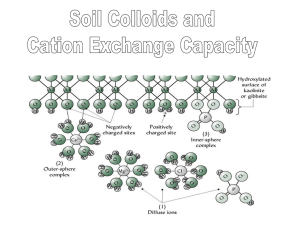
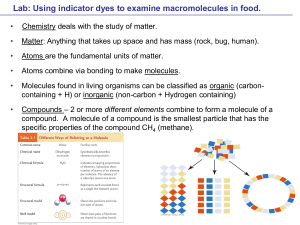
Chemistry Unit Test Study Guide
... 2. List three things that are not made up of matter and do not have mass: 3. What is the difference between a chemical change and a physical change? 4. Give one example of a chemical change. 5. Give one example of a physical change. 6. During the chemical reaction of baking soda and vinegar, bubbles ...
... 2. List three things that are not made up of matter and do not have mass: 3. What is the difference between a chemical change and a physical change? 4. Give one example of a chemical change. 5. Give one example of a physical change. 6. During the chemical reaction of baking soda and vinegar, bubbles ...
Weathering and Erosion
... – Plant roots act as a wedge and widen cracks – Other causes of biotic weathering are digging animals, microscopic plants and animals, algae and fungi. ...
... – Plant roots act as a wedge and widen cracks – Other causes of biotic weathering are digging animals, microscopic plants and animals, algae and fungi. ...
Background
... Clay soil is an orange or blue-ish sticky soil with very few air gaps. Water does not drain through it easily. When it rains, puddles stay on top of clay soil for a long time. Chalky soil is a light brown soil. Water drains through it quickly. Peat is actually not a soil at all and does not contain ...
... Clay soil is an orange or blue-ish sticky soil with very few air gaps. Water does not drain through it easily. When it rains, puddles stay on top of clay soil for a long time. Chalky soil is a light brown soil. Water drains through it quickly. Peat is actually not a soil at all and does not contain ...
OCR Chemistry C2 - Wey Valley School
... photosynthesis (increases O2/decreases CO2); respiration/combustion (decreases O2/increases CO2) Carbon monoxide (CO); Oxides of nitrogen (NOx); sulfur dioxide (SO2) poisonous gas; incomplete combustion of petrol or diesel in car engine photochemical smog and acid rain; formed in the internal combus ...
... photosynthesis (increases O2/decreases CO2); respiration/combustion (decreases O2/increases CO2) Carbon monoxide (CO); Oxides of nitrogen (NOx); sulfur dioxide (SO2) poisonous gas; incomplete combustion of petrol or diesel in car engine photochemical smog and acid rain; formed in the internal combus ...
Age Old Organics
... nitrogen to provide sufficient bacterial conversion of soil microbes into usable nutrient forms. It is an excellent nutrient addition for potting mixes and can be used as a top dressing for gardens. Use at a rate of 8 to 10 lbs per 1,000 sq. ft. for organic lawn maintenance. (Available in: 12 x 1 lb ...
... nitrogen to provide sufficient bacterial conversion of soil microbes into usable nutrient forms. It is an excellent nutrient addition for potting mixes and can be used as a top dressing for gardens. Use at a rate of 8 to 10 lbs per 1,000 sq. ft. for organic lawn maintenance. (Available in: 12 x 1 lb ...
focus Agri - Agri Analysis
... from numerous sources. These can include the breakdown of crop, manure, and other organic residues by soil organisms, the addition of certain fertilizer materials, the conversion of ammonia-nitrogen to nitratenitrogen, and the loss through leaching of basic chemical compounds. Aluminum is part of th ...
... from numerous sources. These can include the breakdown of crop, manure, and other organic residues by soil organisms, the addition of certain fertilizer materials, the conversion of ammonia-nitrogen to nitratenitrogen, and the loss through leaching of basic chemical compounds. Aluminum is part of th ...
Chemistry Content Standards
... a. Compare and contrast atomic/molecular motion in solids, liquids, gases, and plasmas. b. Collect data and calculate the amount of heat given off or taken in by chemical or physical processes. c. Analyzing (both conceptually and quantitatively) flow of energy during change of state (phase). Teacher ...
... a. Compare and contrast atomic/molecular motion in solids, liquids, gases, and plasmas. b. Collect data and calculate the amount of heat given off or taken in by chemical or physical processes. c. Analyzing (both conceptually and quantitatively) flow of energy during change of state (phase). Teacher ...
Reactions Homework Packet
... ____2. How many atoms of oxygen are there in 7 molecules of oxygen gas? II. Balancing Equations-Write balanced equations for each of the following reactions l. Mg + O2 magnesium oxide ...
... ____2. How many atoms of oxygen are there in 7 molecules of oxygen gas? II. Balancing Equations-Write balanced equations for each of the following reactions l. Mg + O2 magnesium oxide ...
Parent material and world soil distribution
... derived from mafic materials which have a buffering effect to increases in the H+ ion ions (e.g. from plant growth, removal of basic cations in farm produce, or nitrate leaching). Where carbonate is present in the soil, as is common over calcareous parent materials (e.g., limestone or dolomite), the ...
... derived from mafic materials which have a buffering effect to increases in the H+ ion ions (e.g. from plant growth, removal of basic cations in farm produce, or nitrate leaching). Where carbonate is present in the soil, as is common over calcareous parent materials (e.g., limestone or dolomite), the ...
