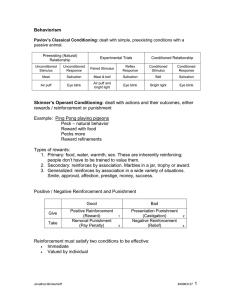
Classical Conditioning
... Learning to do something, or not to do something based on the results. In Classical Conditioning, responses are often involuntary behaviors that are spurred by secondary stimuli. ...
... Learning to do something, or not to do something based on the results. In Classical Conditioning, responses are often involuntary behaviors that are spurred by secondary stimuli. ...
Operant Conditioning
... an organism associates different stimuli that it does not control. Through operant conditioning, the organism associates its behaviors with consequences. Behaviors followed by reinforcements increase; those followed by punishers decrease. This simple but powerful principle has many applications and ...
... an organism associates different stimuli that it does not control. Through operant conditioning, the organism associates its behaviors with consequences. Behaviors followed by reinforcements increase; those followed by punishers decrease. This simple but powerful principle has many applications and ...
Catalog Program and Course Descriptions
... This course covers the topic of behavioral assessment. Behavioral assessment is a large part of any practicing applied behavior analyst’s daily duties. In this course students will take what they have learned in previous courses and practicum experience and apply it to behavior problems of social si ...
... This course covers the topic of behavioral assessment. Behavioral assessment is a large part of any practicing applied behavior analyst’s daily duties. In this course students will take what they have learned in previous courses and practicum experience and apply it to behavior problems of social si ...
Behavior Analysis and Strategy Application after Brain Injury
... Operant Conditioning • But as you probably already noticed, we do not simply react to stimuli in the environment. • Based on our history, we also act in ways that affect or change the environment. S arrangement, mentioned • This is where the R previously, requires examination. ...
... Operant Conditioning • But as you probably already noticed, we do not simply react to stimuli in the environment. • Based on our history, we also act in ways that affect or change the environment. S arrangement, mentioned • This is where the R previously, requires examination. ...
Behaviorism
... teaching behavior a class assignment. Leaves room so students can decide what and how they’re going to do this. Teaching behaviors students have chosen include: Making eye contact with all members of the class Moving around the classroom more frequently Giving more examples from her personal l ...
... teaching behavior a class assignment. Leaves room so students can decide what and how they’re going to do this. Teaching behaviors students have chosen include: Making eye contact with all members of the class Moving around the classroom more frequently Giving more examples from her personal l ...
HERE
... Behaviorism (also called the behaviorist approach) was the primary paradigm in psychology between 1920s to 1950: • Psychology should be seen as a science. Theories need to be supported by empirical data obtained through careful and controlled observation and measurement of behavior. • Behaviourism i ...
... Behaviorism (also called the behaviorist approach) was the primary paradigm in psychology between 1920s to 1950: • Psychology should be seen as a science. Theories need to be supported by empirical data obtained through careful and controlled observation and measurement of behavior. • Behaviourism i ...
File - It does not do to dwell on dreams and forget to live
... unconditioned stimulus and unconditioned response, respectively. The original and most famous example of classical conditioning involved the salivary conditioning of Pavlov's dogs. During his research on the physiology of digestion in dogs, Pavlov noticed that, rather than simply salivating in the p ...
... unconditioned stimulus and unconditioned response, respectively. The original and most famous example of classical conditioning involved the salivary conditioning of Pavlov's dogs. During his research on the physiology of digestion in dogs, Pavlov noticed that, rather than simply salivating in the p ...
skinner theory of operent conditioning and shaping
... reinforcement since it is designed to weaken or eliminate a response rather than increase it. Positive punishment is when unfavorable events or outcomes are given in order to weaken the response that follows Negative punishment is characterized by when an favorable event or outcome is removed af ...
