Science notes on Atoms, Periodic table
... The elements are also placed into groups based upon similar chemical reactions. All elements in the same chemical group share similarities during chemical reactions. The Alkali metals ...
... The elements are also placed into groups based upon similar chemical reactions. All elements in the same chemical group share similarities during chemical reactions. The Alkali metals ...
Representing Elements and Atoms
... Therefore, # protons must = # electrons since they have equal, but opposite charge ...
... Therefore, # protons must = # electrons since they have equal, but opposite charge ...
making models of atoms - Mater Academy Charter Middle/ High
... small particle that makes up most types of matter. Atoms are so mall it would take about 1 million of them lined up in a row to equal the thickness of a human hair. Atoms are made up of even smaller particles. The largest of these particles are protons, neutrons and electrons. The identity of a type ...
... small particle that makes up most types of matter. Atoms are so mall it would take about 1 million of them lined up in a row to equal the thickness of a human hair. Atoms are made up of even smaller particles. The largest of these particles are protons, neutrons and electrons. The identity of a type ...
File
... Even though Dalton’s work was 200 years ago, the basis of it is still valid with only a few modifications. Dalton thought atoms were solid spheres like billiard balls, but we know atoms are made up of smaller parts ...
... Even though Dalton’s work was 200 years ago, the basis of it is still valid with only a few modifications. Dalton thought atoms were solid spheres like billiard balls, but we know atoms are made up of smaller parts ...
Chapter3 atoms
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory (1808) All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different John Dalton elements differ in size, mass, and other properties Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory (1808) All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different John Dalton elements differ in size, mass, and other properties Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... His ideas agreed with later scientific theory, but didn’t explain chemical behavior - was not based on scientific methods – only philosophy ...
... His ideas agreed with later scientific theory, but didn’t explain chemical behavior - was not based on scientific methods – only philosophy ...
Unit 3 - Section 5.1 Introduction to Chemistry
... different number of neutrons. The diagram shows three isotopes of hydrogen: protium (no neutrons), deuterium (1 neutron) and tritium (2 neutrons). Since neutrons has no electrical charge, the chemistry of the element is not impacted. However, the mass of the element changes. Isotopes can be stable o ...
... different number of neutrons. The diagram shows three isotopes of hydrogen: protium (no neutrons), deuterium (1 neutron) and tritium (2 neutrons). Since neutrons has no electrical charge, the chemistry of the element is not impacted. However, the mass of the element changes. Isotopes can be stable o ...
ch4atomicstucture - Duplin County Schools
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
... • If it is true that all atoms have these super tiny negatively charged particles two main questions arise: 1. Because atoms are electrically neutral, they must contain a positive charge to balance out negative electrons 2. Because electrons have so much less mass than atoms, atoms must contain othe ...
... • If it is true that all atoms have these super tiny negatively charged particles two main questions arise: 1. Because atoms are electrically neutral, they must contain a positive charge to balance out negative electrons 2. Because electrons have so much less mass than atoms, atoms must contain othe ...
Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... Directions: Use the terms below to complete the following paragraphs about atoms, atomic mass, and isotopes. Terms may be used more than once. electron cloud ...
... Directions: Use the terms below to complete the following paragraphs about atoms, atomic mass, and isotopes. Terms may be used more than once. electron cloud ...
Chapter 10 - Department Of Computer Science
... Charge is due to moving of electrons, so it seems electron is a truly fundamental particle of matter However, further investigation have revealed that there still exist smaller particles called quarks Theoretically, six types of quarks exist (verified experimentally as well) ...
... Charge is due to moving of electrons, so it seems electron is a truly fundamental particle of matter However, further investigation have revealed that there still exist smaller particles called quarks Theoretically, six types of quarks exist (verified experimentally as well) ...
Chapter Three: Atoms and Atomic Masses
... Suppose a compound is analyzed and is found to contain 6.00 grams of carbon, 2.00 grams of hydrogen, and 8.00 grams of oxygen. What is the percent composition of the compound? ...
... Suppose a compound is analyzed and is found to contain 6.00 grams of carbon, 2.00 grams of hydrogen, and 8.00 grams of oxygen. What is the percent composition of the compound? ...
atom
... from each other, joined, or rearranged in a different combination. Atoms of one element, however, are never changed to atoms of another element as a result of a reaction ...
... from each other, joined, or rearranged in a different combination. Atoms of one element, however, are never changed to atoms of another element as a result of a reaction ...
Matter and Energy
... Properties of Matter Practice 1. Describe each of the following properties as physical or chemical: a. neon is a color gas at room temperature b. apple slices turn brown when exposed to air c. phosphorus will ignite when exposed to air d. at room temperature, mercury is a liquid e. propane gas is c ...
... Properties of Matter Practice 1. Describe each of the following properties as physical or chemical: a. neon is a color gas at room temperature b. apple slices turn brown when exposed to air c. phosphorus will ignite when exposed to air d. at room temperature, mercury is a liquid e. propane gas is c ...
