help assess crop yi ...
EES Review for Final Exam
... How can we protect our water, land and air resources? RCRA, Clean Air Act, Clean Water Act; Reduce, Reuse, Recycle Ch. 5 – Weathering, Soil, and mass movements Mechanical weathering – frost wedging, unloading, biological activity Chemical weathering – need for water Spheroidal weathering Factors tha ...
... How can we protect our water, land and air resources? RCRA, Clean Air Act, Clean Water Act; Reduce, Reuse, Recycle Ch. 5 – Weathering, Soil, and mass movements Mechanical weathering – frost wedging, unloading, biological activity Chemical weathering – need for water Spheroidal weathering Factors tha ...
BIOL 4120: Principles of Ecology Lecture 5: Terrestrial Environment
... Laterization is a process common to soils found in humid environments in the tropical and subtropical regions heavy leaching of nutrients Calcification occurs when evaporation and water uptake by plants exceed precipitation deposition and buildup of alkaline salts (CaCO3) in the subsoil Saliniza ...
... Laterization is a process common to soils found in humid environments in the tropical and subtropical regions heavy leaching of nutrients Calcification occurs when evaporation and water uptake by plants exceed precipitation deposition and buildup of alkaline salts (CaCO3) in the subsoil Saliniza ...
Weathering, Erosion, Deposition: Effects on the Texas
... Explored how the process of weathering, erosion, and deposition have affected the environments in Texas ecoregion. ...
... Explored how the process of weathering, erosion, and deposition have affected the environments in Texas ecoregion. ...
Start Your Garden Indoors
... • Location. Find a sunny window sill or table. Many plant starts will need to be transitioned to a bigger pot at least once before they are ready to move to your garden – plan for extra space. • Make sure to use a sterile potting soil mix. • Use seed flats and six pack pots or make pots out of recyc ...
... • Location. Find a sunny window sill or table. Many plant starts will need to be transitioned to a bigger pot at least once before they are ready to move to your garden – plan for extra space. • Make sure to use a sterile potting soil mix. • Use seed flats and six pack pots or make pots out of recyc ...
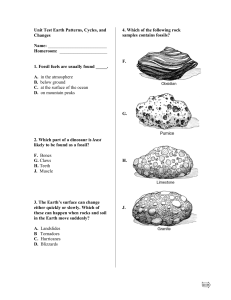
Unit Test Earth Patterns, Cycles, and Changes Name
... H. Digging ditches J. Spraying with water ...
... H. Digging ditches J. Spraying with water ...
Earth and atmosphere Topic Checklist
... the atmosphere The crust is a thin layer of rock The lithosphere, the crust and upper mantle, consists of separates pieces called tectonic plates. Rocks in the Earth’s crust provide many useful substances. The atmosphere is a thin layer of gases including nitrogen and oxygen Magma is molten rock; wh ...
... the atmosphere The crust is a thin layer of rock The lithosphere, the crust and upper mantle, consists of separates pieces called tectonic plates. Rocks in the Earth’s crust provide many useful substances. The atmosphere is a thin layer of gases including nitrogen and oxygen Magma is molten rock; wh ...
Review – Constructive and Destructive Forces
... It erodes more than any other substance (it eroded the Grand Canyon!) Layers of dirt, sand, and soil (typically found at the bottoms of rivers, lakes, and oceans) Hot liquid rock on the Earth's surface The carrying away of rocks and sediment The placing of rocks and sediment It erodes sand dunes in ...
... It erodes more than any other substance (it eroded the Grand Canyon!) Layers of dirt, sand, and soil (typically found at the bottoms of rivers, lakes, and oceans) Hot liquid rock on the Earth's surface The carrying away of rocks and sediment The placing of rocks and sediment It erodes sand dunes in ...
5.2 Notes
... - Rocks can sometimes be identified by appearance. However, if they have been exposed to rain, wind and extreme temperatures, their color and appearance may have changed. - Rocks can also be identified by the type of minerals present (viewed through a microscope) Sediment and Soil Some sediment beco ...
... - Rocks can sometimes be identified by appearance. However, if they have been exposed to rain, wind and extreme temperatures, their color and appearance may have changed. - Rocks can also be identified by the type of minerals present (viewed through a microscope) Sediment and Soil Some sediment beco ...
landscapes
... Chemical Weathering • The process that breaks down rock through chemical changes. • The agents of chemical weathering – Water – Oxygen – Carbon dioxide – Living organisms – Acid rain ...
... Chemical Weathering • The process that breaks down rock through chemical changes. • The agents of chemical weathering – Water – Oxygen – Carbon dioxide – Living organisms – Acid rain ...
