FUNCTIONALBIO Functional biodiversity in forests: diversity of soil
... assemblage of macrofungi compared to that of the other tree species (Figure 1); oak sites had the most diverse macrofungal assemblages on average, but more species were found on Sitka spruce sites. This may be due to more Sitka spruce sites being ...
... assemblage of macrofungi compared to that of the other tree species (Figure 1); oak sites had the most diverse macrofungal assemblages on average, but more species were found on Sitka spruce sites. This may be due to more Sitka spruce sites being ...
• Biodiversity refers to the number and variety of species on Earth
... volcano erupted in 1980, it devastated an entire mountain of life; however, there was one mammal that survived. A small furry gopher species had tunneled underground and eventually found its way to the surface, after the lava cooled. Because this small gopher has adaptations such as fast burrowing c ...
... volcano erupted in 1980, it devastated an entire mountain of life; however, there was one mammal that survived. A small furry gopher species had tunneled underground and eventually found its way to the surface, after the lava cooled. Because this small gopher has adaptations such as fast burrowing c ...
Biodiversity refers to the number and variety of species
... volcano erupted in 1980, it devastated an entire mountain of life; however, there was one mammal that survived. A small furry gopher species had tunneled underground and eventually found its way to the surface, after the lava cooled. Because this small gopher has adaptations such as fast burrowing c ...
... volcano erupted in 1980, it devastated an entire mountain of life; however, there was one mammal that survived. A small furry gopher species had tunneled underground and eventually found its way to the surface, after the lava cooled. Because this small gopher has adaptations such as fast burrowing c ...
BIODIVERSITY
... Captive breeding is mathing of animals in zoos or wildlife preserves. It was the only hope for the California condor, the largest bird in North America. ...
... Captive breeding is mathing of animals in zoos or wildlife preserves. It was the only hope for the California condor, the largest bird in North America. ...
Fact Sheet Contact: Daniel Boone Phone: 928-523
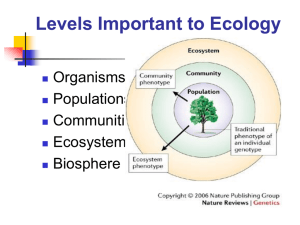
... belowground on their roots. In other words, the genes in one organism, in this case a foundation tree species, can define a much larger community of organisms and even affect ecosystem processes such as nutrient cycling. • Researchers found that a single gene in a plant or animal can affect an entir ...
... belowground on their roots. In other words, the genes in one organism, in this case a foundation tree species, can define a much larger community of organisms and even affect ecosystem processes such as nutrient cycling. • Researchers found that a single gene in a plant or animal can affect an entir ...
Biodiversity is the abundance of different species and ecosystems in
... ecosystem is an ecological community, which together with its environment, functions as a unit. Currently, biodiversity is decreasing at an alarming rate due to human activities. This is referred to as the “biodiversity crisis.” One example of human impact on biodiversity is the clear-cutting of for ...
... ecosystem is an ecological community, which together with its environment, functions as a unit. Currently, biodiversity is decreasing at an alarming rate due to human activities. This is referred to as the “biodiversity crisis.” One example of human impact on biodiversity is the clear-cutting of for ...
Understanding and addressing the causes of biodiversity loss
... Although policy frameworks designed to safeguard biodiversity exist, these measures can be inadequate. The researchers suggest one of the main reasons is that decision makers at all levels fail to design policies that sufficiently protect ecosystem services. For example, a lack of effective property ...
... Although policy frameworks designed to safeguard biodiversity exist, these measures can be inadequate. The researchers suggest one of the main reasons is that decision makers at all levels fail to design policies that sufficiently protect ecosystem services. For example, a lack of effective property ...
Unit 3 Study Guide – The Nature of Ecology
... APES Study Guide Unit 3 – The Nature of Ecology In this unit we see how land use, conservation, and forest management help keep a healthy worldwide biodiversity, and how our modern conservation movement came to be. Reading Miller, Living in the Environment, 15th Edition, Chapter 3, 4 & 7. Major Lab ...
