Chapter 4 PowerPoint
... atoms of any one element differ from those of any other element. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. Atoms of one element, however, ...
... atoms of any one element differ from those of any other element. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. Atoms of one element, however, ...
File
... - The groups of elements can be classified further into 4 categories: (Group categories) 1. The main Group or Representative Elements (Groups IA – VIIA) a) Group IA - alkali metals (Li, Na, K excluding hydrogen which is a non-metal) - Highly reactive metals meaning they combine easily with other ele ...
... - The groups of elements can be classified further into 4 categories: (Group categories) 1. The main Group or Representative Elements (Groups IA – VIIA) a) Group IA - alkali metals (Li, Na, K excluding hydrogen which is a non-metal) - Highly reactive metals meaning they combine easily with other ele ...
Atomic Structure
... Table is determined by its proton number. All elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons, which is the same as the Group number. All elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells. ...
... Table is determined by its proton number. All elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons, which is the same as the Group number. All elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells. ...
11129_evl_ch1_ste_eleve (3)
... 22. One of the lakes of Tibet contains the second largest lithium deposit in the world. This element is used extensively today in cellphone batteries and will also be used, in the near future, in batteries for hybrid or electric cars. In 2008, one battery out of every four sold in the world was manu ...
... 22. One of the lakes of Tibet contains the second largest lithium deposit in the world. This element is used extensively today in cellphone batteries and will also be used, in the near future, in batteries for hybrid or electric cars. In 2008, one battery out of every four sold in the world was manu ...
Ch2 Lecture
... •An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by a chemical reaction. •Each element is identified by a one- or two-letter symbol. •Elements are arranged in the periodic table. •The position of an element in the periodic table tells us much about its chemical prop ...
... •An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by a chemical reaction. •Each element is identified by a one- or two-letter symbol. •Elements are arranged in the periodic table. •The position of an element in the periodic table tells us much about its chemical prop ...
LAB ACTIVITY CALCULATING ATOMIC MASS
... believed to be element 114. The researchers have proposed that the element be named vabeachium (va-beach-e-m), after the city in which it was discovered. The proposed element symbol is Vb. Samples are currently being distributed to all of the local high schools. Each school is to isolate the individ ...
... believed to be element 114. The researchers have proposed that the element be named vabeachium (va-beach-e-m), after the city in which it was discovered. The proposed element symbol is Vb. Samples are currently being distributed to all of the local high schools. Each school is to isolate the individ ...
Chemistry - Rainhill High School
... Describe why the new evidence from the scattering experiment led to a change in the atomic model. ...
... Describe why the new evidence from the scattering experiment led to a change in the atomic model. ...
GEO143_lab_3_atoms_m..
... 2. How does the number of electrons relate to the arrangement? What is the difference in the number of electrons in a 3rd period element and the 2nd period element above it? The elements are arranged in increasing number of electrons. Each element in the 3rd row has eight more electrons than the ele ...
... 2. How does the number of electrons relate to the arrangement? What is the difference in the number of electrons in a 3rd period element and the 2nd period element above it? The elements are arranged in increasing number of electrons. Each element in the 3rd row has eight more electrons than the ele ...
DO NOW - PBworks
... Reminder: Enter the classroom, begin the Do Now immediately, silently and independently. ...
... Reminder: Enter the classroom, begin the Do Now immediately, silently and independently. ...
Ch 17 Properties of Atoms - Effingham County Schools
... and are numbered 1 through 18. Elements in each group have similar properties. The horizontal rows of elements on the periodic table are called periods. The elements increase by one proton and one electron as you go from left to right in a period. ...
... and are numbered 1 through 18. Elements in each group have similar properties. The horizontal rows of elements on the periodic table are called periods. The elements increase by one proton and one electron as you go from left to right in a period. ...
final exam review packet
... Know what can be used to shield yourself from each form of radiation. Be able to identify the missing particle in a transmutation equation. Know the difference between fission and fusion. Know the nuclear process that fuels our sun. ...
... Know what can be used to shield yourself from each form of radiation. Be able to identify the missing particle in a transmutation equation. Know the difference between fission and fusion. Know the nuclear process that fuels our sun. ...
Periodic_Table
... Salt: a compound composed of positive and negative ions arranged in a regular 3D pattern - most reactive group of nonmetals - varying physical properties, similar chemical properties ...
... Salt: a compound composed of positive and negative ions arranged in a regular 3D pattern - most reactive group of nonmetals - varying physical properties, similar chemical properties ...
Note Packet for Students
... Joseph Proust (1754-1826) was a Frenchman that discovered a given compound always contains exactly the same proportions of the elements by weight. This law started being called Proust’s Law and is now named the Law of definite Proportion. John Dalton (1766-1844) found the Law of Multiple Proportions ...
... Joseph Proust (1754-1826) was a Frenchman that discovered a given compound always contains exactly the same proportions of the elements by weight. This law started being called Proust’s Law and is now named the Law of definite Proportion. John Dalton (1766-1844) found the Law of Multiple Proportions ...
Understanding the Atom
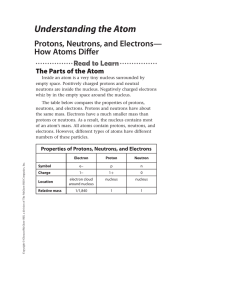
... mass number = number of protons + number of neutrons You can determine any one of these three quantities if you know the value of the other two quantities. For example, to determine the mass number of an atom, you must know the number of neutrons and the number of protons in the atom. The mass numbe ...