... reinforcement since it is designed to weaken or eliminate a response rather than increase it. Positive punishment is when unfavorable events or outcomes are given in order to weaken the response that follows Negative punishment is characterized by when an favorable event or outcome is removed af ...
an introduction to lifespan development
... • Each perspective is based on its own premises and focuses on different aspects of development • Same developmental phenomenon can be examined from a number of perspectives simultaneously • None of the ‘theories’ are sufficient and complete. If they were there would be A Theory of Human Development ...
... • Each perspective is based on its own premises and focuses on different aspects of development • Same developmental phenomenon can be examined from a number of perspectives simultaneously • None of the ‘theories’ are sufficient and complete. If they were there would be A Theory of Human Development ...
A Brief Explanation of Applied Behavior Analysis
... case of problem classroom behavior, the consequence would involve ignoring. However, the extinction contingency requires a concurrent reinforcement contingency to increase the likelihood of a desired classroom behavior to allow the student to achieve the same function. If an alternative behavior is ...
... case of problem classroom behavior, the consequence would involve ignoring. However, the extinction contingency requires a concurrent reinforcement contingency to increase the likelihood of a desired classroom behavior to allow the student to achieve the same function. If an alternative behavior is ...
Learning Learning: A relatively permanent change of an organism`s
... --Mirror Neurons: frontal lobe neurons that fire when performing certain actions or observing another doing so; transform the sight of someone else’s actions into the motor program you would use to do the same thing; may enable imitation, language training, & empathy Albert Bandura: behaviorism pi ...
... --Mirror Neurons: frontal lobe neurons that fire when performing certain actions or observing another doing so; transform the sight of someone else’s actions into the motor program you would use to do the same thing; may enable imitation, language training, & empathy Albert Bandura: behaviorism pi ...
this PDF file
... inacceptable hierarchies, ALAIC and ECREA claim to contribute to this objective ‘by emphasizing the regional specificity and contextual embeddedness of theories, methodologies and research traditions’ and – referring to previous bilateral initiatives – by ‘critically comparing the strengths and weak ...
... inacceptable hierarchies, ALAIC and ECREA claim to contribute to this objective ‘by emphasizing the regional specificity and contextual embeddedness of theories, methodologies and research traditions’ and – referring to previous bilateral initiatives – by ‘critically comparing the strengths and weak ...
File - teacherver.com
... Cognitive Factors in Learning - Classical and Operant conditioning ignored the possibility that cognitive factors such as memory, thinking, planning, expectations setting to be involved in learning. - Cognitive vs. Behavioral: behaviorist do not deny that thinking processes have roles in learning bu ...
... Cognitive Factors in Learning - Classical and Operant conditioning ignored the possibility that cognitive factors such as memory, thinking, planning, expectations setting to be involved in learning. - Cognitive vs. Behavioral: behaviorist do not deny that thinking processes have roles in learning bu ...
Operant Conditioning
... an organism associates different stimuli that it does not control. Through operant conditioning, the organism associates its behaviors with consequences. Behaviors followed by reinforcements increase; those followed by punishers decrease. This simple but powerful principle has many applications and ...
... an organism associates different stimuli that it does not control. Through operant conditioning, the organism associates its behaviors with consequences. Behaviors followed by reinforcements increase; those followed by punishers decrease. This simple but powerful principle has many applications and ...
9.2 Operant Conditioning
... rage, aggression and fear. • 2.) People learn to avoid the person delivering the aversive consequences. • Punishment does not teach appropriate and acceptable behavior. Without positive coaching and modeling, the child may never learn the correct behavior. ...
... rage, aggression and fear. • 2.) People learn to avoid the person delivering the aversive consequences. • Punishment does not teach appropriate and acceptable behavior. Without positive coaching and modeling, the child may never learn the correct behavior. ...
Module 1.1 Foundations of Modern Psychology Lecture Outline
... 1. Believed that free will and conscious choice are essentials of the human experience 2. Emphasizes the importance of self-awareness and becoming an authentic person by being true to oneself D. Physiological perspective 1. Relations between biological process and behavior 2. Emphasizes the roles of ...
