Community Composition, Interactions, and Productivity
... • Set A-D has lower α diversity; one species per habitat dominated community. • Set E-H has lower β diversity; little difference in community between habitats. ...
... • Set A-D has lower α diversity; one species per habitat dominated community. • Set E-H has lower β diversity; little difference in community between habitats. ...
California Biodiversity Council:
... Yet it is also true that today, California's extraordinary diversity is being lost in many important habitats throughout the state. On average, over 20 percent of the naturally occurring species of amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals are classified as endangered, threatened, or "of special conc ...
... Yet it is also true that today, California's extraordinary diversity is being lost in many important habitats throughout the state. On average, over 20 percent of the naturally occurring species of amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals are classified as endangered, threatened, or "of special conc ...
biodiversity
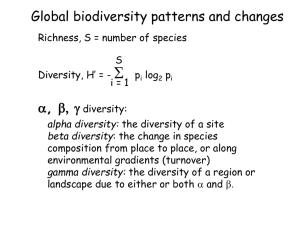
... kinds of organisms within a community or ecosystem – ecological diversity means the richness and complexity of a biological community ...
... kinds of organisms within a community or ecosystem – ecological diversity means the richness and complexity of a biological community ...
alpha diversity
... throughout its range for 151 previously located populations. Striking latitudinal trends in extinction: populations in Mexico 4x more likely to have gone extinct than those in Canada. Habitat loss was similar at southern and northern ends of range, suggesting range contraction due to climate change. ...
... throughout its range for 151 previously located populations. Striking latitudinal trends in extinction: populations in Mexico 4x more likely to have gone extinct than those in Canada. Habitat loss was similar at southern and northern ends of range, suggesting range contraction due to climate change. ...
Ecological Analysis
... provinces, and is related to ecosystem stability and productivity. H2. Population genetic continuity among geographic regions is more extensive for deep-sea species than for surface dwelling ones. H3. Environmental heterogeneity increases the frequency of endemic and cryptic species. H4. High zoopla ...
... provinces, and is related to ecosystem stability and productivity. H2. Population genetic continuity among geographic regions is more extensive for deep-sea species than for surface dwelling ones. H3. Environmental heterogeneity increases the frequency of endemic and cryptic species. H4. High zoopla ...
Unit 9: Ecology A. Definitions 1. biotic(bio = living)
... 1. invasive nonnative species (aka exotic species) were brought here for use as ornamental lawn or garden plants 2. when the invasive organism is able to survive and reproduce, it can invade the natural habitat and crowd out the native species reducing biodiversity 3. habitats with low plant ...
... 1. invasive nonnative species (aka exotic species) were brought here for use as ornamental lawn or garden plants 2. when the invasive organism is able to survive and reproduce, it can invade the natural habitat and crowd out the native species reducing biodiversity 3. habitats with low plant ...
What do Ecologists Study?
... experiments used to test for effects on fitness – Intraspecific: between members of same species; most intense is between males for access to females – Interspecific: between separate species; can lead to competitive exclusion – Scramble: rare in nature; all may get less than needed – Contest: mecha ...
... experiments used to test for effects on fitness – Intraspecific: between members of same species; most intense is between males for access to females – Interspecific: between separate species; can lead to competitive exclusion – Scramble: rare in nature; all may get less than needed – Contest: mecha ...
The Important Role of Ecological Connectivity for
... system - ensures the functionality of the ecosystem. Its multi-functionality can be achieved by supporting and regulating ecosystem services (such as pollination, pest, flood, and erosion control), which also provide for cultural, recreational and aesthetic ecosystem services. Furthermore, the direc ...
... system - ensures the functionality of the ecosystem. Its multi-functionality can be achieved by supporting and regulating ecosystem services (such as pollination, pest, flood, and erosion control), which also provide for cultural, recreational and aesthetic ecosystem services. Furthermore, the direc ...
Communty structure changes after extreme
... reduces the number of species it is not just the lists of organisms that changes, but also, possibly, essential and unique interactions may be lost forever. With their loss we may lose some or all potential for generation of a new diversity of life. Even some of our most prominent institutions dedic ...
... reduces the number of species it is not just the lists of organisms that changes, but also, possibly, essential and unique interactions may be lost forever. With their loss we may lose some or all potential for generation of a new diversity of life. Even some of our most prominent institutions dedic ...
