Plate Tectonics & Evolution
... Australia separated from Antarctica about 50 Myrs ago. This extreme isolation over such a long period of time supports Darwin’s theory of evolution in that this part of the world has the most unique organisms. Australian species have had such limited contact with species from other continents that t ...
... Australia separated from Antarctica about 50 Myrs ago. This extreme isolation over such a long period of time supports Darwin’s theory of evolution in that this part of the world has the most unique organisms. Australian species have had such limited contact with species from other continents that t ...
from random mutation to
... ‘Theorem’: Without inter-specific competition (c_0 = 0) but with intra-specific competition (m_0 > 0), all species will eventually become competitive and coexist at an equilibrium state as the resources become sufficiently abundant. Stable but fragile : A competitive species X is not always competit ...
... ‘Theorem’: Without inter-specific competition (c_0 = 0) but with intra-specific competition (m_0 > 0), all species will eventually become competitive and coexist at an equilibrium state as the resources become sufficiently abundant. Stable but fragile : A competitive species X is not always competit ...
species - Bennatti
... • Mass extinction – loss of large number of species – usually due to catastrophic volcanic eruption or meteor impact – very rare (5 times in 3 billion years) ...
... • Mass extinction – loss of large number of species – usually due to catastrophic volcanic eruption or meteor impact – very rare (5 times in 3 billion years) ...
Biodiversity Name
... It is easier for a biodiverse ecosystems to recover from natural disasters because there are alternative food sources. Healthy biodiversity of species can provide a variety of food (like meat and produce). Many of our medicinal drugs come from plants. All of our wood products come from nature. We ca ...
... It is easier for a biodiverse ecosystems to recover from natural disasters because there are alternative food sources. Healthy biodiversity of species can provide a variety of food (like meat and produce). Many of our medicinal drugs come from plants. All of our wood products come from nature. We ca ...
What is your biodiversity IQ?
... 4. Giant weed grass – an indicator that there has been a disturbance in the wetland area ...
... 4. Giant weed grass – an indicator that there has been a disturbance in the wetland area ...
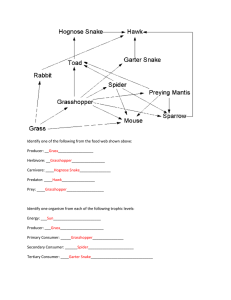
Identify one of the following from the food web shown above
... DDT is a chemical that was used to kill mosquitoes around the lake. Some DDT was later found in the water. According to this food chain, which of these organisms most likely contains the greatest concentration of DDT in its tissues? ...
... DDT is a chemical that was used to kill mosquitoes around the lake. Some DDT was later found in the water. According to this food chain, which of these organisms most likely contains the greatest concentration of DDT in its tissues? ...
Robert Bolen, William Hughes, Dr. Natale Spata Eastport South
... Biodiversity is the variety of life on Earth, including species such as plants, animals, and microorganisms, and the different ecosystems they inhabit. [1] Genetic biodiversity is the variation in genes that exists within a species, which can arise as a subspecies. The purpose of barcoding the speci ...
... Biodiversity is the variety of life on Earth, including species such as plants, animals, and microorganisms, and the different ecosystems they inhabit. [1] Genetic biodiversity is the variation in genes that exists within a species, which can arise as a subspecies. The purpose of barcoding the speci ...
Day 3 (Ch.17-23) - Protection & Recovery
... Continuous, slow rate of extinction over millions of years 1 every 200 years ...
... Continuous, slow rate of extinction over millions of years 1 every 200 years ...
M.L. Anderson, 2009
... zone and draw 90% of our marine-living resources from this region • Life evolved in the ocean 2.7 billion years before terrestrial life. • All except one phyla (33) occur in the ocean while only half exist on land (high phyletic diversity) • 15 phyla are exclusively marine. • Ocean creatures contain ...
... zone and draw 90% of our marine-living resources from this region • Life evolved in the ocean 2.7 billion years before terrestrial life. • All except one phyla (33) occur in the ocean while only half exist on land (high phyletic diversity) • 15 phyla are exclusively marine. • Ocean creatures contain ...
