The Rise of Europe
... that were central to their faith. Jews in Spain were known as Sephardim. Jewish farmers migrated to Western Europe and became known as Ashkenazim. In the late 1000s, Christians persecuted Jews and accused them of being responsible for the death of Jesus. In bad times, antisemitism, or prejudice agai ...
... that were central to their faith. Jews in Spain were known as Sephardim. Jewish farmers migrated to Western Europe and became known as Ashkenazim. In the late 1000s, Christians persecuted Jews and accused them of being responsible for the death of Jesus. In bad times, antisemitism, or prejudice agai ...
chap. 2 world history
... Charlemagne’s empire survived many barbarian attacks. After his death in 814, however, it quickly fell apart. ...
... Charlemagne’s empire survived many barbarian attacks. After his death in 814, however, it quickly fell apart. ...
The Dark Ages_Part 5-9 - 7thgradeworldhistoryperiod6
... 542 AD 1. Did Justinian have a large empire? 2. What percentage of the city population was killed by the Bubonic plague? 3. How did the Bubonic plague arrive in Constantinople? 4. Did Justinian survive the plague? 5. How many people died of the plague? 6. Did other outbreaks of the plague reappear ...
... 542 AD 1. Did Justinian have a large empire? 2. What percentage of the city population was killed by the Bubonic plague? 3. How did the Bubonic plague arrive in Constantinople? 4. Did Justinian survive the plague? 5. How many people died of the plague? 6. Did other outbreaks of the plague reappear ...
Feudalism - Miami Beach Senior High School
... SS.A.2.4.7; SS.B.2.4.3; SS.A.1.4.2; SS.B.2.4.1; SS.A.2.2.4; SS.A.2.4.4 ...
... SS.A.2.4.7; SS.B.2.4.3; SS.A.1.4.2; SS.B.2.4.1; SS.A.2.2.4; SS.A.2.4.4 ...
Chapter Five: Medieval Times to Today
... in return gave him a share of the land called a fief (pg. 108) Manor: a large estate, often including a village and farmlands, ruled by a lord in medieval Europe (pg. 108) Self-Sufficient: able to supply one’s own needs; the residents of a medieval manor were self-sufficient (pg. 109) Serf: a person ...
... in return gave him a share of the land called a fief (pg. 108) Manor: a large estate, often including a village and farmlands, ruled by a lord in medieval Europe (pg. 108) Self-Sufficient: able to supply one’s own needs; the residents of a medieval manor were self-sufficient (pg. 109) Serf: a person ...
Middle Ages
... Law: church law followed by everyone ► Sacraments: important religious ceremonies ► Manor ...
... Law: church law followed by everyone ► Sacraments: important religious ceremonies ► Manor ...
Slide 1 - Mr. Mac`s Wikispace!!
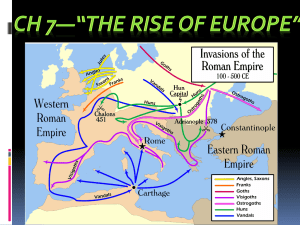
... • Period of change in Western Europe as barbarians were migrating in to areas given up by Romans • As more barbarians moved westward, other tribes were forced to move • Groups categorized by languages and little else • Celtic: Gauls, Britons, Bretons • Germanic: Goths, Frank, Vandals, Saxons • Slavi ...
... • Period of change in Western Europe as barbarians were migrating in to areas given up by Romans • As more barbarians moved westward, other tribes were forced to move • Groups categorized by languages and little else • Celtic: Gauls, Britons, Bretons • Germanic: Goths, Frank, Vandals, Saxons • Slavi ...
Medieval Intro - Blue Valley Schools
... 2. Why did Feudalism become the basis for government during the middle ages? 3. What were the political, social, and economic impacts of Feudalism? 4. Explain the role the Catholic Church played during the Middle Ages. ...