Global Warming, Pollution and Invasive Species…
... temperature of the biosphere Temperatures between 1980 and 2000 rose at a faster rate than during the past 100 years!! The 1990’s were the hottest decade ever recorded….This decade will probably be even hotter! Each year of the 90’s was among the top 15 hottest years since 1880 ...
... temperature of the biosphere Temperatures between 1980 and 2000 rose at a faster rate than during the past 100 years!! The 1990’s were the hottest decade ever recorded….This decade will probably be even hotter! Each year of the 90’s was among the top 15 hottest years since 1880 ...
Relationships Among Organisms
... Animals that eat plants are known as herbivores. Ecologists usually classify the relationship between plants and herbivores as a form of predation. Secondary compounds- compounds produced by plants that are poisonous, bad tasting or irritating. ...
... Animals that eat plants are known as herbivores. Ecologists usually classify the relationship between plants and herbivores as a form of predation. Secondary compounds- compounds produced by plants that are poisonous, bad tasting or irritating. ...
APS Science Curriculum Unit Planner
... Those more likely to survive are also more likely to reproduce. Sexual reproduction produces more genetic diversity than nonsexual reproduction. How genetic variations lead to changes over time. All living things have similar chemical composition. Natural selection may happen through varie ...
... Those more likely to survive are also more likely to reproduce. Sexual reproduction produces more genetic diversity than nonsexual reproduction. How genetic variations lead to changes over time. All living things have similar chemical composition. Natural selection may happen through varie ...
Biodiversity
... • diversity of a place at the level of ecosystems • variety of ecosystems present in a biosphere • variety of species and ecological processes that occur in different physical settings. ...
... • diversity of a place at the level of ecosystems • variety of ecosystems present in a biosphere • variety of species and ecological processes that occur in different physical settings. ...
Factors affecting the variety of species in an ecosystem
... - total variation between all living things on earth - includes variation within a species - and between different species About 1.75 million species studied (BUT 10-100 million could exist) ...
... - total variation between all living things on earth - includes variation within a species - and between different species About 1.75 million species studied (BUT 10-100 million could exist) ...
Ecology_part_21
... These include aggression, decrease in parental care, decreased fertility, and decreased resistance to disease become limiting factors for growth and keep populations below carrying capacity. ...
... These include aggression, decrease in parental care, decreased fertility, and decreased resistance to disease become limiting factors for growth and keep populations below carrying capacity. ...
Biodiversity and Conservation Biology
... • Species numbers are one measure • The other is population numbers of each species • They are mostly on the decline • Which species are on the rise? • By one such measure there has been a 40% reduction in numbers of many species. ...
... • Species numbers are one measure • The other is population numbers of each species • They are mostly on the decline • Which species are on the rise? • By one such measure there has been a 40% reduction in numbers of many species. ...
Identifying Appropriate Conservation/Management Units I
... 1. Identification of natural taxa 2. Allows one to consider evolutionary history in conservation plans 3. DNA barcoding 4. Identify biodiversity hotspots 5. Evaluate changes in regional/global biodiversity in relation to environmental change ...
... 1. Identification of natural taxa 2. Allows one to consider evolutionary history in conservation plans 3. DNA barcoding 4. Identify biodiversity hotspots 5. Evaluate changes in regional/global biodiversity in relation to environmental change ...
Born at Rio 1992
... Despite the fact that governments have fully recognised their responsibility to halt the destruction of nature, and committed to the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity, the mass extinction of species and ecosystems has continued unhindered and completely uncontrolled. Since 1992, biodi ...
... Despite the fact that governments have fully recognised their responsibility to halt the destruction of nature, and committed to the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity, the mass extinction of species and ecosystems has continued unhindered and completely uncontrolled. Since 1992, biodi ...
131 Lecture 1.ppt [Read
... maintained by grazing when grazing is removed, coarse grasses dominate ...
... maintained by grazing when grazing is removed, coarse grasses dominate ...
Biodiversity
... Australia is one of only 12 ‘megadiverse’ countries and its native biodiversity is of global significance. It is estimated that there are more than one million species of plants and animals in Australia. Of particular significance is the high percentage of Australian species found only in Australia ...
... Australia is one of only 12 ‘megadiverse’ countries and its native biodiversity is of global significance. It is estimated that there are more than one million species of plants and animals in Australia. Of particular significance is the high percentage of Australian species found only in Australia ...
