Atoms and the Periodic Table
... a. They do not have the same number of neutrons. b. They do not have the same number of electrons. c. They do not have the same number of protons. d. They have the same mass number 35. The _____________ family of elements contains all of the elements that are inert. a. Halogens c. Alkaline Earth Met ...
... a. They do not have the same number of neutrons. b. They do not have the same number of electrons. c. They do not have the same number of protons. d. They have the same mass number 35. The _____________ family of elements contains all of the elements that are inert. a. Halogens c. Alkaline Earth Met ...
DO NOW
... Read “The Bohr Model and Valence Electrons” from page 141. Take Cornell Notes, defining the following terms: - Bohr Model ...
... Read “The Bohr Model and Valence Electrons” from page 141. Take Cornell Notes, defining the following terms: - Bohr Model ...
Parts of the Atom - centralscience10
... protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons have a ________________ charge and are located in the _____________. The ________________ number tells us how many protons an atom has. Neutrons have a _________________ charge and are also located in the _________________. The atomic mass minus the numbe ...
... protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons have a ________________ charge and are located in the _____________. The ________________ number tells us how many protons an atom has. Neutrons have a _________________ charge and are also located in the _________________. The atomic mass minus the numbe ...
Chemistry Topic III – The Atom
... d. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. e. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are ____________________, ____________________ or ______________________. Atoms of one element, however, are never changed into ...
... d. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. e. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are ____________________, ____________________ or ______________________. Atoms of one element, however, are never changed into ...
Notes powerpoint
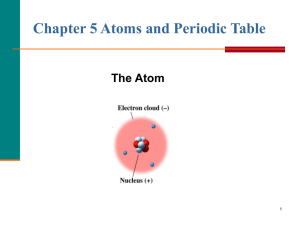
... • The electron cloud is 100,000 times larger than the diameter of the nucleus. • In contrast, each electron in the cloud is much smaller than a single proton. • Because an electron’s mass is small and the electron is moving so quickly around the nucleus, it is impossible to describe its exact locati ...
... • The electron cloud is 100,000 times larger than the diameter of the nucleus. • In contrast, each electron in the cloud is much smaller than a single proton. • Because an electron’s mass is small and the electron is moving so quickly around the nucleus, it is impossible to describe its exact locati ...
Symbols of Elements - Chemistry with Mr. Patmos
... Isotopes of Magnesium In naturally occurring magnesium, there are three isotopes. Isotopes of Mg ...
... Isotopes of Magnesium In naturally occurring magnesium, there are three isotopes. Isotopes of Mg ...
topic1
... principal energy level, but the number of protons in the nucleus increases from one element to the next. This means that the nucleus becomes more positively charged and attracts the electrons more strongly. Therefore, the atomic radius decreases going from left to right across a period. Electronegat ...
... principal energy level, but the number of protons in the nucleus increases from one element to the next. This means that the nucleus becomes more positively charged and attracts the electrons more strongly. Therefore, the atomic radius decreases going from left to right across a period. Electronegat ...
GHW - Louisiana Tech University
... you measure moles directly measured using a chemical balances which give readings in grams? How is this problem get boiled down to: converting amount of a substance from grams to mole, and later converting from moles of products to grams which are actually measured directly. Why is it important that ...
... you measure moles directly measured using a chemical balances which give readings in grams? How is this problem get boiled down to: converting amount of a substance from grams to mole, and later converting from moles of products to grams which are actually measured directly. Why is it important that ...
3. Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... tested an ore of uranium, pitchblende’s ability to emanate ionization radiation found it 300 times stronger than that produced by pure uranium. The Curies reasoned that a very active unknown element (a new unstable later named polonium) must have been produced must exist within the pitchblende in ad ...
... tested an ore of uranium, pitchblende’s ability to emanate ionization radiation found it 300 times stronger than that produced by pure uranium. The Curies reasoned that a very active unknown element (a new unstable later named polonium) must have been produced must exist within the pitchblende in ad ...
