chap 55 SG - Milan Area Schools
... 1. The total amount of energy assimilated by photosynthesis is called _______. 2. The amount of energy assimilated by photosynthesis after the energy used by plants for maintenance and biosynthesis is subtracted is called _______. 3. All organisms that get their energy from a common source (e.g., al ...
... 1. The total amount of energy assimilated by photosynthesis is called _______. 2. The amount of energy assimilated by photosynthesis after the energy used by plants for maintenance and biosynthesis is subtracted is called _______. 3. All organisms that get their energy from a common source (e.g., al ...
Ecosystems Vocabulary
... Habitat-Natural, physical environment of an organism Organism-Any living system Populations-All individuals of a species in a given area Community-Consists of populations of different species that interact ...
... Habitat-Natural, physical environment of an organism Organism-Any living system Populations-All individuals of a species in a given area Community-Consists of populations of different species that interact ...
5 Jargon buster terms to learn adapting extreme
... All the organisms living in the same habitat Competition The fight for resources that are in limited supply by plants and animals in a habitat. This can be within the same population (the same species) or the same community (between different species) Crustacean Arthropod with chalky shell and joint ...
... All the organisms living in the same habitat Competition The fight for resources that are in limited supply by plants and animals in a habitat. This can be within the same population (the same species) or the same community (between different species) Crustacean Arthropod with chalky shell and joint ...
Unit 11-Ecology
... The gradual, sequential regrowth of a species in an area. ◦ Primary succession Development of a community in an area that has not supported life previously, such as bare rock, sand dunes, or an island formed from volcanic eruption. ...
... The gradual, sequential regrowth of a species in an area. ◦ Primary succession Development of a community in an area that has not supported life previously, such as bare rock, sand dunes, or an island formed from volcanic eruption. ...
ecology - Algonac Community Schools
... ◦ Environment changes as species inhabit it- some become extinct in an area, some flourish ◦ Natural disaster may change the ...
... ◦ Environment changes as species inhabit it- some become extinct in an area, some flourish ◦ Natural disaster may change the ...
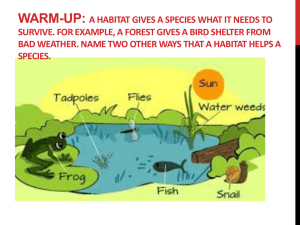
Warm-UP: A habitat gives a species what it needs to survive. For
... GRAB A NOTE SHEET AND LET’S REVIEW OUR ECOSYSTEM VOCAB. ...
... GRAB A NOTE SHEET AND LET’S REVIEW OUR ECOSYSTEM VOCAB. ...
Climate Change and Biodiversity in North America
... • Markets at many levels and scales • Uncertainties are truly large. ...
... • Markets at many levels and scales • Uncertainties are truly large. ...
The Biosphere : Section 3-1 What is Ecology?
... What is ecology? ___________________________________________________________ What does the biosphere contain? ______________________________________________ Levels of Organization (p. 64) 3. Why do ecologists ask questions about events and organisms that range in complexity from an individual to the ...
... What is ecology? ___________________________________________________________ What does the biosphere contain? ______________________________________________ Levels of Organization (p. 64) 3. Why do ecologists ask questions about events and organisms that range in complexity from an individual to the ...
Chap. 16 Ecosystems
... Ecosystem Boundaries Physical boundaries of an ecosystem are not always obvious, also depends of ecosystem ...
... Ecosystem Boundaries Physical boundaries of an ecosystem are not always obvious, also depends of ecosystem ...
AP Biology - lenzapbio
... 10. What is the difference between a food chain and a food web? Which provides a more “full” ecological picture and why? ...
... 10. What is the difference between a food chain and a food web? Which provides a more “full” ecological picture and why? ...
Includes interspecific interactions
... 1. Interspecific Competition (-/-) can lead to the competitive exclusion principle or one species will out compete another and can lead to character displacement Fundimental Niche – Niche a species could have Realized Niche – Portion of the Fundimental Niche a species lives in ...
... 1. Interspecific Competition (-/-) can lead to the competitive exclusion principle or one species will out compete another and can lead to character displacement Fundimental Niche – Niche a species could have Realized Niche – Portion of the Fundimental Niche a species lives in ...
Non Indigenous Species
... Some nonindigenous species could bring benefits, like the quinoa mentioned in Source G. This plant could help malnourished children by giving them protein. But there isn’t much known about what other species will come over with this plant, and if it will survive in a new place. The new habitat that ...
... Some nonindigenous species could bring benefits, like the quinoa mentioned in Source G. This plant could help malnourished children by giving them protein. But there isn’t much known about what other species will come over with this plant, and if it will survive in a new place. The new habitat that ...
Evidence for Evolution Notes
... _____________________, to date rocks containing potassium bearing minerals. 23. Based on chemical analysis, chemists have determined that potassium-40 decays to half its original amount is ________ million years. 24. Errors can occur in radiometric dating if the rock has been _____________________, ...