Unit 5 Test - Ms. Williams
... b. How they formed c. When they formed d. What they are made of Which type of rocks form deep within the Earth’s crust? a. Invasive b. Extrusive c. Intrusive d. All of the above Most igneous rocks that cool rapidly at Earth’s surface have_____________ a. Larger crystals b. Smaller Crystals c. Large ...
... b. How they formed c. When they formed d. What they are made of Which type of rocks form deep within the Earth’s crust? a. Invasive b. Extrusive c. Intrusive d. All of the above Most igneous rocks that cool rapidly at Earth’s surface have_____________ a. Larger crystals b. Smaller Crystals c. Large ...
Practical, Asymmetric Redox-Neutral Chemical Synthesis via Borrowing Hydrogen
... applied areas such as pharmaceuticals, chemical biology and material science. Due to resource constraints, the current trend in synthetic chemistry is not simply about preparing molecules of specific interest, but rather on how to prepare them in a highly efficient and economical manner. The concept ...
... applied areas such as pharmaceuticals, chemical biology and material science. Due to resource constraints, the current trend in synthetic chemistry is not simply about preparing molecules of specific interest, but rather on how to prepare them in a highly efficient and economical manner. The concept ...
PART V
... Weathering of non-acid cations from minerals An example is the weathering of calcium from silicates Ca-silicate + 2H+ ...
... Weathering of non-acid cations from minerals An example is the weathering of calcium from silicates Ca-silicate + 2H+ ...
Soils Quiz Show Powerpoint
... Soil Horizons for 3 Question: The “A” horizon is generally _____ than the horizons below and may be from a few inches to several feet thick. Check Your Answer ...
... Soil Horizons for 3 Question: The “A” horizon is generally _____ than the horizons below and may be from a few inches to several feet thick. Check Your Answer ...
The Hadean Outline •Theories on Formation of Solar System, Universe
... • Persistent in Archean, Proterozoic rock record – oldest known (from South Africa) ~3.2 billion years old Life in the Archean-Amino Acids • Building blocks of life – Composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen • Found on some meteorites • Can form from inorganic settings without free oxygen • ...
... • Persistent in Archean, Proterozoic rock record – oldest known (from South Africa) ~3.2 billion years old Life in the Archean-Amino Acids • Building blocks of life – Composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen • Found on some meteorites • Can form from inorganic settings without free oxygen • ...
Physical Processes Powerpoint
... • Erosion – the movement of weathered materials such as gravel, soil, and sand. • Water • Wind • Glacial • Weathering – the breakdown of rocks at or near the earth’s surface into smaller pieces. ...
... • Erosion – the movement of weathered materials such as gravel, soil, and sand. • Water • Wind • Glacial • Weathering – the breakdown of rocks at or near the earth’s surface into smaller pieces. ...
Growing instructions
... just a few fruits on your plant to grow really big …. remove the others. If your plant starts to grow and to travel too far across your garden cut off the tips of the shoots. These Squash are very good to eat in soups or roasted in the oven but keep the biggest for the Show! GIANT TOMATO Tomatoes ca ...
... just a few fruits on your plant to grow really big …. remove the others. If your plant starts to grow and to travel too far across your garden cut off the tips of the shoots. These Squash are very good to eat in soups or roasted in the oven but keep the biggest for the Show! GIANT TOMATO Tomatoes ca ...
Solutions - Seattle Central
... Indicators are chemical compounds used to detect the presence of other compounds. They change shape in the presence of certain compounds as a result of chemical reactions. ...
... Indicators are chemical compounds used to detect the presence of other compounds. They change shape in the presence of certain compounds as a result of chemical reactions. ...
What is pH?
... Strong bases can burn skin & eyes Turns red litmus paper to blue Bases react more easily with protein than with metal; they are often used for cleaning ...
... Strong bases can burn skin & eyes Turns red litmus paper to blue Bases react more easily with protein than with metal; they are often used for cleaning ...
Curriculum Map and Pacing Guide – Earth Systems
... levels of soil formation and horizons on campus. They will explain these phenomena in terms of the concepts previously learned. (levels 1, 2, 3) ***Construct a model of a ...
... levels of soil formation and horizons on campus. They will explain these phenomena in terms of the concepts previously learned. (levels 1, 2, 3) ***Construct a model of a ...
STEINWAY INTERMEDIATE SCHOOL 141Q A NASA Explorer
... Rock: A solid material made up of minerals, fossils, and/or organic material. Rock Cycle: A natural process constantly being forming, wearing down, and reforming rock. Metamorphic Rock: Rocks formed because of changes to high temperature and/or pressure, and form in foliated layers. Sediment ...
... Rock: A solid material made up of minerals, fossils, and/or organic material. Rock Cycle: A natural process constantly being forming, wearing down, and reforming rock. Metamorphic Rock: Rocks formed because of changes to high temperature and/or pressure, and form in foliated layers. Sediment ...
GEOL 1130 Nutrient Cycles
... • Nitrogen important nutrient for trees – In good salmon years, rainforest trees grow up to three times as fast • Forest ecosystem needs stream ecosystem and stream ecosystem needs forest ecosystems – Implications for salmon management? Most stocks down 90% and some gone ...
... • Nitrogen important nutrient for trees – In good salmon years, rainforest trees grow up to three times as fast • Forest ecosystem needs stream ecosystem and stream ecosystem needs forest ecosystems – Implications for salmon management? Most stocks down 90% and some gone ...