File
... • Person A closes their eyes. • Person B has to touch Person A gently in different areas of the body. • Person A has to identify which part of their body was being touched. ...
... • Person A closes their eyes. • Person B has to touch Person A gently in different areas of the body. • Person A has to identify which part of their body was being touched. ...
Disorders of the Neuromuscular Junction
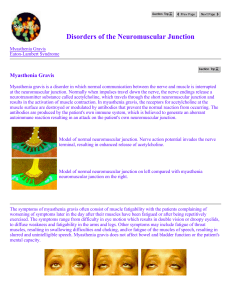
... After a few minutes of rest, the eyelids have returned to near-normal position When the diagnosis of myasthenia gravis is suspected tests will be needed for confirmation of the diagnosis. A tensilon test, which is a relatively simple procedure, involves insertion of a small intravenous catheter thro ...
... After a few minutes of rest, the eyelids have returned to near-normal position When the diagnosis of myasthenia gravis is suspected tests will be needed for confirmation of the diagnosis. A tensilon test, which is a relatively simple procedure, involves insertion of a small intravenous catheter thro ...
File4
... stimulus to visual awareness, the congruity of the prime stimulus with the target stimulus had a significant effect on participants’ pointing trajectories. • Masked unseen word processing extends down to include the formulation of overt ...
... stimulus to visual awareness, the congruity of the prime stimulus with the target stimulus had a significant effect on participants’ pointing trajectories. • Masked unseen word processing extends down to include the formulation of overt ...
dementia - u.arizona.edu
... all the information they could lose, especially all the lobes involved with vision, voluntary eye movements, etc. Also, aphasia & all the different types and which ones are in which lobes and infarction present how, expression, conductive, word salad, you get the idea. Also, know what to do & what n ...
... all the information they could lose, especially all the lobes involved with vision, voluntary eye movements, etc. Also, aphasia & all the different types and which ones are in which lobes and infarction present how, expression, conductive, word salad, you get the idea. Also, know what to do & what n ...
Burners and Stingers
... "electric" shock sensation is often felt. The arm may feel "dead" or numb immediately following the injury, and weakness is common. The symptoms most commonly occur in one arm only. Symptoms usually last seconds to minutes, but in 5 percent to 10 percent of cases, they can last hours, days or even l ...
... "electric" shock sensation is often felt. The arm may feel "dead" or numb immediately following the injury, and weakness is common. The symptoms most commonly occur in one arm only. Symptoms usually last seconds to minutes, but in 5 percent to 10 percent of cases, they can last hours, days or even l ...
UNIT 4: Sensation and Perception I. Overview A. Sensation
... How do we locate sounds? i. Sound will strike one ear faster than it does the other ...
... How do we locate sounds? i. Sound will strike one ear faster than it does the other ...
What happens in a neuron
... and leaking are common occurrences for those affected. Subjects relating to defecation are often socially unacceptable, thus those affected may be beset by feelings of shame and humiliation. What type of nerve does Fecal Incontinence affect? How do you know it was that division of the nervous system ...
... and leaking are common occurrences for those affected. Subjects relating to defecation are often socially unacceptable, thus those affected may be beset by feelings of shame and humiliation. What type of nerve does Fecal Incontinence affect? How do you know it was that division of the nervous system ...
Brain
... • Left: controls movement on the body’s right side and has logic abilities • Right: controls movement on the body’s left side and more for creativity Neuron Forest • Where the work of the brain goes on in individual cells • Signals that form memories and thoughts move through a nerve cell as an elec ...
... • Left: controls movement on the body’s right side and has logic abilities • Right: controls movement on the body’s left side and more for creativity Neuron Forest • Where the work of the brain goes on in individual cells • Signals that form memories and thoughts move through a nerve cell as an elec ...
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Pulmonary - CARE-NMD
... • Awake end-tidal CO2 level should be measured by capnography, if patient non-ambulatory and has any of – Suspected hypoventilation – FVC <50% prediceted – Current use of assisted ventilation ...
... • Awake end-tidal CO2 level should be measured by capnography, if patient non-ambulatory and has any of – Suspected hypoventilation – FVC <50% prediceted – Current use of assisted ventilation ...
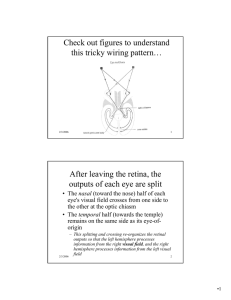
After leaving the retina, the outputs of each eye are split
... – Each V1 does not simply receive input from the opposite eye; the outputs of each retina are split (left half/right half) and then run through the LGN to the appropriate V1 • Just as the image of the world is inverted when projected onto the retina, the retinotopic V1 map is upside down (and the ri ...
... – Each V1 does not simply receive input from the opposite eye; the outputs of each retina are split (left half/right half) and then run through the LGN to the appropriate V1 • Just as the image of the world is inverted when projected onto the retina, the retinotopic V1 map is upside down (and the ri ...
