* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Medieval Intro - Blue Valley Schools
Medieval music wikipedia , lookup
England in the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Wales in the Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
European science in the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Medieval technology wikipedia , lookup
Dark Ages (historiography) wikipedia , lookup
Christianity in the 11th century wikipedia , lookup
Christianity in the 13th century wikipedia , lookup
Medievalism wikipedia , lookup
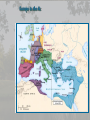
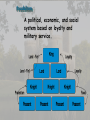
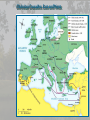
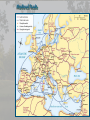
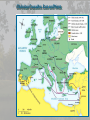
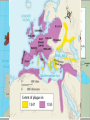
Medieval Intro Bell Ringer: List everything that comes to mind when you think of the term “Middle Ages” (Medieval or Dark Ages) The Late Middle Ages Challenges and Growth Key Terms • • • • • • • • • Feudalism Barter Longbow Nationalism Medieval Catholic Church Crusades Black Death Hundred Years War Great Schism Periodization Roman Empire: 29BC – late 400s AD Early Middle Ages: Late 400’s – 1000 High Middle Ages: 1000 – 1250 Late Middle Ages: 1250 - 1500 Roman Empire Roman Empire Europe in the 6c Feudalism A political, economic, and social system based on loyalty and military service. Carcassonne: A Medieval Castle Parts of a Medieval Castle The Medieval Manor Life on the Medieval Manor Serfs at work Learning Targets 1. What is Feudalism? 2. Why did Feudalism become the basis for government during the middle ages? 3. What were the political, social, and economic impacts of Feudalism? 4. Explain the role the Catholic Church played during the Middle Ages. Medieval Society • Political: fragmented, regional, feudalism • Economic: barter, self-sufficient manors • Religious: Christian, Catholic Church has immense power • Social: classes based on land ownership and titles (Nobles and Peasants). • Intellectual/Arts: Most of the art, literature, and learning took place within the Church. The Medieval Catholic Church • Powerful Institution – owned 1/3 of the land throughout Europe • Headed by the Pope – spiritual leader of Christianity • Collected taxes – Christians expected to give 1/10 of their income The Medieval Catholic Church • Provided aid to the poor and sick • Established hospitals • Kept records on births, marriages, divorces and deaths. • Taught the Christian religion to the people. • Provided spiritual guidance • Provided stability in a harsh and unstable world Learning Targets 1. Analyze and explain how the Crusades, Black Death, Hundred Years War, and the Great Schism destroy Feudalism and diminish the power and prestige of the Catholic Church Christian Crusades: East and West Setting Out on Crusade Pope Urban II: Preaching a Crusade Medieval Trade Christian Crusades: East and West Challenges I. Hundred Years War: (1337-1453) England vs. France • Causes – English rulers wanted to keep French lands of their Norman ancestors – French kings wanted to extend their own power in France – 1337, Edward III claimed the French throne – Once fighting began economic rivalry and growing sense of national pride made it difficult for either side to stop • Effects – In France, national feeling grew and the kings expanded their power – In England, Parliament gained “power of the purse” and kings began looking at trading ventures overseas – The longbow and cannon made soldier more important and knights less valuable – Castles and knights became obsolete – Monarchs came to need large armies instead of feudal vassals Notable events and people • Battle of Poitier (1356) – English victory led by Edward the Black Prince • Battle of Agincourt (1415) – English victory led by Henry V • Joan of Arc: Led French troops to victories between 1429 and 1431 – Executed by the English Bring out your dead! Challenges II. The Black Death • Spread to Europe by 1347 – Would kill 1 in 3 Europeans by What were the symptoms of the plague? Cures? • Medieval people did not know about germs causing disease. They did not understand that plague was spread by rats and fleas. They thought that people’s bodies were poisoned. • If the swellings burst and the poison came out people sometimes survived. It seemed sensible to draw out the poison. Medieval cure number 1 The swellings should be softened with figs and cooked onions. The onions should be mixed with yeast and butter. Then open the swellings with a knife. Medieval cure number 2 Frogs breath through their skin – so the thought was that by taking a live frog & putting its belly on the sore the poison would be drawn out. The frog will swell up and burst. Keep doing this with further frogs until they stop bursting. Some people say that a dried toad will do the job better. Challenges II. The Black Death: Social and Economic decline • Social Effects – Some people turned to magic and witchcraft for cures. – Others believed they were being punished by God. – Some people turned to wild pleasure, believing the end was inevitable. – Normal life broke down. – Individuals turned away from neighbors and relatives to avoid contagion. – Christians blamed and persecuted Jews. • Economic Effects – As workers died, production declined. – Surviving workers demanded higher wages. As the cost of labor soared, inflation, or rising prices, broke out. – Landowners abandoned farming, forcing villagers to look for work in the towns. – Unable to find work, peasants revolted. III. The Great Schism Challenges (1378-1417) • Also referred to as the Babylonian Captivity • Time from 1305-1377 when the Pope was exiled to Avignon, France • 1377 Pope moved back to Rome and died 1378 • Italian elected Urban VI at Rome; • Frenchman elected Clement VII at Avignon • Church now had two popes Consequences of the Great Schism • The Babylonian Captivity and Great Schism damaged the spiritual authority of the papacy • weakened the political influence of the popes • Kings and nobles throughout Europe began to reassert control over church Growth I. Cultural Achievements • Early Middle Ages – cultural decline • High Middle Ages – cultural development • Architecture – Gothic • Higher education • Philosophy – Scholasticism • Literature – Vernacular Rise of Nationalism • • • • Russia/Ottoman Empire England/France Spain/Portugal HRE/Italy