File
... communities that live in an ecosystem. 2. All organisms in a particular ecosystem have adaptations that help them survive there. 3. An adaptation is a characteristic that helps an organism live and reproduce in a particular environment. 4. In order for organisms to live in harsh environments, very l ...
... communities that live in an ecosystem. 2. All organisms in a particular ecosystem have adaptations that help them survive there. 3. An adaptation is a characteristic that helps an organism live and reproduce in a particular environment. 4. In order for organisms to live in harsh environments, very l ...
Fertilizers - PNW District
... powdered or solid form, are composed of synthetic chemicals and/or minerals: ...
... powdered or solid form, are composed of synthetic chemicals and/or minerals: ...
Soil erosion demonstration instructions
... the bin wall down to the top of the potting soil and no wider than half the width of the side. When the opposite end of the erosion box is elevated, this missing section will be where the water and soil erode out of the box during the demonstration. c. In one of the bins, liberally cover the surface ...
... the bin wall down to the top of the potting soil and no wider than half the width of the side. When the opposite end of the erosion box is elevated, this missing section will be where the water and soil erode out of the box during the demonstration. c. In one of the bins, liberally cover the surface ...
9G Environmental Chemistry - Prairie Rose School Division
... acid rain – Rainwater that is more acidic than normal because acidic gases have dissolved in it. humus – Soil material that is the decaying remains of dead plants and animals. global warming – The increased greenhouse effect that some scientists think is causing climate change. greenhouse effect ...
... acid rain – Rainwater that is more acidic than normal because acidic gases have dissolved in it. humus – Soil material that is the decaying remains of dead plants and animals. global warming – The increased greenhouse effect that some scientists think is causing climate change. greenhouse effect ...
File
... acid rain – Rainwater that is more acidic than normal because acidic gases have dissolved in it. humus – Soil material that is the decaying remains of dead plants and animals. global warming – The increased greenhouse effect that some scientists think is causing climate change. greenhouse effect ...
... acid rain – Rainwater that is more acidic than normal because acidic gases have dissolved in it. humus – Soil material that is the decaying remains of dead plants and animals. global warming – The increased greenhouse effect that some scientists think is causing climate change. greenhouse effect ...
PowerPoint
... must be mixed to compensate for lacking materials; soilless media can be purchased ready to use. Soil that is not sterilized contains weed seeds, insect eggs and disease organisms. Sterilizing soil involves both equipment and labor costs which add to the total cost. ...
... must be mixed to compensate for lacking materials; soilless media can be purchased ready to use. Soil that is not sterilized contains weed seeds, insect eggs and disease organisms. Sterilizing soil involves both equipment and labor costs which add to the total cost. ...
Assessment of grass root effects on soil piping in sandy soils using
... Soil piping is a complex land degradation process, which involves the hydraulic removal of soil particles by subsurface flow. This process is frequently underestimated and omitted in most soil erosion studies. However, during the last decades several studies reported the importance of soil piping in ...
... Soil piping is a complex land degradation process, which involves the hydraulic removal of soil particles by subsurface flow. This process is frequently underestimated and omitted in most soil erosion studies. However, during the last decades several studies reported the importance of soil piping in ...
Weathering, soil formation and initial ecosystem evolution on a
... resolved sampling of a high variable natural system. In particular, plants and microorganisms can increase the rate of weathering of minerals by taking up ions from the soil solution, removing the dissolution products of minerals, and through the exudation of protons, low molecular weight organic ac ...
... resolved sampling of a high variable natural system. In particular, plants and microorganisms can increase the rate of weathering of minerals by taking up ions from the soil solution, removing the dissolution products of minerals, and through the exudation of protons, low molecular weight organic ac ...
Karst Vocabulary
... Erosion – The loosening and movement of rocks and soil by wind, water, and ice Ferry – a commercial service with terminals and boats for transporting persons, automobiles, etc. across a river or other comparatively small body of water Ford – a place where a river or other body of water is shallow e ...
... Erosion – The loosening and movement of rocks and soil by wind, water, and ice Ferry – a commercial service with terminals and boats for transporting persons, automobiles, etc. across a river or other comparatively small body of water Ford – a place where a river or other body of water is shallow e ...
APES review topics
... O layer- organic material, decaying life A layer- topsoil, humus B layer- subsoil, some broken parent material C layer- parent material bedrock Infiltration: the downward movement of water through soil. Leaching: dissolving of minerals and organic matter in upper layers carrying them to lower layers ...
... O layer- organic material, decaying life A layer- topsoil, humus B layer- subsoil, some broken parent material C layer- parent material bedrock Infiltration: the downward movement of water through soil. Leaching: dissolving of minerals and organic matter in upper layers carrying them to lower layers ...