Rivals: Athens vs. Sparta
... • Compared the political structures in different Greek city-states • Wrote a book called “Politics” – Idea form of government is a balance between a monarchy, aristocracy, and democracy – Middle class is the best suited to rule because they know how to command AND obey ...
... • Compared the political structures in different Greek city-states • Wrote a book called “Politics” – Idea form of government is a balance between a monarchy, aristocracy, and democracy – Middle class is the best suited to rule because they know how to command AND obey ...
Rome and the Roots of Western Civilization
... culture and added ideas of its own. The mixing of Greek, Hellenistic, and Roman culture produced a new culture called Greco-Roman culture. This is also often called classical civilization. Roman artists, philosophers, and writers did not just copy Greek works. They created a style of their own for t ...
... culture and added ideas of its own. The mixing of Greek, Hellenistic, and Roman culture produced a new culture called Greco-Roman culture. This is also often called classical civilization. Roman artists, philosophers, and writers did not just copy Greek works. They created a style of their own for t ...
Section Two: The Greek City-States
... A military State • Stayed in the army until 60 • Women & men lived apart • Women expected to remain fit to bear & raise healthy children • Men expected to be brave in battle, to win or be killed ...
... A military State • Stayed in the army until 60 • Women & men lived apart • Women expected to remain fit to bear & raise healthy children • Men expected to be brave in battle, to win or be killed ...
Philosopher Biographies
... Socrates believed that philosophy should achieve practical results for the greater well-being of society. He attempted to establish an ethical system based on human reason rather than theological doctrine. He pointed out that human choice was motivated by the desire for happiness. Ultimate wisdom co ...
... Socrates believed that philosophy should achieve practical results for the greater well-being of society. He attempted to establish an ethical system based on human reason rather than theological doctrine. He pointed out that human choice was motivated by the desire for happiness. Ultimate wisdom co ...
Ancient Greece Golden Age
... 1. List two ways that Athens was different than Sparta 2. What is a Greek ‘Polis’? 3. List one invention the Greeks came up with. 4. The Greek “religion” was based upon ______, stories that were passed down over time about all their gods. ...
... 1. List two ways that Athens was different than Sparta 2. What is a Greek ‘Polis’? 3. List one invention the Greeks came up with. 4. The Greek “religion” was based upon ______, stories that were passed down over time about all their gods. ...
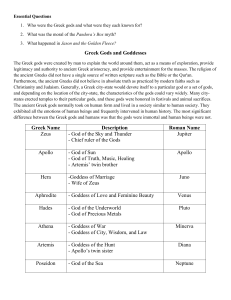
Greek Gods and Goddesses
... The Greek gods were created by man to explain the world around them, act as a means of exploration, provide legitimacy and authority to ancient Greek aristocracy, and provide entertainment for the masses. The religion of the ancient Greeks did not have a single source of written scripture such as th ...
... The Greek gods were created by man to explain the world around them, act as a means of exploration, provide legitimacy and authority to ancient Greek aristocracy, and provide entertainment for the masses. The religion of the ancient Greeks did not have a single source of written scripture such as th ...
Classical Greek Culture Learning Station Information Sheets
... people could be seated in a way that let them see what was going on down in the orchestra pit - the stage area. The entire seating section was called the Theatron, which is the origin of our word "theatre". Part of the reason plays were so important is that originally plays were performed to honor D ...
... people could be seated in a way that let them see what was going on down in the orchestra pit - the stage area. The entire seating section was called the Theatron, which is the origin of our word "theatre". Part of the reason plays were so important is that originally plays were performed to honor D ...
Early Greece Guided Notes
... • There also may be a connection to the Biblical Exodus in Egypt. The civilization lingered until about 1400-1250 BC, until the ___________________ conquered what was left of the Minoan civilization. 5) MYCENEA (Write in quick facts) ...
... • There also may be a connection to the Biblical Exodus in Egypt. The civilization lingered until about 1400-1250 BC, until the ___________________ conquered what was left of the Minoan civilization. 5) MYCENEA (Write in quick facts) ...
