Unit_1_The_Atom
... for the three laws. His atomic theory states: 1. All matter is composed of atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical; atoms of different elements are different. 3. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple wholenumber ratios to form ...
... for the three laws. His atomic theory states: 1. All matter is composed of atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical; atoms of different elements are different. 3. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple wholenumber ratios to form ...
Atoms and Elements: Are they Related?
... • What are the most commonly occurring elements in the food labels? • What items seemed to have the most amount of elements in them? • Can you predict what that means about the food item? • Why do you think the baby formula has such a variety of elements? • Can you predict what the other items on th ...
... • What are the most commonly occurring elements in the food labels? • What items seemed to have the most amount of elements in them? • Can you predict what that means about the food item? • Why do you think the baby formula has such a variety of elements? • Can you predict what the other items on th ...
Powerpoint
... for the three laws. His atomic theory states: 1. All matter is composed of atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical; atoms of different elements are different. 3. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple wholenumber ratios to form ...
... for the three laws. His atomic theory states: 1. All matter is composed of atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical; atoms of different elements are different. 3. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple wholenumber ratios to form ...
Unit 1 Powerpoint Notes
... for the three laws. His atomic theory states: 1. All matter is composed of atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical; atoms of different elements are different. 3. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple wholenumber ratios to form ...
... for the three laws. His atomic theory states: 1. All matter is composed of atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical; atoms of different elements are different. 3. Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed. 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple wholenumber ratios to form ...
Historical Development of the Periodic Table
... • Argon, first of the noble gases to be discovered.appeared to be totally unreactive • Its identification lead Ramsay to suggest this new gas was part of a new group of elements with zero valency coming after Group VII • Other members of the the new group VIII were subsequently isolated and identifi ...
... • Argon, first of the noble gases to be discovered.appeared to be totally unreactive • Its identification lead Ramsay to suggest this new gas was part of a new group of elements with zero valency coming after Group VII • Other members of the the new group VIII were subsequently isolated and identifi ...
Historical Development of the Periodic Table Periodic Table of the
... increasing atomic mass. • This is known as his Periodic Law. Nevertheless he placed greater importance on properties than on atomic mass values. • He was able to predict, with great accuracy, the properties of the elements that should fit into the gaps he had left. ...
... increasing atomic mass. • This is known as his Periodic Law. Nevertheless he placed greater importance on properties than on atomic mass values. • He was able to predict, with great accuracy, the properties of the elements that should fit into the gaps he had left. ...
sample
... iron, have been known for thousands of years. Others have been discovered much more recently. Helium, often used in balloons, was discovered in 1895. Americium, used in smoke alarms, was discovered only in 1944. Scientists continue to discover new elements today. The atomic number (proton number) of ...
... iron, have been known for thousands of years. Others have been discovered much more recently. Helium, often used in balloons, was discovered in 1895. Americium, used in smoke alarms, was discovered only in 1944. Scientists continue to discover new elements today. The atomic number (proton number) of ...
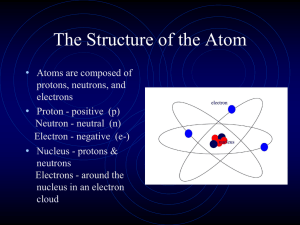
Understanding the Atom - Verona Public Schools
... atom’s mass and positive charge is concentrated in a small area in the center of the atom called the nucleus. • Additional research showed that the positive charge in the nucleus was made of positively charged particles called protons. ...
... atom’s mass and positive charge is concentrated in a small area in the center of the atom called the nucleus. • Additional research showed that the positive charge in the nucleus was made of positively charged particles called protons. ...
atom - geraldinescience
... • Atoms that contain too many or two few neutrons are unstable and lose energy through radioactive decay to form a stable nucleus. • Few exist in nature—most have already decayed to stable forms. ...
... • Atoms that contain too many or two few neutrons are unstable and lose energy through radioactive decay to form a stable nucleus. • Few exist in nature—most have already decayed to stable forms. ...
Isotopes - Ms. Bergman`s Classes at DCIS Montbello
... How many electrons are in the isotope 23Na? Na has 11 protons, so if its neutral it has 11 electrons ...
... How many electrons are in the isotope 23Na? Na has 11 protons, so if its neutral it has 11 electrons ...