Document
... 55. An element with atomic number-26 is _____. A) Ca B) Fe C) Co D) Ni 56. The element [Ne]3s1 is in the _____ group. A) 1st B) 2nd C) 13th D) 17th 57. The element [Ne]3s23p3 is in the _____ group. A) 13th B) 2nd C) 15th D) 17th 58. The element [Ar]4s23d8 is a/an _____. A) alkali metal B) transition ...
... 55. An element with atomic number-26 is _____. A) Ca B) Fe C) Co D) Ni 56. The element [Ne]3s1 is in the _____ group. A) 1st B) 2nd C) 13th D) 17th 57. The element [Ne]3s23p3 is in the _____ group. A) 13th B) 2nd C) 15th D) 17th 58. The element [Ar]4s23d8 is a/an _____. A) alkali metal B) transition ...
Historical Background: Atoms
... observations at the end of the 18th century: that compounds are the result of the reaction of specific ratios of masses of the elements that form the compound. This rule became known as the law of constant composition. Even though this law appeared to be valid for the chemical reactions that had bee ...
... observations at the end of the 18th century: that compounds are the result of the reaction of specific ratios of masses of the elements that form the compound. This rule became known as the law of constant composition. Even though this law appeared to be valid for the chemical reactions that had bee ...
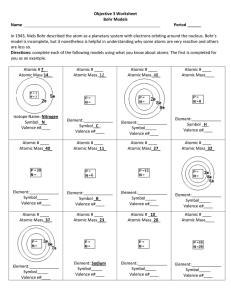
Objective 3 Worksheet Bohr Models Name Period In 1943, Niels
... Objective 3 Worksheet Bohr Models Name ...
... Objective 3 Worksheet Bohr Models Name ...
Isotopes
... Obj: understand the conclusions of Bohr’s nuclear atom. Use isotopic composition to calculate average atomic mass. ESQ: How are isotopes similar? Different? How do you calculate the average atomic mass of an isotope? ...
... Obj: understand the conclusions of Bohr’s nuclear atom. Use isotopic composition to calculate average atomic mass. ESQ: How are isotopes similar? Different? How do you calculate the average atomic mass of an isotope? ...
Chapter 2 Law of Conservation of Mass Law of Conservation of Mass
... gold foil, and most did, but some were deflected slightly and a few bounced backwards. – The deflected particles led to the hypothesis of the ...
... gold foil, and most did, but some were deflected slightly and a few bounced backwards. – The deflected particles led to the hypothesis of the ...
CHAPTER-4 STRUCTURE OF THE ATOM
... 2. If it is the outermost orbit, then it should have not more than 8 electrons. 3. There should be step-wise filling of electrons in different orbits, i.e., electrons are not accompanied in a given orbit if the earlier orbits or shells are incompletely filled. Q.7: Define valency by taking examples ...
... 2. If it is the outermost orbit, then it should have not more than 8 electrons. 3. There should be step-wise filling of electrons in different orbits, i.e., electrons are not accompanied in a given orbit if the earlier orbits or shells are incompletely filled. Q.7: Define valency by taking examples ...
3. Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... from various sources. Curies tested an ore of uranium, pitchblende’s ability to emanate ionization radiation found it 300 times stronger than that produced by pure uranium. The Curies reasoned that a very active unknown element (a new unstable later named polonium) must have been produced must exist ...
... from various sources. Curies tested an ore of uranium, pitchblende’s ability to emanate ionization radiation found it 300 times stronger than that produced by pure uranium. The Curies reasoned that a very active unknown element (a new unstable later named polonium) must have been produced must exist ...
Nuclear physics is the subfield of physics that studies the building
... was a fundamental entity – perhaps the building block scientists had been looking for. Rutherford named the hydrogen nucleus the proton, from the Greek word protos meaning "first." The process of changing one atom into another by hitting it with an energetic particle is called artificial transmutati ...
... was a fundamental entity – perhaps the building block scientists had been looking for. Rutherford named the hydrogen nucleus the proton, from the Greek word protos meaning "first." The process of changing one atom into another by hitting it with an energetic particle is called artificial transmutati ...
