Period`3:`Regional`
... is an Arabic word meaning ― striving in the way of God, but it is often translated as ―holy war. Refer to an armed struggle fought in the defense of Islam to please Allah A mosque is a place of worship for followers of the Islamic faith A tower attached to a mosque, used for call to prayer community ...
... is an Arabic word meaning ― striving in the way of God, but it is often translated as ―holy war. Refer to an armed struggle fought in the defense of Islam to please Allah A mosque is a place of worship for followers of the Islamic faith A tower attached to a mosque, used for call to prayer community ...
chapters 9-10 quiz
... A) The Arab threat to the Byzantine Empire was permanently removed. B) The position of small farmers in the empire was weakened as a result of heavy taxation, resulting in greater aristocratic estates. C) The Byzantine Empire was able to recover the provinces of Syria and Egypt, thus regaining valua ...
... A) The Arab threat to the Byzantine Empire was permanently removed. B) The position of small farmers in the empire was weakened as a result of heavy taxation, resulting in greater aristocratic estates. C) The Byzantine Empire was able to recover the provinces of Syria and Egypt, thus regaining valua ...
A Treatise on the Origin, Translation, and State of the Roman Empire
... providently and usefully ordained for the good state of the Church and the Christian people so that an ordination of such great imperial sublimity— which was owed not to blood, but to virtue—proceeded not by way of succession, but election (as in q. Moyses), so that one not just noble, but worth ...
... providently and usefully ordained for the good state of the Church and the Christian people so that an ordination of such great imperial sublimity— which was owed not to blood, but to virtue—proceeded not by way of succession, but election (as in q. Moyses), so that one not just noble, but worth ...
MedievalSummary [Autosaved]
... • Where: Gaul, France, Western Europe • When: 732 • Why: he pushed the Muslims back, out of Europe, which showed God was on the Christians’ side= WE stays Christian ...
... • Where: Gaul, France, Western Europe • When: 732 • Why: he pushed the Muslims back, out of Europe, which showed God was on the Christians’ side= WE stays Christian ...
File
... The year before Charlemagne died in 814, he crowned his only living son Louis the Pious, emperor. Louis the Pious was a devoutly ...
... The year before Charlemagne died in 814, he crowned his only living son Louis the Pious, emperor. Louis the Pious was a devoutly ...
Episode 6: Charlemagne
... 805 at his capital in Aachen, Germany • Octagonal plan based on earlier Byzantine churches in Italy • Most ornate church in northern Europe for centuries ...
... 805 at his capital in Aachen, Germany • Octagonal plan based on earlier Byzantine churches in Italy • Most ornate church in northern Europe for centuries ...
Chapter 18-1
... Whom might a pope choose to excommunicate? Why did some popes eventually begin to live like royalty? How did becoming king in England and France differ from how it was done in the Holy Roman Empire? In what region did many bishops not recognize the pope’s authority? Why did Pope Leo IX believe that ...
... Whom might a pope choose to excommunicate? Why did some popes eventually begin to live like royalty? How did becoming king in England and France differ from how it was done in the Holy Roman Empire? In what region did many bishops not recognize the pope’s authority? Why did Pope Leo IX believe that ...
The Middle Ages in Chaucer`s Europe
... 10th and 11th centuries saw greater stability come to the lands of Western Europe. With the brief exception of the Mongol incursions, major barbarian invasions had ceased. 11th to 14th century saw an explosion in population. trade grew throughout Europe as the dangers of travel were reduced, a ...
... 10th and 11th centuries saw greater stability come to the lands of Western Europe. With the brief exception of the Mongol incursions, major barbarian invasions had ceased. 11th to 14th century saw an explosion in population. trade grew throughout Europe as the dangers of travel were reduced, a ...
The Middle Ages in Europe REVIEW - What were the major reasons
... Empire collapsed in one day, or even in weeks or months. It took years and it happened so slowly that most people did not even know it was taking place. But slowly, Roman culture ended. The period of time between the end of the Roman Empire and the beginning of the modern world is known as the Middl ...
... Empire collapsed in one day, or even in weeks or months. It took years and it happened so slowly that most people did not even know it was taking place. But slowly, Roman culture ended. The period of time between the end of the Roman Empire and the beginning of the modern world is known as the Middl ...