... _____________________, to date rocks containing potassium bearing minerals. 23. Based on chemical analysis, chemists have determined that potassium-40 decays to half its original amount is ________ million years. 24. Errors can occur in radiometric dating if the rock has been _____________________, ...
evidence for evolution
... Correlating evolutionary theories with geologic history helps explain the distribution of species, past and present ...
... Correlating evolutionary theories with geologic history helps explain the distribution of species, past and present ...
04 Climate and Ecosystems
... radiation strikes different parts of the Earth’s surfaces at different angles. This also causes SEASONS ...
... radiation strikes different parts of the Earth’s surfaces at different angles. This also causes SEASONS ...
Evolution - Cloudfront.net
... What is Evolution? • Change of an organism over time. • Modern orgs descended from past orgs. • Charles Darwin ! ...
... What is Evolution? • Change of an organism over time. • Modern orgs descended from past orgs. • Charles Darwin ! ...
Topic G Outline Bio - wfs
... Outline the factors that affect the distribution of plant species, including temperature, water, light, soil pH, salinity and mineral nutrients. G.1.2 Explain the factors that affect the distribution of animal species, including temperature, water, breeding sites, food supply and territory. G.1.3 De ...
... Outline the factors that affect the distribution of plant species, including temperature, water, light, soil pH, salinity and mineral nutrients. G.1.2 Explain the factors that affect the distribution of animal species, including temperature, water, breeding sites, food supply and territory. G.1.3 De ...
Cornell Notes Template - Ms. Doran`s Biology Class
... 1. A niche is the range of physical and biological conditions in which a species lives and the way the species obtains what it needs to survive and reproduce a. Aka it’s role in the ecosystem b. Niche-Involves: i. Resources available-any necessity of life En 2: Give an example of a resource: ii. Phy ...
... 1. A niche is the range of physical and biological conditions in which a species lives and the way the species obtains what it needs to survive and reproduce a. Aka it’s role in the ecosystem b. Niche-Involves: i. Resources available-any necessity of life En 2: Give an example of a resource: ii. Phy ...
Evolution Worksheet #2
... 27) What percent of all species that have ever lived are now extinct? ____________________ 28) Explain the concept of Punctuated Equilibrium, and describe how it differs from Gradualism. ______________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________ ...
... 27) What percent of all species that have ever lived are now extinct? ____________________ 28) Explain the concept of Punctuated Equilibrium, and describe how it differs from Gradualism. ______________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________ ...
File
... Evolutionary theory predicts that features of ancestors that no longer have a function for that species will become smaller over time until they are ______________________________. 7. ____________________________ structures can be used for the same purpose and can be superficially similar in const ...
... Evolutionary theory predicts that features of ancestors that no longer have a function for that species will become smaller over time until they are ______________________________. 7. ____________________________ structures can be used for the same purpose and can be superficially similar in const ...
biodiversity hotspot
... • A method to identify regions/places where most common extinctions occur and people invest money to save and preserve it ...
... • A method to identify regions/places where most common extinctions occur and people invest money to save and preserve it ...
Sample exam questions
... 5. For the following pairs of terms provide a concise definition for each that will clearly distinguish between the two terms. Be sure to include how the two terms are related to one another. A. homologous structure / analogous structure ...
... 5. For the following pairs of terms provide a concise definition for each that will clearly distinguish between the two terms. Be sure to include how the two terms are related to one another. A. homologous structure / analogous structure ...
Biogeography

Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. Organisms and biological communities often vary in a regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, isolation and habitat area. Phytogeography is the branch of biogeography that studies the distribution of plants. Zoogeography is the branch that studies distribution of animals.Knowledge of spatial variation in the numbers and types of organisms is as vital to us today as it was to our early human ancestors, as we adapt to heterogeneous but geographically predictable environments. Biogeography is an integrative field of inquiry that unites concepts and information from ecology, evolutionary biology, geology, and physical geography.Modern biogeographic research combines information and ideas from many fields, from the physiological and ecological constraints on organismal dispersal to geological and climatological phenomena operating at global spatial scales and evolutionary time frames.The short-term interactions within a habitat and species of organisms describe the ecological application of biogeography. Historical biogeography describes the long-term, evolutionary periods of time for broader classifications of organisms. Early scientists, beginning with Carl Linnaeus, contributed theories to the contributions of the development of biogeography as a science. Beginning in the mid-18th century, Europeans explored the world and discovered the biodiversity of life. Linnaeus initiated the ways to classify organisms through his exploration of undiscovered territories.The scientific theory of biogeography grows out of the work of Alexander von Humboldt (1769–1859), Hewett Cottrell Watson (1804–1881), Alphonse de Candolle (1806–1893), Alfred Russel Wallace (1823–1913), Philip Lutley Sclater (1829–1913) and other biologists and explorers.