Lesson 1 what is biodiversity
... Large areas of tropical rainforests, the poles, and deserts not yet explored Climate change affecting biodiversity Continuing evolution and speciation Many species becoming endangered or are becoming ...
... Large areas of tropical rainforests, the poles, and deserts not yet explored Climate change affecting biodiversity Continuing evolution and speciation Many species becoming endangered or are becoming ...
Extinction of Species
... – Larger populations more resilient than smaller ones because of diverse gene pool and greater differentiation in alleles to cope with selection pressures ...
... – Larger populations more resilient than smaller ones because of diverse gene pool and greater differentiation in alleles to cope with selection pressures ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions – Chapters 1 and 2
... make room for human settlements or agriculture. In some areas, desertification follows removal of tree cover or heavy grazing of grasslands. 3. Dams and channelization destroy habitats. Dams flood some areas and deprive others of water, and they change the qualities of water such as its temperature, ...
... make room for human settlements or agriculture. In some areas, desertification follows removal of tree cover or heavy grazing of grasslands. 3. Dams and channelization destroy habitats. Dams flood some areas and deprive others of water, and they change the qualities of water such as its temperature, ...
Exam 7 Review - Iowa State University
... 14.) Conservation efforts to revive the Illinois Prairie Chicken were threatened by_____ A) lack of genetic variability B)lack of sanctuary ...
... 14.) Conservation efforts to revive the Illinois Prairie Chicken were threatened by_____ A) lack of genetic variability B)lack of sanctuary ...
Biodiversity
Global Biodiversity is the variety of different types of life found on Earth and the variations within species. It is a measure of the variety of organisms present in different ecosystems. This can refer to genetic variation, ecosystem variation, or species variation (number of species) within an area, biome, or planet. Terrestrial biodiversity tends to be highest near the equator, which seems to be the result of the warm climate and high primary productivity. Biodiversity is not distributed evenly on Earth. It is the richest in the tropics. Marine biodiversity tends to be highest along coasts in the Western Pacific, where sea surface temperature is highest and in the mid-latitudinal band in all oceans. There are latitudinal gradients in species diversity. Biodiversity generally tends to cluster in hotspots, and has been increasing through time but will be likely to slow in the future.The number and variety of plants, animals and other organisms that exist is known as biodiversity. It is an essential component of nature and it ensures the survival of human species by providing food, fuel, shelter, medicines and other resources to mankind. The richness of biodiversity depends on the climatic conditions and area of the region. All species of plants taken together are known as flora and about 70,000 species of plants are known till date. All species of animals taken together are known as fauna which includes birds, mammals, fish, reptiles, insects, crustaceans, molluscs, etc.Rapid environmental changes typically cause mass extinctions. More than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described. The total amount of related DNA base pairs on Earth is estimated at 5.0 x 1037, and weighs 50 billion tonnes. In comparison, the total mass of the biosphere has been estimated to be as much as 4 TtC (trillion tons of carbon).The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years old. The earliest undisputed evidence of life on Earth dates at least from 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era after a geological crust started to solidify following the earlier molten Hadean Eon. There are microbial mat fossils found in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone discovered in Western Australia. Other early physical evidence of a biogenic substance is graphite in 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks discovered in Western Greenland. Since life began on Earth, five major mass extinctions and several minor events have led to large and sudden drops in biodiversity. The Phanerozoic eon (the last 540 million years) marked a rapid growth in biodiversity via the Cambrian explosion—a period during which the majority of multicellular phyla first appeared. The next 400 million years included repeated, massive biodiversity losses classified as mass extinction events. In the Carboniferous, rainforest collapse led to a great loss of plant and animal life. The Permian–Triassic extinction event, 251 million years ago, was the worst; vertebrate recovery took 30 million years. The most recent, the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, occurred 65 million years ago and has often attracted more attention than others because it resulted in the extinction of the dinosaurs.The period since the emergence of humans has displayed an ongoing biodiversity reduction and an accompanying loss of genetic diversity. Named the Holocene extinction, the reduction is caused primarily by human impacts, particularly habitat destruction. Conversely, biodiversity impacts human health in a number of ways, both positively and negatively.The United Nations designated 2011–2020 as the United Nations Decade on Biodiversity.