BIOMES
... Biomes are dependent on both climate and the physical environment. There are a number of different biomes that occur in North America ...
... Biomes are dependent on both climate and the physical environment. There are a number of different biomes that occur in North America ...
Populations, Communities, and Species Interactions Environmental
... to live in a particular environment. • Population-level phenomenon, not the individual. • * Over evolutionary time, not the lifespan of an individual. ...
... to live in a particular environment. • Population-level phenomenon, not the individual. • * Over evolutionary time, not the lifespan of an individual. ...
Think like an Ecologist… a scientist who studies the relationships
... Ecotourism: Environmentally, culturally, and scientifically responsible tourism of unusual or interesting ecological sites. It safeguards the nature of the attraction and serves to strengthen conservation and scientific research efforts in the area. Endangered species: Wild species with so few indiv ...
... Ecotourism: Environmentally, culturally, and scientifically responsible tourism of unusual or interesting ecological sites. It safeguards the nature of the attraction and serves to strengthen conservation and scientific research efforts in the area. Endangered species: Wild species with so few indiv ...
Biodiversity Exam
... native species because of____________________ of resources. _______________________ is the ...
... native species because of____________________ of resources. _______________________ is the ...
Chapter 50 - An Introduction to Ecology and the Biosphere The
... Disturbance and Succession A. Primary Succession: When there is not even soil left (glacier, ...
... Disturbance and Succession A. Primary Succession: When there is not even soil left (glacier, ...
Ecology - wlhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
... replenished by natural processes in a reasonable amount of time Ex: fossil fuels ...
... replenished by natural processes in a reasonable amount of time Ex: fossil fuels ...
Ecology Unit/Chapter Title: Ecology/ Chapters 52
... 4.A.5 Communities are composed of populations of organisms that interact in complex ways. 4.A.6 Interactions among living systems and with their environment result in the movement of matter and energy. 4.B.4 Interactions between and within populations influence patterns of species distribution and a ...
... 4.A.5 Communities are composed of populations of organisms that interact in complex ways. 4.A.6 Interactions among living systems and with their environment result in the movement of matter and energy. 4.B.4 Interactions between and within populations influence patterns of species distribution and a ...
Biogeography 3/e
... Taiga is the Russian word for forest and is the largest biome in the world. It stretches over Eurasia and North America. The taiga is located near the top of the world, just below the tundra biome. The winters in the taiga are very cold with only snowfall. The summers are warm, rainy, and humid. A l ...
... Taiga is the Russian word for forest and is the largest biome in the world. It stretches over Eurasia and North America. The taiga is located near the top of the world, just below the tundra biome. The winters in the taiga are very cold with only snowfall. The summers are warm, rainy, and humid. A l ...
Ecosystem
... • All the organisms that live in a given habitat and affect one another as part of the food web or through their various influences on the ...
... • All the organisms that live in a given habitat and affect one another as part of the food web or through their various influences on the ...
Environmental Science Chapter 10 Study Guide Genetic Diversity
... 4. __Biodiversity___ is important to ecosystems because it helps populations adapt to ecological changes. (10.1) 5. _Species diversity_ is usually referred to as biodiversity. (10.1) 6. Benefits of biodiversity: a _variety__ of food sources, sources of new medicines__, and aesthetic or _personal enj ...
... 4. __Biodiversity___ is important to ecosystems because it helps populations adapt to ecological changes. (10.1) 5. _Species diversity_ is usually referred to as biodiversity. (10.1) 6. Benefits of biodiversity: a _variety__ of food sources, sources of new medicines__, and aesthetic or _personal enj ...
I. Earth Systems and Resources (10–15%)
... © 2010 The College Board. Visit the College Board on the Web: www.collegeboard.com ...
... © 2010 The College Board. Visit the College Board on the Web: www.collegeboard.com ...
Further Reading
... species, populations to ecosystems. The earth sustains millions of different species, many of which have not yet been discovered. According to the United Nations Convention on Biodiversity, which was adopted at the 1992 Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro as an important component of sustainable developm ...
... species, populations to ecosystems. The earth sustains millions of different species, many of which have not yet been discovered. According to the United Nations Convention on Biodiversity, which was adopted at the 1992 Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro as an important component of sustainable developm ...
Aquaculture is the farming of freshwater and saltwater organisms
... provide essential habitat. They also function as bioindicators, groups or types of biological resources that can be used to assess the environmental condition. We are offering an exciting opportunity for students to participate in further developing these organisms as bioindicator of ecosystem condi ...
... provide essential habitat. They also function as bioindicators, groups or types of biological resources that can be used to assess the environmental condition. We are offering an exciting opportunity for students to participate in further developing these organisms as bioindicator of ecosystem condi ...
Biodiversity
... • Plants, animals and other organisms used in: – Food – Clothing – Medicine – Other products ...
