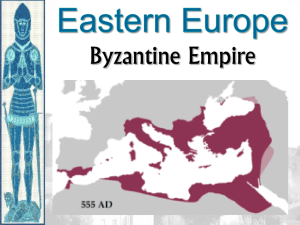
Chapter 16 PART ONE - Western Europe During the Early Middle
... the Fall of Rome Europe was plagued by constant warfare Warfare disrupted trade, Learning declined; destroyed Europe’s cities, & Few people could forced people to rural areas read or write Greco-Roman culture was forgotten ...
... the Fall of Rome Europe was plagued by constant warfare Warfare disrupted trade, Learning declined; destroyed Europe’s cities, & Few people could forced people to rural areas read or write Greco-Roman culture was forgotten ...
Powerpoint Chapter 9 - German Societies HIS 111
... **Please watch these videos as the information is important in understanding the final collapse of the Roman Empire and the measure of Germanic/Hunnic tribes that came against it. ...
... **Please watch these videos as the information is important in understanding the final collapse of the Roman Empire and the measure of Germanic/Hunnic tribes that came against it. ...
Medieval Pwr Pt SCHS-1
... • West = breakdown of Roman society, law, custom, language • Byzantine East = retain Roman laws, customs, urban-centered life, & Greek language • Both = Christian, BUT – Great Schism = 1054; final division between Eastern Orthodox (led by patriarch) and Roman Catholic (led by pope) Christianity ...
... • West = breakdown of Roman society, law, custom, language • Byzantine East = retain Roman laws, customs, urban-centered life, & Greek language • Both = Christian, BUT – Great Schism = 1054; final division between Eastern Orthodox (led by patriarch) and Roman Catholic (led by pope) Christianity ...
Middle Ages ppt
... barbarianAfter kingdoms that conquered Rome, the Fall of Rome Europe was plagued by constant warfare Warfare disrupted trade, Learning declined; destroyed Europe’s cities, & Few people could forced people to rural areas read or write Greco-Roman culture was forgotten ...
... barbarianAfter kingdoms that conquered Rome, the Fall of Rome Europe was plagued by constant warfare Warfare disrupted trade, Learning declined; destroyed Europe’s cities, & Few people could forced people to rural areas read or write Greco-Roman culture was forgotten ...
Middle Ages - Georgetown ISD
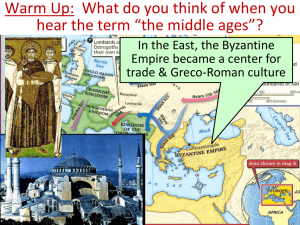
... Warm Up: What happened to Europe after the fall of the Roman Empire? In the East, the Byzantine Empire became a center for trade & Greco-Roman culture ...
... Warm Up: What happened to Europe after the fall of the Roman Empire? In the East, the Byzantine Empire became a center for trade & Greco-Roman culture ...
Middle_Ages
... Warm Up: What happened to Europe after the fall of the Roman Empire? In the East, the Byzantine Empire became a center for trade & Greco-Roman culture ...
... Warm Up: What happened to Europe after the fall of the Roman Empire? In the East, the Byzantine Empire became a center for trade & Greco-Roman culture ...
File
... Warm Up: What happened to Europe after the fall of the Roman Empire? In the East, the Byzantine Empire became a center for trade & Greco-Roman culture ...
... Warm Up: What happened to Europe after the fall of the Roman Empire? In the East, the Byzantine Empire became a center for trade & Greco-Roman culture ...
Warm Up: What happened to Europe after the fall of the Roman
... Warm Up: What happened to Europe after the fall of the Roman Empire? In the East, the Byzantine Empire became a center for trade & Greco-Roman culture ...
... Warm Up: What happened to Europe after the fall of the Roman Empire? In the East, the Byzantine Empire became a center for trade & Greco-Roman culture ...
WHI.10 The Middle Ages printable notes
... Mediterranean Basin/ Post-Roman Empire: The West The East Middle Ages- Feudalism Byzantine Empire- Emperors Roman Catholic Christianity Eastern Orthodox Christianity Latin language Greek language Pope as religious leader Patriarch as religious leader Rome as capital Constantinople as capital II. Med ...