Document
... the diversity: everything else being equal • Data does not support this theory – Can be supported when put in the context of length of growing season (stability hypothesis) ...
... the diversity: everything else being equal • Data does not support this theory – Can be supported when put in the context of length of growing season (stability hypothesis) ...
Tigris-Euphrates Equitable Water Allocation
... Marshes and Tigris Euphrates watershed. It is imperative to synthesize scientific information and to collaborate on scientific research between stakeholders and scientists throughout the basin. Building a strong international community network will help with the development of viable solutions to re ...
... Marshes and Tigris Euphrates watershed. It is imperative to synthesize scientific information and to collaborate on scientific research between stakeholders and scientists throughout the basin. Building a strong international community network will help with the development of viable solutions to re ...
What is biodiversity? Why is it important? What threatens biodiversity
... Biodiversity is not distributed evenly across the planet: ...
... Biodiversity is not distributed evenly across the planet: ...
Biodiversity Quiz - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... ____ 2. More than one half of the world’s species live in tropical forests. ____ 3. About 10 million species have been identified by scientists. ____ 4. The Earth has many more species than it needs. ____ 5. More species are of no direct benefit to humans. ____ 6. Some habitats have more species tha ...
... ____ 2. More than one half of the world’s species live in tropical forests. ____ 3. About 10 million species have been identified by scientists. ____ 4. The Earth has many more species than it needs. ____ 5. More species are of no direct benefit to humans. ____ 6. Some habitats have more species tha ...
Global Strategy for Plant Conservation
... Plants are universally recognized as a vital part of the world’s biological diversity and an essential resource for the planet. In addition to the small number of crop plants used for basic food and fibres, many thousands of wild plants have great economic and cultural importance and potential, prov ...
... Plants are universally recognized as a vital part of the world’s biological diversity and an essential resource for the planet. In addition to the small number of crop plants used for basic food and fibres, many thousands of wild plants have great economic and cultural importance and potential, prov ...
General Biology – Diversity of Life
... [these kingdoms periodically change; originally there were 2 - plants and animals; until a few years ago taxonomists had settled on 5 kingdoms. However in the past couple of years genetic research has has shown that there are probably at least 9 to 12 equivalent kingdoms of life. In this course we w ...
... [these kingdoms periodically change; originally there were 2 - plants and animals; until a few years ago taxonomists had settled on 5 kingdoms. However in the past couple of years genetic research has has shown that there are probably at least 9 to 12 equivalent kingdoms of life. In this course we w ...
- Google Sites
... longer come in contact, so their genes no longer mix. If there is no contact, the mutations that occur in one population cannot spread to the other. Populations can be separated in many ways. Life’s diversification results from numerous speciation events. Speciation and extinction together determine ...
... longer come in contact, so their genes no longer mix. If there is no contact, the mutations that occur in one population cannot spread to the other. Populations can be separated in many ways. Life’s diversification results from numerous speciation events. Speciation and extinction together determine ...
CONSERVATION496.5 KB
... Some experts estimate that one animal species is wiped off the face of the Earth every hour. With the ravages of pollution, shrinking habitats and the ever-expanding human population, the situation is likely to get worse. Zoos are turning to cryogenics in their efforts to stockpile genetic material ...
... Some experts estimate that one animal species is wiped off the face of the Earth every hour. With the ravages of pollution, shrinking habitats and the ever-expanding human population, the situation is likely to get worse. Zoos are turning to cryogenics in their efforts to stockpile genetic material ...
Abstract
... the demographic and ecological forces on the species throughout its survival in different environmental conditions. Cyprus cedar (C. brevifolia) is an important endemic tree of the Cyprus flora, with narrow distribution in a sole fragmented population in the Paphos forest. The species is included in ...
... the demographic and ecological forces on the species throughout its survival in different environmental conditions. Cyprus cedar (C. brevifolia) is an important endemic tree of the Cyprus flora, with narrow distribution in a sole fragmented population in the Paphos forest. The species is included in ...