Overview Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... number. The mass of the atom is so small that there is a ...
... number. The mass of the atom is so small that there is a ...
Lesson 12: Atoms By Numbers
... The atomic mass of an atom determined by summing the number of protons and neutrons is not identical to the average atomic mass of the element given in the periodic table. If you change the number of protons in an atom, you also change the elemental identity of that atom. ...
... The atomic mass of an atom determined by summing the number of protons and neutrons is not identical to the average atomic mass of the element given in the periodic table. If you change the number of protons in an atom, you also change the elemental identity of that atom. ...
Final Exam Review Day 1 - teacherstroh
... Yesterday we talked about matter… If you keep breaking down matter further and further, you will get to something called the… ...
... Yesterday we talked about matter… If you keep breaking down matter further and further, you will get to something called the… ...
Overview Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
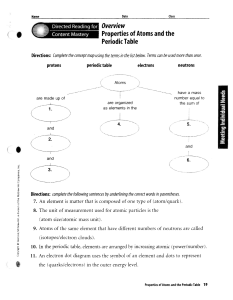
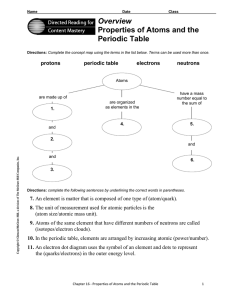
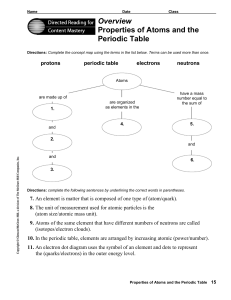
... 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit). 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called (isotopes/electron clouds). 10. In the periodic table, elements are arranged by increasing atomic (power/number). 11. An electron ...
... 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit). 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called (isotopes/electron clouds). 10. In the periodic table, elements are arranged by increasing atomic (power/number). 11. An electron ...
Atomic Structure 3: ISOTOPES
... neutrons. Different atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes — they have the same atomic number and the same number of protons, but they have different atomic masses and different numbers of neutrons. EXAMPLE: ...
... neutrons. Different atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes — they have the same atomic number and the same number of protons, but they have different atomic masses and different numbers of neutrons. EXAMPLE: ...
INTRODUCTION TO THE PERIODIC TABLE
... After the death of Democritus, however, the great philosopher Aristotle (384-322 BCE) argued persuasively against the concept of atoms. Aristotle thought the earth was composed of matter, which he believed was made up of four elements: earth, air, fire, and water. He explained the differences in dif ...
... After the death of Democritus, however, the great philosopher Aristotle (384-322 BCE) argued persuasively against the concept of atoms. Aristotle thought the earth was composed of matter, which he believed was made up of four elements: earth, air, fire, and water. He explained the differences in dif ...
Atomic structure and radioactive decay
... of the alpha particles must have been due to the gold foil. How can these results be explained in terms of atoms? 7 of 23 ...
... of the alpha particles must have been due to the gold foil. How can these results be explained in terms of atoms? 7 of 23 ...
Promethium

Promethium, originally prometheum, is a chemical element with symbol Pm and atomic number 61. All of its isotopes are radioactive; it is one of only two such elements that are followed in the periodic table by elements with stable forms, a distinction shared with technetium. Chemically, promethium is a lanthanide, which forms salts when combined with other elements. Promethium shows only one stable oxidation state of +3; however, a few +2 compounds may exist.In 1902, Bohuslav Brauner suggested there was an element with properties intermediate between those of the known elements neodymium (60) and samarium (62); this was confirmed in 1914 by Henry Moseley who, having measured the atomic numbers of all the elements then known, found there was an element with atomic number 61. In 1926, an Italian and an American group claimed to have isolated a sample of element 61; both ""discoveries"" were soon proven to be false. In 1938, during a nuclear experiment conducted at Ohio State University, a few radioactive nuclides were produced that certainly were not radioisotopes of neodymium or samarium, but there was a lack of chemical proof that element 61 was produced, and the discovery was not generally recognized. Promethium was first produced and characterized at Oak Ridge National Laboratory in 1945 by the separation and analysis of the fission products of uranium fuel irradiated in a graphite reactor. The discoverers proposed the name ""prometheum"" (the spelling was subsequently changed), derived from Prometheus, the Titan in Greek mythology who stole fire from Mount Olympus and brought it down to humans, to symbolize ""both the daring and the possible misuse of mankind's intellect"". However, a sample of the metal was made only in 1963.There are two possible sources for natural promethium: rare decays of natural europium-151 (producing promethium-147), and uranium (various isotopes). Practical applications exist only for chemical compounds of promethium-147, which are used in luminous paint, atomic batteries, and thickness measurement devices, even though promethium-145 is the most stable promethium isotope. Because natural promethium is exceedingly scarce, it is typically synthesized by bombarding uranium-235 (enriched uranium) with thermal neutrons to produce promethium-147.