... Mediterranean Basin/ Post-Roman Empire: The West The East Middle Ages- Feudalism Byzantine Empire- Emperors Roman Catholic Christianity Eastern Orthodox Christianity Latin language Greek language Pope as religious leader Patriarch as religious leader Rome as capital Constantinople as capital II. Med ...
Middle_Ages - Cobb Learning
... of Rome Europe was plagued by constant warfare Warfare disrupted trade, Learning declined; destroyed Europe’s cities, & Few people could forced people to rural areas read or write Greco-Roman culture was forgotten ...
... of Rome Europe was plagued by constant warfare Warfare disrupted trade, Learning declined; destroyed Europe’s cities, & Few people could forced people to rural areas read or write Greco-Roman culture was forgotten ...
Development of Feudalism
... The Church, with the help of Frankish rulers had converted many Frankish rulers to Christianity Missionaries spread Christianity to the Germanic and Celtic tribes that bordered the old Roman Empire Many Europeans along the coast converted to Christianity due to fear of Muslim ...
... The Church, with the help of Frankish rulers had converted many Frankish rulers to Christianity Missionaries spread Christianity to the Germanic and Celtic tribes that bordered the old Roman Empire Many Europeans along the coast converted to Christianity due to fear of Muslim ...
The Fall of Ancient Rome and the Rise of the Middle Ages
... Jesus Christ: Talks to everyone about ...
... Jesus Christ: Talks to everyone about ...
The Middle Ages
... In return, Leo placed a crown on Charlemagne and named him the “Emperor of the Romans” which secured the relationship between Frankish kings and the papacy Charlemagne became the first ruler of the Holy Roman Empire, a dynasty that would last for more ...
... In return, Leo placed a crown on Charlemagne and named him the “Emperor of the Romans” which secured the relationship between Frankish kings and the papacy Charlemagne became the first ruler of the Holy Roman Empire, a dynasty that would last for more ...
Early Middle Ages AD 500
... Christianity Rules Pope Gregory the Great Made the papacy an office of political & spiritual power Foresaw a churchly kingdom, ruled by a pope – this idea became a central part of the Middle Ages Charles Martel – “The ...
... Christianity Rules Pope Gregory the Great Made the papacy an office of political & spiritual power Foresaw a churchly kingdom, ruled by a pope – this idea became a central part of the Middle Ages Charles Martel – “The ...
Chapter 4, Section 2
... On Christmas Day of 800, Charlemagne was crowned the head of the Roman Empire in the West, which became known as the Holy Roman Empire. Charlemagne died in 814, and the empire was broken up between his sons and grandsons. These kingdoms were the foundations for modern, Germany, Italy, France and Spa ...
... On Christmas Day of 800, Charlemagne was crowned the head of the Roman Empire in the West, which became known as the Holy Roman Empire. Charlemagne died in 814, and the empire was broken up between his sons and grandsons. These kingdoms were the foundations for modern, Germany, Italy, France and Spa ...
Middle Ages - Pearland ISD
... barbarianAfter kingdoms that conquered Rome, the Fall of Rome Europe was plagued by constant warfare Warfare disrupted trade, Learning declined; destroyed Europe’s cities, & Few people could forced people to rural areas read or write Greco-Roman culture was forgotten ...
... barbarianAfter kingdoms that conquered Rome, the Fall of Rome Europe was plagued by constant warfare Warfare disrupted trade, Learning declined; destroyed Europe’s cities, & Few people could forced people to rural areas read or write Greco-Roman culture was forgotten ...
The Rise of Europe 500 - 1300
... The Germanic Kingdoms– •Strongest Germanic kingdom was the Franks. •Under the leadership of Clovis, the Franks conquered much of the old Western Roman Empire. •Clovis converted to Christianity and gained a powerful ally in the Church. •Charles Martel defeated the Muslims at the Battle of Tours and ...
... The Germanic Kingdoms– •Strongest Germanic kingdom was the Franks. •Under the leadership of Clovis, the Franks conquered much of the old Western Roman Empire. •Clovis converted to Christianity and gained a powerful ally in the Church. •Charles Martel defeated the Muslims at the Battle of Tours and ...
Middle Ages (1 of 2) - Pineda Ancient History
... Time period a.k.a. “Dark Ages” because there was little learning or trade ...
