Quantitative periodic table – dominoes
... How many times heavier is an arsenic atom compared to a hydrogen atom? ...
... How many times heavier is an arsenic atom compared to a hydrogen atom? ...
atomic mass
... particles called atoms 2.Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in these properties. ...
... particles called atoms 2.Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different elements differ in these properties. ...
atom
... Atoms of the same element are identical, those of different atoms are different. Atoms of different elements combine in whole number ratios to form compounds. Chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of atoms. No new atoms are created or destroyed. ...
... Atoms of the same element are identical, those of different atoms are different. Atoms of different elements combine in whole number ratios to form compounds. Chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of atoms. No new atoms are created or destroyed. ...
Elements
... the nucleus) The maximum number of valence electrons for any element is eight which is the most stable valence electron configuration Only noble gases have the maximum number 5 of the 6 noble gases have eight valence electrons Helium (the exception) has only two valence electrons ...
... the nucleus) The maximum number of valence electrons for any element is eight which is the most stable valence electron configuration Only noble gases have the maximum number 5 of the 6 noble gases have eight valence electrons Helium (the exception) has only two valence electrons ...
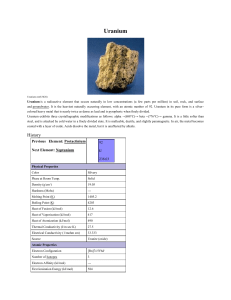
Uranium
... which means that atoms of uranium are unstable and decay by emitting particles and energy. Uranium decays very slowly by emitting an alpha particle. The half-life of uranium-238 is about 4.5 billion years, which means it is not very radioactive. In fact, its very long half-life (and thus low radioac ...
... which means that atoms of uranium are unstable and decay by emitting particles and energy. Uranium decays very slowly by emitting an alpha particle. The half-life of uranium-238 is about 4.5 billion years, which means it is not very radioactive. In fact, its very long half-life (and thus low radioac ...
Key Concept Summary - Bellingham High School
... Dalton’s theory enables us to set up a scale of relative atomic masses. He cannot measure the exact mass of atoms but relative mass. E.g. Consider calcium sulfide, which consists of 55.6% calcium by mass and 44.4% sulfur by mass. Suppose there is one calcium atom for each sulfur atom in calcium sulf ...
... Dalton’s theory enables us to set up a scale of relative atomic masses. He cannot measure the exact mass of atoms but relative mass. E.g. Consider calcium sulfide, which consists of 55.6% calcium by mass and 44.4% sulfur by mass. Suppose there is one calcium atom for each sulfur atom in calcium sulf ...
Unit 3 PowerPoint
... eight electrons, corresponding to the electron configuration of a noble gas, such as neon or argon • Orbital notation (diagram) -A way to show how many electrons are in an orbital for a given element. They can either be shown with arrows or circles ...
... eight electrons, corresponding to the electron configuration of a noble gas, such as neon or argon • Orbital notation (diagram) -A way to show how many electrons are in an orbital for a given element. They can either be shown with arrows or circles ...
Elements
... have some chemical and physical properties of metals and other properties of nonmetals. In the periodic table, the metalloids lie along the border between metals and nonmetals. ...
... have some chemical and physical properties of metals and other properties of nonmetals. In the periodic table, the metalloids lie along the border between metals and nonmetals. ...
Honors Mid-Term Review Sheet
... 81. How many lone pairs of electrons are in the Lewis dot structure for H2O? 82. Draw the Lewis dot structures for the following: CO, CO2, N2, and O2. 83. Define intermolecular forces and intramolecular forces. 84. Define London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole attractions, and hydrogen bonding. 85. ...
... 81. How many lone pairs of electrons are in the Lewis dot structure for H2O? 82. Draw the Lewis dot structures for the following: CO, CO2, N2, and O2. 83. Define intermolecular forces and intramolecular forces. 84. Define London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole attractions, and hydrogen bonding. 85. ...
OCR AS LEVEL CHEMISTRY A 1.1.1 ATOMS 1.2.1 ELECTRON
... Use this mass spectrum to help you complete the table below. isotope ...
... Use this mass spectrum to help you complete the table below. isotope ...
Grade 11 Unit 4 - Amazon Web Services
... This section is designed to help you get a better idea and appreciation for eight scientists who made great contributions to the development of our present-day atomic theory. Information on each scientist is taken from the “Atomic Pioneer Series.” United States Energy Research and Development Admini ...
... This section is designed to help you get a better idea and appreciation for eight scientists who made great contributions to the development of our present-day atomic theory. Information on each scientist is taken from the “Atomic Pioneer Series.” United States Energy Research and Development Admini ...
2.4 The Periodic Table
... shells. Within each shell, electrons are grouped into subshells, and within each subshell into orbitals. s orbitals are spherical; p orbitals are dumbbell-shaped. Each shell can hold a specific number of electrons. The first shell can hold 2 electrons, the second shell can hold 8 electrons, and the ...
... shells. Within each shell, electrons are grouped into subshells, and within each subshell into orbitals. s orbitals are spherical; p orbitals are dumbbell-shaped. Each shell can hold a specific number of electrons. The first shell can hold 2 electrons, the second shell can hold 8 electrons, and the ...
Welcome to Chemistry 1001
... whole number ratios to form compounds Chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of atoms. No new atoms are created or destroyed. ...