ExamView - chap 4 retake 2013.tst
... A. the number of different isotopes of an element B. the number of atoms in 1 g of an element C. the number of neutrons in a nucleus D. the number of protons or electrons in a neutral atom E. the total number of neutrons and protons in a nucleus ____ 18. Which of the following is correct concerning ...
... A. the number of different isotopes of an element B. the number of atoms in 1 g of an element C. the number of neutrons in a nucleus D. the number of protons or electrons in a neutral atom E. the total number of neutrons and protons in a nucleus ____ 18. Which of the following is correct concerning ...
February Homework Packet
... 10. Which statement best describes the nucleus of an aluminum atom? (1) It has a charge of -13 and is surrounded by a total of 10 electrons. (2) It has a charge of -13 and is surrounded by a total of 13 electrons. (3) It has a charge of +13 and is surrounded by a total of 10 electrons. (4) It has a ...
... 10. Which statement best describes the nucleus of an aluminum atom? (1) It has a charge of -13 and is surrounded by a total of 10 electrons. (2) It has a charge of -13 and is surrounded by a total of 13 electrons. (3) It has a charge of +13 and is surrounded by a total of 10 electrons. (4) It has a ...
ISOTOPIC NOTATION isotopes are atoms with the same number of
... a) 53 neutrons b) 53 protons C) 26 neutrons & 27 protons d) 26 protons & 27 neutrons _______2. The mass of one atom of an isotope is 9.746 x 10-23 g. One atomic mass unit has the mass of 1.6606 x 10-24 g. The atomic mass of this isotope is a) 5.870 amu b) 16.18 amu c) 58.69 amu d) 1.627 amu ...
... a) 53 neutrons b) 53 protons C) 26 neutrons & 27 protons d) 26 protons & 27 neutrons _______2. The mass of one atom of an isotope is 9.746 x 10-23 g. One atomic mass unit has the mass of 1.6606 x 10-24 g. The atomic mass of this isotope is a) 5.870 amu b) 16.18 amu c) 58.69 amu d) 1.627 amu ...
Key - Seattle Central College
... – Lanthanide series: Ce-Lu, also called rare earth metals, make up <0.005% of Earth's crust – Actinide series: Th-Lr, also called transuranium elements, generally all man-made and exist for only very short periods of time before decaying to other elements Periodic Law: ...
... – Lanthanide series: Ce-Lu, also called rare earth metals, make up <0.005% of Earth's crust – Actinide series: Th-Lr, also called transuranium elements, generally all man-made and exist for only very short periods of time before decaying to other elements Periodic Law: ...
Atomic Nature of Matter
... defined an element to be a basic substance that cannot be broken down into any simpler substance after it is isolated from a compound, but can be combined with other elements to form compounds. To date, 105 different elements have been confirmed to exist, and researchers claim to have discovered thr ...
... defined an element to be a basic substance that cannot be broken down into any simpler substance after it is isolated from a compound, but can be combined with other elements to form compounds. To date, 105 different elements have been confirmed to exist, and researchers claim to have discovered thr ...
Atoms and Elements
... • Atoms in a compound are often electrically charged, these are called_______________. Valence Electrons and Ion Charge • The ________________electrons in an atom are called the _____________________. • Metals form ___________by losing their valence electrons to get the same number of electrons as t ...
... • Atoms in a compound are often electrically charged, these are called_______________. Valence Electrons and Ion Charge • The ________________electrons in an atom are called the _____________________. • Metals form ___________by losing their valence electrons to get the same number of electrons as t ...
Chapter 3
... subatomic particles are very small when measured in grams. Atomic masses are expressed on a relative mass scale. One atom is assigned a mass, and all others are measured relative to it. ▶ The basis for the relative atomic mass scale is an atom of carbon that contains 6 protons and 6 neutrons. This c ...
... subatomic particles are very small when measured in grams. Atomic masses are expressed on a relative mass scale. One atom is assigned a mass, and all others are measured relative to it. ▶ The basis for the relative atomic mass scale is an atom of carbon that contains 6 protons and 6 neutrons. This c ...
File
... existence of a then unknown element X with a mass of 68. He also predicted that an oxide of X would have the formula X 2O3. On the modern Periodic Table, what is the group number and period number of element X? 90. Fluorine is a Group 17 element. Fluorine is the most electronegative and reactive of ...