... Time period a.k.a. “Dark Ages” because there was little learning or trade ...
Middle Ages
... portion of Europe under his authority as King from 481-511 CE Converted to Christianity. Overtook Germanic peoples by military conquest. Lost power to Charles the Hammer of the Carolingian Family - later to be headed by Charlemagne. ...
... portion of Europe under his authority as King from 481-511 CE Converted to Christianity. Overtook Germanic peoples by military conquest. Lost power to Charles the Hammer of the Carolingian Family - later to be headed by Charlemagne. ...
Charlemagne Unites Germanic Kingdoms.key
... The Germanic stress on personal ties made it impossible to establish orderly government for ...
... The Germanic stress on personal ties made it impossible to establish orderly government for ...
Chapters 11-13 Test Review
... 1. Under the ______________ Empire’s rule, China suffered constant threats of death and destruction. 2. The __________ Dynasty restored the glory of the Chinese Empire. 3. Korea was strongly influenced by _________________ culture, but also maintained it’s own identity. 4. Countries of Southeast As ...
... 1. Under the ______________ Empire’s rule, China suffered constant threats of death and destruction. 2. The __________ Dynasty restored the glory of the Chinese Empire. 3. Korea was strongly influenced by _________________ culture, but also maintained it’s own identity. 4. Countries of Southeast As ...
The Early Middle Ages
... After winning a battle in 496, King Clovis established a Christian kingdom in Western Europe. It was one of many kingdoms that developed when Roman authority collapsed. ...
... After winning a battle in 496, King Clovis established a Christian kingdom in Western Europe. It was one of many kingdoms that developed when Roman authority collapsed. ...
Germanic Kingdoms Unite Under Charlemagne
... Invasions Trigger Changes in Western Europe By the end of the ________ century, invaders from many different German groups overran the Roman Empire in the west. Their arrival and the collapse of Roman rule had several ______. The ___________ attacks put a halt to all trade, as it was not safe to mov ...
... Invasions Trigger Changes in Western Europe By the end of the ________ century, invaders from many different German groups overran the Roman Empire in the west. Their arrival and the collapse of Roman rule had several ______. The ___________ attacks put a halt to all trade, as it was not safe to mov ...
NAME Chapter 13: European Middle Ages Focus The Roman
... ____ 13. All of the following could be said about the tournaments held in the Middle Ages EXCEPT that they were A. used to test courage. B. free of actual bloodshed. C. a form of spectator sport. ____ 14. Eleanor of Aquitaine is famous for A. writing The Song of Roland. B. weaving the Bayeux Tapestr ...
... ____ 13. All of the following could be said about the tournaments held in the Middle Ages EXCEPT that they were A. used to test courage. B. free of actual bloodshed. C. a form of spectator sport. ____ 14. Eleanor of Aquitaine is famous for A. writing The Song of Roland. B. weaving the Bayeux Tapestr ...
Early Europe until 1453
... – Attacks from without (especially Turks) – 1071 – lost battle at Manzikert to Seljuk Turks • Asked for help against Muslims from Western Christians • 1095 – First Crusade begins ...
... – Attacks from without (especially Turks) – 1071 – lost battle at Manzikert to Seljuk Turks • Asked for help against Muslims from Western Christians • 1095 – First Crusade begins ...
Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages or Early Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from the 5th century to the 10th century. The Early Middle Ages followed the decline of the Western Roman Empire and preceded the High Middle Ages (c. 1001–1300). The period saw a continuation of trends begun during late classical antiquity, including population decline, especially in urban centres, a decline of trade, and increased immigration. The period has been labelled the ""Dark Ages"", a characterization highlighting the relative scarcity of literary and cultural output from this time, especially in Northwestern Europe. However, the Eastern Roman Empire, or Byzantine Empire, continued to survive, and in the 7th century the Islamic caliphates conquered swaths of formerly Roman territory.Many of these trends were reversed later in the period. In 800 the title of emperor was revived in Western Europe by Charlemagne, whose Carolingian Empire greatly affected later European social structure and history. Europe experienced a return to systematic agriculture in the form of the feudal system, which introduced such innovations as three-field planting and the heavy plow. Barbarian migration stabilized in much of Europe, although the north was greatly affected by the Viking expansion.