... APES Study Guide Unit 3 – The Nature of Ecology In this unit we see how land use, conservation, and forest management help keep a healthy worldwide biodiversity, and how our modern conservation movement came to be. Reading Miller, Living in the Environment, 15th Edition, Chapter 3, 4 & 7. Major Lab ...
Community Ecology
... Passes on up the trophic levels Travels one way Due to entropy, less energy available at the top ...
... Passes on up the trophic levels Travels one way Due to entropy, less energy available at the top ...
Includes interspecific interactions
... 1. Interspecific Competition (-/-) can lead to the competitive exclusion principle or one species will out compete another and can lead to character displacement Fundimental Niche – Niche a species could have Realized Niche – Portion of the Fundimental Niche a species lives in ...
... 1. Interspecific Competition (-/-) can lead to the competitive exclusion principle or one species will out compete another and can lead to character displacement Fundimental Niche – Niche a species could have Realized Niche – Portion of the Fundimental Niche a species lives in ...
Biodiversity is everyone`s business
... What biodiversity do we have? Australia is one of only 12 ‘megadiverse’ countries and its native biodiversity is of global significance. It is estimated that there are more than one million species of plants and animals in Australia. Of particular significance is the high percentage of Australian sp ...
... What biodiversity do we have? Australia is one of only 12 ‘megadiverse’ countries and its native biodiversity is of global significance. It is estimated that there are more than one million species of plants and animals in Australia. Of particular significance is the high percentage of Australian sp ...
Biodiversity Threats
... To manage Golden Gate Highlands National Park in a collaborative learning environment as part of an ecologically functional and sustainable patchwork of different land uses in the region that ensures the persistence of the natural and cultural heritage for the benefit and enjoyment of all. SANParks ...
... To manage Golden Gate Highlands National Park in a collaborative learning environment as part of an ecologically functional and sustainable patchwork of different land uses in the region that ensures the persistence of the natural and cultural heritage for the benefit and enjoyment of all. SANParks ...
Community Composition, Interactions, and Productivity
... • Set A-D has lower α diversity; one species per habitat dominated community. • Set E-H has lower β diversity; little difference in community between habitats. ...
... • Set A-D has lower α diversity; one species per habitat dominated community. • Set E-H has lower β diversity; little difference in community between habitats. ...
COMMUNITY AND POPULATION ECOLOGY
... Succession in lakes filling in to form bogs and then meadows. ...
... Succession in lakes filling in to form bogs and then meadows. ...
Exam practice answers
... It lowers the biodiversity of plants by loss of plant species; it lowers the biodiversity of animals by loss of animal species that feed on/nest in (lost) plant species; loss of genetic diversity as alleles of some genes lost from small(er) populations. ...
... It lowers the biodiversity of plants by loss of plant species; it lowers the biodiversity of animals by loss of animal species that feed on/nest in (lost) plant species; loss of genetic diversity as alleles of some genes lost from small(er) populations. ...
Ch 6 Humans in the Biosphere
... trends seen in the data suggest that average global surface temperatures will increase by 1 to 2 degrees Celsius by the year ...
... trends seen in the data suggest that average global surface temperatures will increase by 1 to 2 degrees Celsius by the year ...
Environmental Challenges
... average surface temperature Partly caused by increased amounts of carbon dioxide escaping into the air ...
... average surface temperature Partly caused by increased amounts of carbon dioxide escaping into the air ...
Genetic Diversity
... 1.4 Classifying Types of Biodiversity There are 3 types of Biological Diversity: 1. ________________________________ 2. ________________________________ 3. ________________________________ ...
... 1.4 Classifying Types of Biodiversity There are 3 types of Biological Diversity: 1. ________________________________ 2. ________________________________ 3. ________________________________ ...
Species Concept
... • What is “genetic diversity” within a species? • What is meant by “species diversity” within an ecosystem? • Can there be genetic diversity within an ecosystem? ...
... • What is “genetic diversity” within a species? • What is meant by “species diversity” within an ecosystem? • Can there be genetic diversity within an ecosystem? ...
Chapter 7
... • Genetic Diversity – total number of genes in a species • Habitat Diversity – different kinds of habitats in an area • Species Diversity – has 3 qualities – Species Richness: total # of species – Species Evenness: relative abundance – Species Dominance: most abundant ...