Dr John R Gibbins
... Constanius meanwhile dallied in Constantinople in the face of an approaching Persian army under Shapur in ...
... Constanius meanwhile dallied in Constantinople in the face of an approaching Persian army under Shapur in ...
Frankish Kingdom
... on all of the Germanic tribes and peoples living in Central and Eastern Europe causing them to move west to fight for new territories. Many tribes were not able to establish their own strong governments – they either became allies of more powerful peoples and eventually merged with them, or they wer ...
... on all of the Germanic tribes and peoples living in Central and Eastern Europe causing them to move west to fight for new territories. Many tribes were not able to establish their own strong governments – they either became allies of more powerful peoples and eventually merged with them, or they wer ...
Middle Ages Final Exam Review
... *Describe how Germanic tribes carved Europe into small kingdoms. *Explain how Charlemagne briefly reunited much of Western Europe and what happened to his empire after his death. 1. What change signaled the beginning of the Middle Ages? 2. Describe the Germanic kingdoms that conquered much of Wester ...
... *Describe how Germanic tribes carved Europe into small kingdoms. *Explain how Charlemagne briefly reunited much of Western Europe and what happened to his empire after his death. 1. What change signaled the beginning of the Middle Ages? 2. Describe the Germanic kingdoms that conquered much of Wester ...
The Middle Ages -
... Jerusalem & kept it during the First Crusade the Second & Third Crusades More Crusades were fought, but Christians never regained the ...
... Jerusalem & kept it during the First Crusade the Second & Third Crusades More Crusades were fought, but Christians never regained the ...
Global History Final Review Pascale Dugue Early Peoples and
... blending. Alexandria became the foremost center of commerce and Hellenistic civilization. Their art and much of their information dominated roman culture. Alexander the Great- His father was assassinated and Alex became the king at age 20 ruling Greece and Macedonia He wanted to attack and get reven ...
... blending. Alexandria became the foremost center of commerce and Hellenistic civilization. Their art and much of their information dominated roman culture. Alexander the Great- His father was assassinated and Alex became the king at age 20 ruling Greece and Macedonia He wanted to attack and get reven ...
File
... location of Mexico City. Olmec – The Olmec lived in south-central Mexico. They build huge temples and offered human sacrifices. They also developed an accurate calendar and used hieroglyphics. The Olmec are best remembered for their giant statues of heads, which are located on the sides of mountains ...
... location of Mexico City. Olmec – The Olmec lived in south-central Mexico. They build huge temples and offered human sacrifices. They also developed an accurate calendar and used hieroglyphics. The Olmec are best remembered for their giant statues of heads, which are located on the sides of mountains ...
Note Taking Study Guide - Prentice Hall Bridge page
... into France, Charles Martel and his Frankish warriors fought them at the battle of Tours in 732. Muslims ruled in Spain, but did not advance farther into Western Europe. In 768, Charles Martel’s grandson, also named Charles, became king of the Franks. He built an empire covering what are now France, ...
... into France, Charles Martel and his Frankish warriors fought them at the battle of Tours in 732. Muslims ruled in Spain, but did not advance farther into Western Europe. In 768, Charles Martel’s grandson, also named Charles, became king of the Franks. He built an empire covering what are now France, ...
The Byzantine Empire - Hickory High School
... and Italy until the Ostrogoths, another Germanic tribe, took control of Italy in the fifth century. By 500, the Western Roman Empire had been replaced by a number of states ruled by German kings. The merging of Romans and Germans took different forms in the various Germanic kingdoms. Both the kingdo ...
... and Italy until the Ostrogoths, another Germanic tribe, took control of Italy in the fifth century. By 500, the Western Roman Empire had been replaced by a number of states ruled by German kings. The merging of Romans and Germans took different forms in the various Germanic kingdoms. Both the kingdo ...
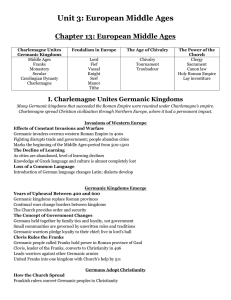
Unit 3: European Middle Ages Chapter 13
... ruled all of the lands where Roman Catholicism dominated, except modern-day England and Ireland. However, unlike the old Roman Empire in which Rome was the center of both political power and religious influence, Charlemagne’s kingdom was centered in Aachen, a northern European city. The unity forged ...