I. The Nervous System
... 3. dendrites- carries impulses toward the cell body. 4. axon- carries impulses away from the cell body. 5. myelin sheath- covers part of some axons. 6. synapse – at the end of the axon E. Nerve Impulse- an electrical impulse conducted along a nerve fiber. 1. resting potential- the electrical charge ...
... 3. dendrites- carries impulses toward the cell body. 4. axon- carries impulses away from the cell body. 5. myelin sheath- covers part of some axons. 6. synapse – at the end of the axon E. Nerve Impulse- an electrical impulse conducted along a nerve fiber. 1. resting potential- the electrical charge ...
Chapter 35 The Nervous System
... 3. dendrites- carries impulses toward the cell body. 4. axon- carries impulses away from the cell body. 5. myelin sheath- covers part of some axons. 6. synapse – at the end of the axon E. Nerve Impulse- an electrical impulse conducted along a nerve fiber. 1. resting potential- the electrical charge ...
... 3. dendrites- carries impulses toward the cell body. 4. axon- carries impulses away from the cell body. 5. myelin sheath- covers part of some axons. 6. synapse – at the end of the axon E. Nerve Impulse- an electrical impulse conducted along a nerve fiber. 1. resting potential- the electrical charge ...
m5zn_e06294c55d2e0eb
... - Each spinal nerve is connected to the spinal cord by two roots: the anterior root and the posterior root. The anterior root carrying nerve impulses away from the central nervous system ( efferent fibers) go to skeletal muscle and cause them to contract are called motor fibers. Their cells of origi ...
... - Each spinal nerve is connected to the spinal cord by two roots: the anterior root and the posterior root. The anterior root carrying nerve impulses away from the central nervous system ( efferent fibers) go to skeletal muscle and cause them to contract are called motor fibers. Their cells of origi ...
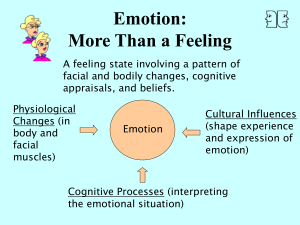
Emotion: More Than a Feeling
... An emotion-provoking stimulus activates a brain center called the “thalamus”, which simultaneously sends messages to the cortex, producing the feeling of an emotion, to the viscera, producing arousal, and to the skeletal muscles, producing behavior. Fear ...
... An emotion-provoking stimulus activates a brain center called the “thalamus”, which simultaneously sends messages to the cortex, producing the feeling of an emotion, to the viscera, producing arousal, and to the skeletal muscles, producing behavior. Fear ...
KKDP5: The effects of chronic changes to the functioning of the
... Two types of medications can be used — those that can be converted into dopamine by neurons and those that mimic the role of dopamine and are able to effectively stimulate reception of dopamine by neurons within crucial motor areas by causing neurons to react as they would to dopamine. ...
... Two types of medications can be used — those that can be converted into dopamine by neurons and those that mimic the role of dopamine and are able to effectively stimulate reception of dopamine by neurons within crucial motor areas by causing neurons to react as they would to dopamine. ...
Somatosensory modalities - Center for Neural Science
... Receptive fields determine spatial properties! • The receptive field of a sensory neuron defines the spatial location where it responds to stimuli of the appropriate energy! ...
... Receptive fields determine spatial properties! • The receptive field of a sensory neuron defines the spatial location where it responds to stimuli of the appropriate energy! ...
PowerPoint 프레젠테이션
... → others derive from the somatosensory areas of the parietal lobe. regulate the flow of somatosensory information to the brain. → axons from the cortex pass through the internal capsule. → course through the base of the cerebral peduncle in the midbrain. → then pass through the pons and collect to f ...
... → others derive from the somatosensory areas of the parietal lobe. regulate the flow of somatosensory information to the brain. → axons from the cortex pass through the internal capsule. → course through the base of the cerebral peduncle in the midbrain. → then pass through the pons and collect to f ...
Allochiria

Allochiria (from the Greek meaning ""other hand"") is a neurological disorder in which the patient responds to stimuli presented to one side of their body as if the stimuli had been presented at the opposite side. It is associated with spatial transpositions, usually symmetrical, of stimuli from one side of the body (or of the space) to the opposite one. Thus a touch to the left arm will be reported as a touch to the right arm, which is also known as somatosensory allochiria. If the auditory or visual senses are affected, sounds (a person's voice for instance) will be reported as being heard on the opposite side to that on which they occur and objects presented visually will be reported as having been presented on the opposite side. Often patients may express allochiria in their drawing while copying an image. Allochiria often co-occurs with unilateral neglect and, like hemispatial neglect, the disorder arises commonly from damage to the right parietal lobe.Allochiria is often confused with alloesthesia, also known as false allochiria. True allochiria is a symptom of dyschiria and unilateral neglect. Dyschiria is a disorder in the localization of sensation due to various degrees of dissociation and cause impairment in one side causing the inability to tell which side of the body was touched.