... 1. Believed that free will and conscious choice are essentials of the human experience 2. Emphasizes the importance of self-awareness and becoming an authentic person by being true to oneself D. Physiological perspective 1. Relations between biological process and behavior 2. Emphasizes the roles of ...
chapter 1: basic concepts of behavior and behavior management
... rate, duration, or intensity. Operant conditioning has its roots in the animal research conducted by Thorndike (1905, 1911) and Skinner (1938, 1953). Thorndike demonstrated the relationship between reinforcement and rates of learning. Skinner, whose name is synonymous with operant conditioning and b ...
... rate, duration, or intensity. Operant conditioning has its roots in the animal research conducted by Thorndike (1905, 1911) and Skinner (1938, 1953). Thorndike demonstrated the relationship between reinforcement and rates of learning. Skinner, whose name is synonymous with operant conditioning and b ...
punishment
... Punishment can create strong negative emotions that can interfere with learning the desired response. For all of these reasons, punishment should be used sparingly and only when other operant conditioning procedures either cannot be used or will not work. ...
... Punishment can create strong negative emotions that can interfere with learning the desired response. For all of these reasons, punishment should be used sparingly and only when other operant conditioning procedures either cannot be used or will not work. ...
Principles of Behavior Modification (PSY333)
... How to get generalization to occur E.g. mathematics: Balancing checkbook • Train in the target situation: Balance Checkbook in store • Vary Training Conditions: Extraneous stimuli present • Program Common Stimuli: the checkbook itself (common learning materials). • Train sufficient stimulus exempla ...
... How to get generalization to occur E.g. mathematics: Balancing checkbook • Train in the target situation: Balance Checkbook in store • Vary Training Conditions: Extraneous stimuli present • Program Common Stimuli: the checkbook itself (common learning materials). • Train sufficient stimulus exempla ...
Intro to Animal Behavior
... Social behaviors in animals can be related to courtship and mating, caring for young, defense, obtaining food, establishing or maintaining territory or periodic cycles. Successful behaviors promote survival of the individual animal and its future generations. Courtship consists of behaviors that h ...
... Social behaviors in animals can be related to courtship and mating, caring for young, defense, obtaining food, establishing or maintaining territory or periodic cycles. Successful behaviors promote survival of the individual animal and its future generations. Courtship consists of behaviors that h ...
THE SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY OF ORGANIZATIONS
... Past approaches to the study of social problems and social behaviour have been limited by a lack of adequate conceptual tools. This limitation has been manifest both in psychology and sociology, although in different ways. Psychologists have been characteristically unable or willing to deal with the ...
... Past approaches to the study of social problems and social behaviour have been limited by a lack of adequate conceptual tools. This limitation has been manifest both in psychology and sociology, although in different ways. Psychologists have been characteristically unable or willing to deal with the ...
Picture from Ladies` Home Journal
... when it recurs, they will be more likely to recur; those which are accompanied or closely followed by discomfort to the animal will, other things being equal, have their connections to the situation weakened, so that, when it recurs, they will be less likely to occur. ...
... when it recurs, they will be more likely to recur; those which are accompanied or closely followed by discomfort to the animal will, other things being equal, have their connections to the situation weakened, so that, when it recurs, they will be less likely to occur. ...
Learning
... Prescribing undesired activity Physical aggression Drawbacks: Punished behavior is not forgotten, it is suppressed Physical punishment increases aggression through modeling Can also create fear that will generalize Does not tell you “what to do”! Punishment if used swiftly, works best when ...
... Prescribing undesired activity Physical aggression Drawbacks: Punished behavior is not forgotten, it is suppressed Physical punishment increases aggression through modeling Can also create fear that will generalize Does not tell you “what to do”! Punishment if used swiftly, works best when ...
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vIbZB6rNLZ4
... Primary v. Secondary Reinforcers Primary Reinforcer • Things that are in themselves rewarding. ...
... Primary v. Secondary Reinforcers Primary Reinforcer • Things that are in themselves rewarding. ...