... whole number ratios to form compounds Chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of atoms. No new atoms are created or destroyed. ...
Periodic Law
... The groups in the periodic table have "A" and "B" designations. The elements in the A groups, which appear in two parts—two at the beginning and six at the end of the table—are known as the main group elements. Those in the B groups, which are in between the two A group divisions, are called transit ...
... The groups in the periodic table have "A" and "B" designations. The elements in the A groups, which appear in two parts—two at the beginning and six at the end of the table—are known as the main group elements. Those in the B groups, which are in between the two A group divisions, are called transit ...
Lecture 4
... chemically combined • Two or more substances in different proportions • Substances that can be separated by physical methods Example: Pasta and water can be separated with a strainer. ...
... chemically combined • Two or more substances in different proportions • Substances that can be separated by physical methods Example: Pasta and water can be separated with a strainer. ...
Building Atoms - Community Science Workshop Network
... element, and the first letter is always capitalized. For some elements one or two letters from the element's common name are used, such as C for carbon, while others are based on their Latin names ...
... element, and the first letter is always capitalized. For some elements one or two letters from the element's common name are used, such as C for carbon, while others are based on their Latin names ...
2013 atoms
... positively charged anode. Years later, scientists determined that the rays were composed of positively charged subatomic particles called protons. ...
... positively charged anode. Years later, scientists determined that the rays were composed of positively charged subatomic particles called protons. ...
Atomic Number
... radioisotopes, and the high-energy particles given off in this process are referred to as ionizing radiation, or radioactivity. – Three common forms of radioactivity are alpha (a) and beta (b) particles and gamma (g) rays. – An X-ray is also a form of ionizing radiation, although it is not caused by ...
... radioisotopes, and the high-energy particles given off in this process are referred to as ionizing radiation, or radioactivity. – Three common forms of radioactivity are alpha (a) and beta (b) particles and gamma (g) rays. – An X-ray is also a form of ionizing radiation, although it is not caused by ...
Chapter 2 Atoms and Radioactivity Outline 2.1 Atoms and Their
... radioisotopes, and the high-energy particles given off in this process are referred to as ionizing radiation, or radioactivity. – Three common forms of radioactivity are alpha (a) and beta (b) particles and gamma (g) rays. – An X-ray is also a form of ionizing radiation, although it is not caused by ...
... radioisotopes, and the high-energy particles given off in this process are referred to as ionizing radiation, or radioactivity. – Three common forms of radioactivity are alpha (a) and beta (b) particles and gamma (g) rays. – An X-ray is also a form of ionizing radiation, although it is not caused by ...
Practice Packet
... 22. The lines on the visible light spectrum for the gases above represent a) electrons jumping to the same excited state or energy level. b) electrons falling back down to their ground state from the same energy level. c) electrons jumping to multiple excited states or energy levels. d) electrons fa ...
... 22. The lines on the visible light spectrum for the gases above represent a) electrons jumping to the same excited state or energy level. b) electrons falling back down to their ground state from the same energy level. c) electrons jumping to multiple excited states or energy levels. d) electrons fa ...
The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
... series) -- atomic #58 – 71 • They are shiny, reactive metals that are often used to make alloys. • Actinide Series: (also called the Actinoid series) -- atomic #90 – 103 • Have unstable arrangements or protons and neutrons • All are radioactive and most are man-made ...
... series) -- atomic #58 – 71 • They are shiny, reactive metals that are often used to make alloys. • Actinide Series: (also called the Actinoid series) -- atomic #90 – 103 • Have unstable arrangements or protons and neutrons • All are radioactive and most are man-made ...
atom - West Ada
... on identifying the elements. Remember the box on the Periodic Table has all the information we need to identify an element. The largest number is the atomic mass. • The atomic mass is found by adding the protons and the neutrons. • The smallest number is the atomic number, which equals the number of ...
... on identifying the elements. Remember the box on the Periodic Table has all the information we need to identify an element. The largest number is the atomic mass. • The atomic mass is found by adding the protons and the neutrons. • The smallest number is the atomic number, which equals the number of ...
Neptunium
.png?width=300)
Neptunium is a chemical element with symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactive actinide metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element. Its position in the periodic table just after uranium, named after the planet Uranus, led to it being named after Neptune, the next planet beyond Uranus. A neptunium atom has 93 protons and 93 electrons, of which seven are valence electrons. Neptunium metal is silvery and tarnishes when exposed to air. The element occurs in three allotropic forms and it normally exhibits five oxidation states, ranging from +3 to +7. It is radioactive, pyrophoric, and can accumulate in bones, which makes the handling of neptunium dangerous.Although many false claims of its discovery were made over the years, the element was first synthesized by Edwin McMillan and Philip H. Abelson at the Berkeley Radiation Laboratory in 1940. Since then, most neptunium has been and still is produced by neutron irradiation of uranium in nuclear reactors. The vast majority is generated as a by-product in conventional nuclear power reactors. While neptunium itself has no commercial uses at present, it is widely used as a precursor for the formation of plutonium-238, used in radioisotope thermal generators. Neptunium has also been used in detectors of high-energy neutrons.The most stable isotope of neptunium, neptunium-237, is a by-product of nuclear reactors and plutonium production. It, and the isotope neptunium-239, are also found in trace amounts in uranium ores due to neutron capture reactions and beta decay.