... • Plants, animals and other organisms used in: – Food – Clothing – Medicine – Other products ...
APES Alec Humphries Chapter 8 Guided Reading 1: Explain how
... 1: Define and give an example of each of the following: * Convergent Evolution The independent evolution of similar features in species of different lineages. Ex: wings, birds have different kinds of them but some cannot fly. * Divergent Evolution The accumulation of differences between groups which ...
... 1: Define and give an example of each of the following: * Convergent Evolution The independent evolution of similar features in species of different lineages. Ex: wings, birds have different kinds of them but some cannot fly. * Divergent Evolution The accumulation of differences between groups which ...
Ch 4 Ecosystems and Communites
... Occurs when organisms attempt to use the same limited ecological resource in the same place at the same time Intraspecific Competition Between ...
... Occurs when organisms attempt to use the same limited ecological resource in the same place at the same time Intraspecific Competition Between ...
4.2_Niches_and_Community
... Occurs when organisms attempt to use the same limited ecological resource in the same place at the same time Intraspecific Competition Between ...
... Occurs when organisms attempt to use the same limited ecological resource in the same place at the same time Intraspecific Competition Between ...
Unit Curriculum Map for Environmental Science
... Collect data Relate data to real life problems Do research Use technology Identify and report on endangered species Assessment(s) Students will get to choose an endangered species off the current endangered species list. They will need to create a brochure about their organism. The require ...
... Collect data Relate data to real life problems Do research Use technology Identify and report on endangered species Assessment(s) Students will get to choose an endangered species off the current endangered species list. They will need to create a brochure about their organism. The require ...
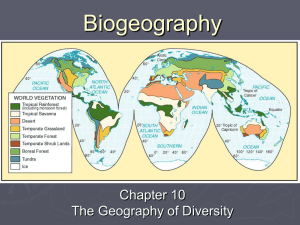
Chapter 10: The Geography of Diversity
... the organism on the left occurs in a hot desert habitat and the one on the right occurs in a cold tundra environment ...
... the organism on the left occurs in a hot desert habitat and the one on the right occurs in a cold tundra environment ...
Changes Over Time
... • Plants are called producers. This is because they produce their own food(glucose) through photosynthesis. • H2O+ CO2 + light --→ C6H12O6 + O2 + energy Glucose is C6H12O6 ...
... • Plants are called producers. This is because they produce their own food(glucose) through photosynthesis. • H2O+ CO2 + light --→ C6H12O6 + O2 + energy Glucose is C6H12O6 ...
Community Ecology
... • Repopulating barren lands • Determining most important species to conserve • Predicting how communities will recover, after disturbance • Predicting community resilience to disturbance • Quantifying what is present for conservation and where it would be ...
... • Repopulating barren lands • Determining most important species to conserve • Predicting how communities will recover, after disturbance • Predicting community resilience to disturbance • Quantifying what is present for conservation and where it would be ...
Ch. 3 Reading questions 1. What is an ecosystem and
... 1. Why is it challenging to determine the # of species on Earth? 2. Why are estimates of species diversity valuable to environmental scientists? 3. What is the difference between species richness and evenness? Why are they both important measures? 4. Describe the 3 main ways that evolution happens. ...
... 1. Why is it challenging to determine the # of species on Earth? 2. Why are estimates of species diversity valuable to environmental scientists? 3. What is the difference between species richness and evenness? Why are they both important measures? 4. Describe the 3 main ways that evolution happens. ...
Biogeography

Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. Organisms and biological communities often vary in a regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, isolation and habitat area. Phytogeography is the branch of biogeography that studies the distribution of plants. Zoogeography is the branch that studies distribution of animals.Knowledge of spatial variation in the numbers and types of organisms is as vital to us today as it was to our early human ancestors, as we adapt to heterogeneous but geographically predictable environments. Biogeography is an integrative field of inquiry that unites concepts and information from ecology, evolutionary biology, geology, and physical geography.Modern biogeographic research combines information and ideas from many fields, from the physiological and ecological constraints on organismal dispersal to geological and climatological phenomena operating at global spatial scales and evolutionary time frames.The short-term interactions within a habitat and species of organisms describe the ecological application of biogeography. Historical biogeography describes the long-term, evolutionary periods of time for broader classifications of organisms. Early scientists, beginning with Carl Linnaeus, contributed theories to the contributions of the development of biogeography as a science. Beginning in the mid-18th century, Europeans explored the world and discovered the biodiversity of life. Linnaeus initiated the ways to classify organisms through his exploration of undiscovered territories.The scientific theory of biogeography grows out of the work of Alexander von Humboldt (1769–1859), Hewett Cottrell Watson (1804–1881), Alphonse de Candolle (1806–1893), Alfred Russel Wallace (1823–1913), Philip Lutley Sclater (1829–1913) and other biologists and explorers.