... 2. Why did Feudalism become the basis for government during the middle ages? 3. What were the political, social, and economic impacts of Feudalism? 4. Explain the role the Catholic Church played during the Middle Ages. ...
The Middle Ages
... Germanic kingdoms arose as the power of the Romans receded. In the fifth and sixth centuries, the Visigoths and Vandals established kingdoms in Spain and North Africa, while the Ostrogoths and Lombards established kingdoms in Italy. The most powerful and long-lasting Germanic empires, however, were ...
... Germanic kingdoms arose as the power of the Romans receded. In the fifth and sixth centuries, the Visigoths and Vandals established kingdoms in Spain and North Africa, while the Ostrogoths and Lombards established kingdoms in Italy. The most powerful and long-lasting Germanic empires, however, were ...
Chapter 7-9 W.C. I.
... preserving details of the early German kingdoms for historians, principles of Roman law were also incorporated. • The Rule of Law – Legal Codes – Wergeld ...
... preserving details of the early German kingdoms for historians, principles of Roman law were also incorporated. • The Rule of Law – Legal Codes – Wergeld ...
middle ages ppt
... – Dante Alighieri wrote The Divine Comedy (1321) -- Italian – Geoffery Chaucer wrote The Canterbury Tales (1387-1400) -- English – Christine de Pisan wrote The City of Ladies (1405) – French ...
... – Dante Alighieri wrote The Divine Comedy (1321) -- Italian – Geoffery Chaucer wrote The Canterbury Tales (1387-1400) -- English – Christine de Pisan wrote The City of Ladies (1405) – French ...
The Later Middle Ages
... 1. In some cities, such as Florence, nearly ½ the population died 2. Economy in towns suffered significantly (while the countryside was less affected by the plague) The plague accelerated an economic decline that had been in effect since the early 14th century 3. In some areas workers enjoyed high ...
... 1. In some cities, such as Florence, nearly ½ the population died 2. Economy in towns suffered significantly (while the countryside was less affected by the plague) The plague accelerated an economic decline that had been in effect since the early 14th century 3. In some areas workers enjoyed high ...
AP EUROPEAN HISTORY CHAPTER 12 SUMMARY – “The Rise of
... Rome began as a city in 753 BC and graduated into a far-flung empire ruling the entire Mediterranean basin by the second century AD. This process did not involve a predetermined path, and was aided by luck, circumstance, and sheer determination. Certainly the Romans deserve recognition for their con ...
... Rome began as a city in 753 BC and graduated into a far-flung empire ruling the entire Mediterranean basin by the second century AD. This process did not involve a predetermined path, and was aided by luck, circumstance, and sheer determination. Certainly the Romans deserve recognition for their con ...
CHAPTER 10 A New Civilization Emerges in Western Europe
... The High Middle Ages. Postclassical Western civilization reached its high point during the 12th and 13th centuries. Creative tensions among feudal political forms, emerging monarchies, and the authority of the church produced major changes in political, religious, intellectual, social, and economic ...
... The High Middle Ages. Postclassical Western civilization reached its high point during the 12th and 13th centuries. Creative tensions among feudal political forms, emerging monarchies, and the authority of the church produced major changes in political, religious, intellectual, social, and economic ...
Charlemagne Unites Germanic Kingdoms
... domo—mayor of the palace • In 719, major domo Charles Martel becomes more powerful than king • Defeats Muslims from Spain at Tours in 732; becomes a Christian hero • Son, Pepin, begins Carolingian Dynasty— family that ruled 751–987 NEXT ...
... domo—mayor of the palace • In 719, major domo Charles Martel becomes more powerful than king • Defeats Muslims from Spain at Tours in 732; becomes a Christian hero • Son, Pepin, begins Carolingian Dynasty— family that ruled 751–987 NEXT ...
Dark/Middle Ages Study Guide
... 14. Who were knights? What were they hired to do? In return for their service, what were they given? 15. Why was the tournament important to a knight? 16. Who did knights end up fighting most of the time instead of foreign invaders? Why? 17. Who was Charlemagne? What did he try to do? How did he try ...