World History - Athens
... a. Western Asia, by the Caspian Sea b. Northern Europe, by the Baltic Sea c. Southern Europe, by the Mediterranean Sea d. Western Europe, by the Atlantic Ocean 2. How were Ancient Greek city-states different from modern U.S. states? a. Each city-state had its own laws; U.S. states do not b. No centr ...
... a. Western Asia, by the Caspian Sea b. Northern Europe, by the Baltic Sea c. Southern Europe, by the Mediterranean Sea d. Western Europe, by the Atlantic Ocean 2. How were Ancient Greek city-states different from modern U.S. states? a. Each city-state had its own laws; U.S. states do not b. No centr ...
Ancient Cultures - Athens
... a. Western Asia, by the Caspian Sea b. Northern Europe, by the Baltic Sea c. Southern Europe, by the Mediterranean Sea d. Western Europe, by the Atlantic Ocean 2. How were Ancient Greek city-states different from modern U.S. states? a. Each city-state had its own laws; U.S. states do not b. No centr ...
... a. Western Asia, by the Caspian Sea b. Northern Europe, by the Baltic Sea c. Southern Europe, by the Mediterranean Sea d. Western Europe, by the Atlantic Ocean 2. How were Ancient Greek city-states different from modern U.S. states? a. Each city-state had its own laws; U.S. states do not b. No centr ...
Ancient Rome music
... The lute, the true forerunner of the guitar (cithara), is considered a medieval instrument but was played by the ancient Romans. The Roman lute had three strings and was not as popular as the lyre or the cithara, but was easier to play. The cithara, was the premier musical instrument of ancient ...
... The lute, the true forerunner of the guitar (cithara), is considered a medieval instrument but was played by the ancient Romans. The Roman lute had three strings and was not as popular as the lyre or the cithara, but was easier to play. The cithara, was the premier musical instrument of ancient ...
Passport to Ancient Greece
... returned to start the Academy, a school that would operate for more than 900 years. Plato described his idea of an ideal society in his most famous book, the Republic. Plato did not believe in democracy. He argued in favor of an “aristocracy of merit,” rule by the best and the wisest people. Plato b ...
... returned to start the Academy, a school that would operate for more than 900 years. Plato described his idea of an ideal society in his most famous book, the Republic. Plato did not believe in democracy. He argued in favor of an “aristocracy of merit,” rule by the best and the wisest people. Plato b ...
Διαφάνεια 1
... or as stable (or as welldocumented) as that of Athens. It remains a unique and intriguing experiment in direct democracy where the people do not elect representatives to vote on their behalf but vote on legislation and executive bills in their own right. The participants participated with no referen ...
... or as stable (or as welldocumented) as that of Athens. It remains a unique and intriguing experiment in direct democracy where the people do not elect representatives to vote on their behalf but vote on legislation and executive bills in their own right. The participants participated with no referen ...
Compares Greece and Rome
... One of the most striking of these so-called veristic (superrealistic) portraits is of an unidentified patrician. ...
... One of the most striking of these so-called veristic (superrealistic) portraits is of an unidentified patrician. ...
Art History 1 Greece Art Study Guide After Aegean cultures
... PRE-HELLENISTIC (LATE CLASSICAL): 404-325 BCE. Praxiteles (Prax-it-tuh-leez), one of the best known of the Greek sculptors is working at this time. Most “Greek” sculptures that we have today are actually not Greek but are Roman copies. Original sculptures from the classical are rare, but the “Herme ...
... PRE-HELLENISTIC (LATE CLASSICAL): 404-325 BCE. Praxiteles (Prax-it-tuh-leez), one of the best known of the Greek sculptors is working at this time. Most “Greek” sculptures that we have today are actually not Greek but are Roman copies. Original sculptures from the classical are rare, but the “Herme ...
Timeline for Ancient Greece
... 479 B.C. – Greeks defeat Persian army at the Battle of Plateae 477 B.C. – Delian league lead by Athens 472 B.C. – Aeschylus writes first surviving play, The Persians 470 B.C. – Socrates, Greek Philosopher is born 465 B.C. – Helot revolt against Sparta 461 B.C. – First Peloponnesian Wars begin, last ...