LESSON 1 Defining biodiversity
... Diversity within a species is necessary to maintain biodiversity. Genetic diversity plays a very important role in survival and adaptability of a species because when a species’ environment changes, slight gene variations are necessary for it to adapt and survive. A species that has a large degree o ...
... Diversity within a species is necessary to maintain biodiversity. Genetic diversity plays a very important role in survival and adaptability of a species because when a species’ environment changes, slight gene variations are necessary for it to adapt and survive. A species that has a large degree o ...
Environmental Science 2
... • Why? – environmental pressures allow for individual/species change ...
... • Why? – environmental pressures allow for individual/species change ...
Threats to marine biodiversity in the Mediterranean
... invasion of alien species (NIS non indigenous species) and climate change. These threats affect the greatest number of taxa; some of them come from maritime traffic (collisions, pollution, noise) and aquaculture (alien species, diseases, habitat destruction, pollution). The relevant role of climate ...
... invasion of alien species (NIS non indigenous species) and climate change. These threats affect the greatest number of taxa; some of them come from maritime traffic (collisions, pollution, noise) and aquaculture (alien species, diseases, habitat destruction, pollution). The relevant role of climate ...
Biodiversity
Global Biodiversity is the variety of different types of life found on Earth and the variations within species. It is a measure of the variety of organisms present in different ecosystems. This can refer to genetic variation, ecosystem variation, or species variation (number of species) within an area, biome, or planet. Terrestrial biodiversity tends to be highest near the equator, which seems to be the result of the warm climate and high primary productivity. Biodiversity is not distributed evenly on Earth. It is the richest in the tropics. Marine biodiversity tends to be highest along coasts in the Western Pacific, where sea surface temperature is highest and in the mid-latitudinal band in all oceans. There are latitudinal gradients in species diversity. Biodiversity generally tends to cluster in hotspots, and has been increasing through time but will be likely to slow in the future.The number and variety of plants, animals and other organisms that exist is known as biodiversity. It is an essential component of nature and it ensures the survival of human species by providing food, fuel, shelter, medicines and other resources to mankind. The richness of biodiversity depends on the climatic conditions and area of the region. All species of plants taken together are known as flora and about 70,000 species of plants are known till date. All species of animals taken together are known as fauna which includes birds, mammals, fish, reptiles, insects, crustaceans, molluscs, etc.Rapid environmental changes typically cause mass extinctions. More than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described. The total amount of related DNA base pairs on Earth is estimated at 5.0 x 1037, and weighs 50 billion tonnes. In comparison, the total mass of the biosphere has been estimated to be as much as 4 TtC (trillion tons of carbon).The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years old. The earliest undisputed evidence of life on Earth dates at least from 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era after a geological crust started to solidify following the earlier molten Hadean Eon. There are microbial mat fossils found in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone discovered in Western Australia. Other early physical evidence of a biogenic substance is graphite in 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks discovered in Western Greenland. Since life began on Earth, five major mass extinctions and several minor events have led to large and sudden drops in biodiversity. The Phanerozoic eon (the last 540 million years) marked a rapid growth in biodiversity via the Cambrian explosion—a period during which the majority of multicellular phyla first appeared. The next 400 million years included repeated, massive biodiversity losses classified as mass extinction events. In the Carboniferous, rainforest collapse led to a great loss of plant and animal life. The Permian–Triassic extinction event, 251 million years ago, was the worst; vertebrate recovery took 30 million years. The most recent, the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, occurred 65 million years ago and has often attracted more attention than others because it resulted in the extinction of the dinosaurs.The period since the emergence of humans has displayed an ongoing biodiversity reduction and an accompanying loss of genetic diversity. Named the Holocene extinction, the reduction is caused primarily by human impacts, particularly habitat destruction. Conversely, biodiversity impacts human health in a number of ways, both positively and negatively.The United Nations designated 2011–2020 as the United Nations Decade on Biodiversity.