... ruled all of the lands where Roman Catholicism dominated, except modern-day England and Ireland. However, unlike the old Roman Empire in which Rome was the center of both political power and religious influence, Charlemagne’s kingdom was centered in Aachen, a northern European city. The unity forged ...
Early Medieval Art Notes
... Armed conflict and competition fierce between tribes. Collapse of trade and towns Loss of literacy Rise of Romance (Roman-based) languages o By the 800’s, French, Spanish, Italian and other Romance languages had evolved from Latin Spread of Christianity ...
... Armed conflict and competition fierce between tribes. Collapse of trade and towns Loss of literacy Rise of Romance (Roman-based) languages o By the 800’s, French, Spanish, Italian and other Romance languages had evolved from Latin Spread of Christianity ...
The Middle Ages - Marie Sklodowska Curie Metro High School
... – Trade and towns grew together: As trade increased, people moved from manors into towns. As workers were needed in trade centers, people moved back to urban places and towns grew larger. Many were former serfs who became peasant workers: By living in town for a year a person who had been a serf cou ...
... – Trade and towns grew together: As trade increased, people moved from manors into towns. As workers were needed in trade centers, people moved back to urban places and towns grew larger. Many were former serfs who became peasant workers: By living in town for a year a person who had been a serf cou ...
Chapter 1: Early Spanish Explorers
... 4. Cities got smaller, and most people survived by farming or soldiering. 5. Because there was no need for architecture or ship-building, people forgot how to do those things. 6. Renaissance scholars looked down on the period from 500-800, and referred to this time as the “Dark Ages”. 7. Eventually, ...
... 4. Cities got smaller, and most people survived by farming or soldiering. 5. Because there was no need for architecture or ship-building, people forgot how to do those things. 6. Renaissance scholars looked down on the period from 500-800, and referred to this time as the “Dark Ages”. 7. Eventually, ...
Unit Three Absolutism in Eastern Europe
... 2. Ottoman Empire: could not maintain possessions in eastern Europe and the Balkans in the face of Austrian and Russian expansion a. Ottoman Empire was built on expansion. The Sultan had absolute power in the empire. After 1560 the decline in western expansion resulted in the gradual disintegrat ...
... 2. Ottoman Empire: could not maintain possessions in eastern Europe and the Balkans in the face of Austrian and Russian expansion a. Ottoman Empire was built on expansion. The Sultan had absolute power in the empire. After 1560 the decline in western expansion resulted in the gradual disintegrat ...
Unit Three Absolutism in Eastern Europe - AP EURO
... 4. Ineffective Habsburg rule in HRE forced monarchs to consolidate power within the Austrian empire a. Reorganization of Bohemia after 30 Years’ War was a major ...
... 4. Ineffective Habsburg rule in HRE forced monarchs to consolidate power within the Austrian empire a. Reorganization of Bohemia after 30 Years’ War was a major ...
Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages or Early Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from the 5th century to the 10th century. The Early Middle Ages followed the decline of the Western Roman Empire and preceded the High Middle Ages (c. 1001–1300). The period saw a continuation of trends begun during late classical antiquity, including population decline, especially in urban centres, a decline of trade, and increased immigration. The period has been labelled the ""Dark Ages"", a characterization highlighting the relative scarcity of literary and cultural output from this time, especially in Northwestern Europe. However, the Eastern Roman Empire, or Byzantine Empire, continued to survive, and in the 7th century the Islamic caliphates conquered swaths of formerly Roman territory.Many of these trends were reversed later in the period. In 800 the title of emperor was revived in Western Europe by Charlemagne, whose Carolingian Empire greatly affected later European social structure and history. Europe experienced a return to systematic agriculture in the form of the feudal system, which introduced such innovations as three-field planting and the heavy plow. Barbarian migration stabilized in much of Europe, although the north was greatly affected by the Viking expansion.



![MedievalSummary [Autosaved]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008419770_1-40a03e93739b961f0ed6522195b5d239-300x300.png)