... • Genetic Diversity – total number of genes in a species • Habitat Diversity – different kinds of habitats in an area • Species Diversity – has 3 qualities – Species Richness: total # of species – Species Evenness: relative abundance – Species Dominance: most abundant ...
What is Biodiversity?
... In 2002, Governments set 2010 as a deadline to achieve a significant reduction in the rate of loss of biodiversity for reducing poverty. All assessments of progress indicate that we are far from reaching this goal. The year 2010 is critical because it is time to reflect about what needs to be done i ...
... In 2002, Governments set 2010 as a deadline to achieve a significant reduction in the rate of loss of biodiversity for reducing poverty. All assessments of progress indicate that we are far from reaching this goal. The year 2010 is critical because it is time to reflect about what needs to be done i ...
document
... – High repro. Rate, so overgrow quickly – Is filtering water of Lake Michigan very well….good or bad??!?!?! More light, more growth of plants, may be better habitat for fish…or not. – $500 billion in next 10 years! • deliberate release of invasive species – Kudzu, from Japan to US 1876 (ornamental p ...
... – High repro. Rate, so overgrow quickly – Is filtering water of Lake Michigan very well….good or bad??!?!?! More light, more growth of plants, may be better habitat for fish…or not. – $500 billion in next 10 years! • deliberate release of invasive species – Kudzu, from Japan to US 1876 (ornamental p ...
Biodiversity
Global Biodiversity is the variety of different types of life found on Earth and the variations within species. It is a measure of the variety of organisms present in different ecosystems. This can refer to genetic variation, ecosystem variation, or species variation (number of species) within an area, biome, or planet. Terrestrial biodiversity tends to be highest near the equator, which seems to be the result of the warm climate and high primary productivity. Biodiversity is not distributed evenly on Earth. It is the richest in the tropics. Marine biodiversity tends to be highest along coasts in the Western Pacific, where sea surface temperature is highest and in the mid-latitudinal band in all oceans. There are latitudinal gradients in species diversity. Biodiversity generally tends to cluster in hotspots, and has been increasing through time but will be likely to slow in the future.The number and variety of plants, animals and other organisms that exist is known as biodiversity. It is an essential component of nature and it ensures the survival of human species by providing food, fuel, shelter, medicines and other resources to mankind. The richness of biodiversity depends on the climatic conditions and area of the region. All species of plants taken together are known as flora and about 70,000 species of plants are known till date. All species of animals taken together are known as fauna which includes birds, mammals, fish, reptiles, insects, crustaceans, molluscs, etc.Rapid environmental changes typically cause mass extinctions. More than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described. The total amount of related DNA base pairs on Earth is estimated at 5.0 x 1037, and weighs 50 billion tonnes. In comparison, the total mass of the biosphere has been estimated to be as much as 4 TtC (trillion tons of carbon).The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years old. The earliest undisputed evidence of life on Earth dates at least from 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era after a geological crust started to solidify following the earlier molten Hadean Eon. There are microbial mat fossils found in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone discovered in Western Australia. Other early physical evidence of a biogenic substance is graphite in 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks discovered in Western Greenland. Since life began on Earth, five major mass extinctions and several minor events have led to large and sudden drops in biodiversity. The Phanerozoic eon (the last 540 million years) marked a rapid growth in biodiversity via the Cambrian explosion—a period during which the majority of multicellular phyla first appeared. The next 400 million years included repeated, massive biodiversity losses classified as mass extinction events. In the Carboniferous, rainforest collapse led to a great loss of plant and animal life. The Permian–Triassic extinction event, 251 million years ago, was the worst; vertebrate recovery took 30 million years. The most recent, the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, occurred 65 million years ago and has often attracted more attention than others because it resulted in the extinction of the dinosaurs.The period since the emergence of humans has displayed an ongoing biodiversity reduction and an accompanying loss of genetic diversity. Named the Holocene extinction, the reduction is caused primarily by human impacts, particularly habitat destruction. Conversely, biodiversity impacts human health in a number of ways, both positively and negatively.The United Nations designated 2011–2020 as the United Nations Decade on Biodiversity.