... 479 B.C. – Greeks defeat Persian army at the Battle of Plateae 477 B.C. – Delian league lead by Athens 472 B.C. – Aeschylus writes first surviving play, The Persians 470 B.C. – Socrates, Greek Philosopher is born 465 B.C. – Helot revolt against Sparta 461 B.C. – First Peloponnesian Wars begin, last ...
Greek City States
... B. Thucydides – Most famous Greek historian who wrote A History of the Peloponnesian Wars after he was exiled for losing a battle. For his writings, he interviewed both sides of the war (Spartans and Athenians) and he checked facts. He thought that humans were responsible for war. C. Athens Strategy ...
... B. Thucydides – Most famous Greek historian who wrote A History of the Peloponnesian Wars after he was exiled for losing a battle. For his writings, he interviewed both sides of the war (Spartans and Athenians) and he checked facts. He thought that humans were responsible for war. C. Athens Strategy ...
Ancient Greece Golden Age of Athens
... “Wise men speak because they have something to say; fools because they have to say something.” Plato 428 – 328 B.C. Thought to be one of the greatest philosopher ever Follow reason not emotion Wrote down what Socrates said Aristotle was Plato’s student ...
... “Wise men speak because they have something to say; fools because they have to say something.” Plato 428 – 328 B.C. Thought to be one of the greatest philosopher ever Follow reason not emotion Wrote down what Socrates said Aristotle was Plato’s student ...
Ancient Greece - Harrison High School
... had conquered most of Greece by the time of his death 336 BC-Alexander from Macedonia (north of Greece) becomes King (age 20) 334 BC-Alexander invades Persian empire & wins major victory in Asia Minor ...
... had conquered most of Greece by the time of his death 336 BC-Alexander from Macedonia (north of Greece) becomes King (age 20) 334 BC-Alexander invades Persian empire & wins major victory in Asia Minor ...
The Story of Ancient Greece
... peninsula. • A peninsula is a body of land surrounded by water on three sides. • The rest of Greece is made up of islands. ...
... peninsula. • A peninsula is a body of land surrounded by water on three sides. • The rest of Greece is made up of islands. ...
Greek History - Area C Registration
... 16) The confidence and wealth in the aftermath of victory over Persia is most famously expressed in what? a) Temple Aphaia b) gigantomachy c) Temple of Zeus d) Acropolis ...
... 16) The confidence and wealth in the aftermath of victory over Persia is most famously expressed in what? a) Temple Aphaia b) gigantomachy c) Temple of Zeus d) Acropolis ...
Plato and the Republic
... democracy in which the unwise and untutored are accorded as much power as those who are steeped in knowledge and who deliberate in a rational fashion. ...
... democracy in which the unwise and untutored are accorded as much power as those who are steeped in knowledge and who deliberate in a rational fashion. ...
Art History 101, Class 1—Ancient and Medieval Art
... Athens never fully recovered from war with Sparta in 404 BC. But it retained its reputation as an artistic and intellectual center; Plato and Aristotle lived during this era, known as the late classical period. Artists now began to challenge the long-established standards for ideal body proportions ...
... Athens never fully recovered from war with Sparta in 404 BC. But it retained its reputation as an artistic and intellectual center; Plato and Aristotle lived during this era, known as the late classical period. Artists now began to challenge the long-established standards for ideal body proportions ...
History of science in classical antiquity

The history of science in classical antiquity encompasses both those inquiries into the workings of the universe aimed at such practical goals as establishing a reliable calendar or determining how to cure a variety of illnesses and those abstract investigations known as natural philosophy. The ancient peoples who are considered the first scientists may have thought of themselves as natural philosophers, as practitioners of a skilled profession (for example, physicians), or as followers of a religious tradition (for example, temple healers). The encyclopedic works of Aristotle, Archimedes, Hippocrates, Galen, Ptolemy, Euclid, and others spread throughout the world. These works and the important commentaries on them were the wellspring of science.