... mass number = number of protons + number of neutrons You can determine any one of these three quantities if you know the value of the other two quantities. For example, to determine the mass number of an atom, you must know the number of neutrons and the number of protons in the atom. The mass numbe ...
Atomic structure and periodic table review questions What is an
... 1. What is an atom mostly made up of? 2. The two sub-atomic particles found in the nucleus are? 3. Another name for the two sub-atomic particles found in the nucleus is ____________. 4. What are the sub-atomic particles found outside of the nucleus? 5. Which particle has a positive charge? 6. Which ...
... 1. What is an atom mostly made up of? 2. The two sub-atomic particles found in the nucleus are? 3. Another name for the two sub-atomic particles found in the nucleus is ____________. 4. What are the sub-atomic particles found outside of the nucleus? 5. Which particle has a positive charge? 6. Which ...
Modern Physics
... • An atom is stable (not radioactive) if it is in the belt of stability • An atom is unstable (radioactive) if it is outside the belt of stability • All elements beyond number 83, Bismuth are unstable - WHY? ...
... • An atom is stable (not radioactive) if it is in the belt of stability • An atom is unstable (radioactive) if it is outside the belt of stability • All elements beyond number 83, Bismuth are unstable - WHY? ...
atomic number on the periodic table
... • Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian scientist born in Siberia in 1834, is known as the father of the periodic table of the elements • The periodic table is designed to help you predict chemical and physical properties of elements ...
... • Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian scientist born in Siberia in 1834, is known as the father of the periodic table of the elements • The periodic table is designed to help you predict chemical and physical properties of elements ...
Atom notes - WordPress.com
... ELEMENT: One of the __________ known _____________ substances. Listed on the periodic table. ATOM: ______________________ piece of matter that still retains the properties of that matter. ______________________ in the world is made of atoms. NUCLEUS: _________________ of the atom; _________________ ...
... ELEMENT: One of the __________ known _____________ substances. Listed on the periodic table. ATOM: ______________________ piece of matter that still retains the properties of that matter. ______________________ in the world is made of atoms. NUCLEUS: _________________ of the atom; _________________ ...
Follow the steps to find the number
... 3. The number of electrons in a sodium +1 ion. Multiply by the number of protons in an atom of Sn. Divide by the number of neutrons in at atom of H-2. Multiply by the number of electrons in an atom of neutral barium. 4. The number of electrons in Cu. Subtract the number of neutrons in F. Multiply by ...
... 3. The number of electrons in a sodium +1 ion. Multiply by the number of protons in an atom of Sn. Divide by the number of neutrons in at atom of H-2. Multiply by the number of electrons in an atom of neutral barium. 4. The number of electrons in Cu. Subtract the number of neutrons in F. Multiply by ...
atoms
... and neutrons. Some nuclei are unstable because they have too many or too few neutrons. This is especially true for heavier elements such as uranium and plutonium. • The release of nuclear particles and energy is called radioactive decay. • In these nuclei, repulsion builds up. The nucleus must relea ...
... and neutrons. Some nuclei are unstable because they have too many or too few neutrons. This is especially true for heavier elements such as uranium and plutonium. • The release of nuclear particles and energy is called radioactive decay. • In these nuclei, repulsion builds up. The nucleus must relea ...
Chapter 17 - murraysphysical
... Name of element followed by mass number identifies the isotopes. ...
... Name of element followed by mass number identifies the isotopes. ...
ChemCh4of2011
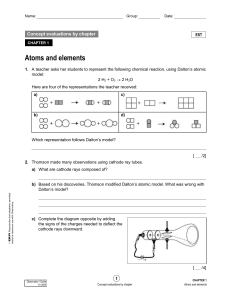
... Conclusions from the Study of the Electron Cathode rays have identical properties regardless of the element used to produce them. All elements must contain identically charged electrons. Atoms are neutral, so there must be positive particles in the atom to balance the negative charge of the elec ...
... Conclusions from the Study of the Electron Cathode rays have identical properties regardless of the element used to produce them. All elements must contain identically charged electrons. Atoms are neutral, so there must be positive particles in the atom to balance the negative charge of the elec ...
Intro to Chemistry
... The number of protons, electrons, and neutrons in an element predicts their behavior under a variety of conditions inside and outside the body. ...
... The number of protons, electrons, and neutrons in an element predicts their behavior under a variety of conditions inside and outside the body. ...
Neptunium
.png?width=300)
Neptunium is a chemical element with symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactive actinide metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element. Its position in the periodic table just after uranium, named after the planet Uranus, led to it being named after Neptune, the next planet beyond Uranus. A neptunium atom has 93 protons and 93 electrons, of which seven are valence electrons. Neptunium metal is silvery and tarnishes when exposed to air. The element occurs in three allotropic forms and it normally exhibits five oxidation states, ranging from +3 to +7. It is radioactive, pyrophoric, and can accumulate in bones, which makes the handling of neptunium dangerous.Although many false claims of its discovery were made over the years, the element was first synthesized by Edwin McMillan and Philip H. Abelson at the Berkeley Radiation Laboratory in 1940. Since then, most neptunium has been and still is produced by neutron irradiation of uranium in nuclear reactors. The vast majority is generated as a by-product in conventional nuclear power reactors. While neptunium itself has no commercial uses at present, it is widely used as a precursor for the formation of plutonium-238, used in radioisotope thermal generators. Neptunium has also been used in detectors of high-energy neutrons.The most stable isotope of neptunium, neptunium-237, is a by-product of nuclear reactors and plutonium production. It, and the isotope neptunium-239, are also found in trace amounts in uranium ores due to neutron capture reactions and beta decay.