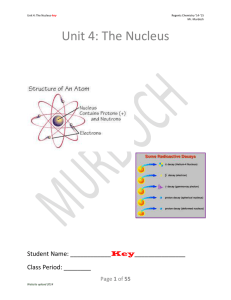
Unit 4: The Nucleus
... approximate mass of either a proton or neutron. 3. Atomic Number: The number that identifies an element, equal to an atom’s number of protons. 4. Deflect: Change in direction due to an outside force. 5. Emit: To give off something. 6. Half-life: The time it takes for half the mass of a radioactive i ...
... approximate mass of either a proton or neutron. 3. Atomic Number: The number that identifies an element, equal to an atom’s number of protons. 4. Deflect: Change in direction due to an outside force. 5. Emit: To give off something. 6. Half-life: The time it takes for half the mass of a radioactive i ...
Gizmo Lab Bohr Models 2014
... The Periodic Table is an organized list of all of the different types of atoms called elements. Elements are pure substances that are made up of only one kind of atom. Iron is an element because it is composed of only one kind of atom. Water is also a pure substance, but it contains two different ki ...
... The Periodic Table is an organized list of all of the different types of atoms called elements. Elements are pure substances that are made up of only one kind of atom. Iron is an element because it is composed of only one kind of atom. Water is also a pure substance, but it contains two different ki ...
по темі “Atoms and Molecules. The Periodic Table”
... II. Read the text «Atoms and Molecules». Answer the following questions on the text. 1. What is called an atom? 2. Who was the first scientist to put forward the theory that all matter was composed of atoms? 3. Who is the founder of modern atomic theory? 4. All of the atoms of a particular element ...
... II. Read the text «Atoms and Molecules». Answer the following questions on the text. 1. What is called an atom? 2. Who was the first scientist to put forward the theory that all matter was composed of atoms? 3. Who is the founder of modern atomic theory? 4. All of the atoms of a particular element ...
How many protons, electrons and neutrons are in an atom of krypton
... charged electrons. Atoms must have equal numbers of protons and electrons. In our example, an atom of krypton must contain 36 electrons since it contains 36 protons. Electrons are arranged around atoms in a special way. If you need to know how the electrons are arranged around an atom, take a look ...
... charged electrons. Atoms must have equal numbers of protons and electrons. In our example, an atom of krypton must contain 36 electrons since it contains 36 protons. Electrons are arranged around atoms in a special way. If you need to know how the electrons are arranged around an atom, take a look ...
Entry Task
... • Most elements are metals • Elements that conduct electricity and heat well and have a shiny appearance • Shaped easily by pounding, bending or being drawn into a long wire • Solid at room temperature-except for mercury which is a liquid ...
... • Most elements are metals • Elements that conduct electricity and heat well and have a shiny appearance • Shaped easily by pounding, bending or being drawn into a long wire • Solid at room temperature-except for mercury which is a liquid ...
Neptunium
.png?width=300)
Neptunium is a chemical element with symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactive actinide metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element. Its position in the periodic table just after uranium, named after the planet Uranus, led to it being named after Neptune, the next planet beyond Uranus. A neptunium atom has 93 protons and 93 electrons, of which seven are valence electrons. Neptunium metal is silvery and tarnishes when exposed to air. The element occurs in three allotropic forms and it normally exhibits five oxidation states, ranging from +3 to +7. It is radioactive, pyrophoric, and can accumulate in bones, which makes the handling of neptunium dangerous.Although many false claims of its discovery were made over the years, the element was first synthesized by Edwin McMillan and Philip H. Abelson at the Berkeley Radiation Laboratory in 1940. Since then, most neptunium has been and still is produced by neutron irradiation of uranium in nuclear reactors. The vast majority is generated as a by-product in conventional nuclear power reactors. While neptunium itself has no commercial uses at present, it is widely used as a precursor for the formation of plutonium-238, used in radioisotope thermal generators. Neptunium has also been used in detectors of high-energy neutrons.The most stable isotope of neptunium, neptunium-237, is a by-product of nuclear reactors and plutonium production. It, and the isotope neptunium-239, are also found in trace amounts in uranium ores due to neutron capture reactions and beta decay.