... 14. Who were knights? What were they hired to do? In return for their service, what were they given? 15. Why was the tournament important to a knight? 16. Who did knights end up fighting most of the time instead of foreign invaders? Why? 17. Who was Charlemagne? What did he try to do? How did he try ...
Unit V Test – Global Connections Name: 1. In order to supply food to
... E. Theocratic government. ...
... E. Theocratic government. ...
7th grade Chapter 19 review
... with an iron blade. Plow made deeper cuts in the soil and meant less time in the fields for peasants. Horse collar was also important because a horse could then pull the plow and moves faster then oxen Harnessing water and wind power for mills to grind ...
... with an iron blade. Plow made deeper cuts in the soil and meant less time in the fields for peasants. Horse collar was also important because a horse could then pull the plow and moves faster then oxen Harnessing water and wind power for mills to grind ...
The New Millennium
... Organization Because many towns were on land that belonged to lords or old Roman towns that belonged to bishops, these communities were first under feudal authority Townspeople (burghers) began obtaining charters to break from the feudal system and set up assemblies ...
... Organization Because many towns were on land that belonged to lords or old Roman towns that belonged to bishops, these communities were first under feudal authority Townspeople (burghers) began obtaining charters to break from the feudal system and set up assemblies ...
February 13th and 17th
... Middle Ages from about 500 to 1000 C.E. in terms of its impact on Western civilization by ...
... Middle Ages from about 500 to 1000 C.E. in terms of its impact on Western civilization by ...
1. After collapse of Rome
... A. Germanic peoples built on Rome’s: i. Use of Latin Language ii. Classical ideas iii. Christianity ...
... A. Germanic peoples built on Rome’s: i. Use of Latin Language ii. Classical ideas iii. Christianity ...
The Medieval Period: Introduction
... The Three Invasions – The Magyars • The Magyars originally came from Western Russia. • Like another ‘barbarian’ tribe (The Huns) they were excellent horseman and could shoot arrows while riding. • They carried out a series of raids and managed to left a path of destruction from Eastern Europe to So ...
... The Three Invasions – The Magyars • The Magyars originally came from Western Russia. • Like another ‘barbarian’ tribe (The Huns) they were excellent horseman and could shoot arrows while riding. • They carried out a series of raids and managed to left a path of destruction from Eastern Europe to So ...
Dawes Severalty Act (1887)
... moldboard: heavy plow introduced in northern Europe during the Middle Ages; permitted deeper cultivation of heavier soils. three-field system: one third of land left uplanted each year to increase fertility. Clovis: King of the Franks; converted to Christianity ca. 496. Carolingians: royal house of ...
... moldboard: heavy plow introduced in northern Europe during the Middle Ages; permitted deeper cultivation of heavier soils. three-field system: one third of land left uplanted each year to increase fertility. Clovis: King of the Franks; converted to Christianity ca. 496. Carolingians: royal house of ...
Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages or Early Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from the 5th century to the 10th century. The Early Middle Ages followed the decline of the Western Roman Empire and preceded the High Middle Ages (c. 1001–1300). The period saw a continuation of trends begun during late classical antiquity, including population decline, especially in urban centres, a decline of trade, and increased immigration. The period has been labelled the ""Dark Ages"", a characterization highlighting the relative scarcity of literary and cultural output from this time, especially in Northwestern Europe. However, the Eastern Roman Empire, or Byzantine Empire, continued to survive, and in the 7th century the Islamic caliphates conquered swaths of formerly Roman territory.Many of these trends were reversed later in the period. In 800 the title of emperor was revived in Western Europe by Charlemagne, whose Carolingian Empire greatly affected later European social structure and history. Europe experienced a return to systematic agriculture in the form of the feudal system, which introduced such innovations as three-field planting and the heavy plow. Barbarian migration stabilized in much of Europe, although the north was greatly affected by the Viking expansion.