... existence of a then unknown element X with a mass of 68. He also predicted that an oxide of X would have the formula X 2O3. On the modern Periodic Table, what is the group number and period number of element X? 90. Fluorine is a Group 17 element. Fluorine is the most electronegative and reactive of ...
Chapter 3—Time and Geology
... half-life (39): The time in which one-half of an original amount of a radioactive atoms decays to daughter products. Holocene Series (34): A term sometimes used to designate the period of time since the last major episode of glaciation. The term is equivalent to Holocene and ranges from 10,000-12,0 ...
... half-life (39): The time in which one-half of an original amount of a radioactive atoms decays to daughter products. Holocene Series (34): A term sometimes used to designate the period of time since the last major episode of glaciation. The term is equivalent to Holocene and ranges from 10,000-12,0 ...
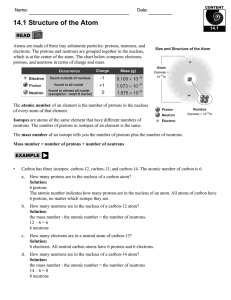
14.1 Structure of the Atom
... You have learned that atoms are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. The electrons occupy energy levels that surround the nucleus in the form of an “electron cloud.” The electrons that are involved in forming chemical bonds are called valence electrons. Atoms can have up to eight valence el ...
... You have learned that atoms are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. The electrons occupy energy levels that surround the nucleus in the form of an “electron cloud.” The electrons that are involved in forming chemical bonds are called valence electrons. Atoms can have up to eight valence el ...
Period:______ Table Number
... 45. A(n) ELEMENT is a pure substance that can not be broken down into any other substance by some physical or chemical method and from which all more complex forms of matter or substances are made when they are combined together in different ways and in different amounts. P. 9, 70, VCR: Atoms and Mo ...
... 45. A(n) ELEMENT is a pure substance that can not be broken down into any other substance by some physical or chemical method and from which all more complex forms of matter or substances are made when they are combined together in different ways and in different amounts. P. 9, 70, VCR: Atoms and Mo ...
02_Lecture SK
... • Energy given off spontaneously from the nucleus of an atom is called nuclear radiation. • Elements that emit radiation are said to be radioactive. • Radiation is a form of energy that we get from natural and human-made sources. • In 1896, Henri Becquerel got an exposure on a photographic plate by ...
... • Energy given off spontaneously from the nucleus of an atom is called nuclear radiation. • Elements that emit radiation are said to be radioactive. • Radiation is a form of energy that we get from natural and human-made sources. • In 1896, Henri Becquerel got an exposure on a photographic plate by ...
Document
... Check for Understanding Aqueous potassium nitrate and a precipitate of barium chromate are formed when aqueous solutions of barium nitrate and potassium chromate are mixed. Ba(NO3)2 (aq) + K2CrO4 (aq) ...
... Check for Understanding Aqueous potassium nitrate and a precipitate of barium chromate are formed when aqueous solutions of barium nitrate and potassium chromate are mixed. Ba(NO3)2 (aq) + K2CrO4 (aq) ...
Neptunium
.png?width=300)
Neptunium is a chemical element with symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactive actinide metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element. Its position in the periodic table just after uranium, named after the planet Uranus, led to it being named after Neptune, the next planet beyond Uranus. A neptunium atom has 93 protons and 93 electrons, of which seven are valence electrons. Neptunium metal is silvery and tarnishes when exposed to air. The element occurs in three allotropic forms and it normally exhibits five oxidation states, ranging from +3 to +7. It is radioactive, pyrophoric, and can accumulate in bones, which makes the handling of neptunium dangerous.Although many false claims of its discovery were made over the years, the element was first synthesized by Edwin McMillan and Philip H. Abelson at the Berkeley Radiation Laboratory in 1940. Since then, most neptunium has been and still is produced by neutron irradiation of uranium in nuclear reactors. The vast majority is generated as a by-product in conventional nuclear power reactors. While neptunium itself has no commercial uses at present, it is widely used as a precursor for the formation of plutonium-238, used in radioisotope thermal generators. Neptunium has also been used in detectors of high-energy neutrons.The most stable isotope of neptunium, neptunium-237, is a by-product of nuclear reactors and plutonium production. It, and the isotope neptunium-239, are also found in trace amounts in uranium ores due to neutron capture reactions and beta decay.