Chapter 04s
... • An atom of any element is electrically neutral; the net charge of an atom is zero. • In an atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons. number of protons = number of electrons • For example, an atom of aluminum has 13 protons and 13 electrons. The net charge is zero. 13 protons ...
... • An atom of any element is electrically neutral; the net charge of an atom is zero. • In an atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons. number of protons = number of electrons • For example, an atom of aluminum has 13 protons and 13 electrons. The net charge is zero. 13 protons ...
Elements of Chemical Structure and Inorganic Nomenclature
... wall may be constructed from a basic unit, the brick. In trying to find this basic unit, they separated matter by all the methods (chemical and physical) available to them until they could not separate it any further. They felt this separation must result in the building block of matter, which they ...
... wall may be constructed from a basic unit, the brick. In trying to find this basic unit, they separated matter by all the methods (chemical and physical) available to them until they could not separate it any further. They felt this separation must result in the building block of matter, which they ...
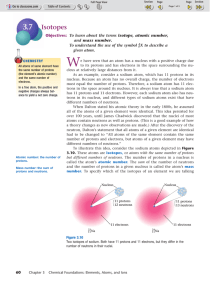
Isotopes
... must equal the number of protons. Therefore, a sodium atom has 11 electrons in the space around its nucleus. It is always true that a sodium atom has 11 protons and 11 electrons. However, each sodium atom also has neutrons in its nucleus, and different types of sodium atoms exist that have different ...
... must equal the number of protons. Therefore, a sodium atom has 11 electrons in the space around its nucleus. It is always true that a sodium atom has 11 protons and 11 electrons. However, each sodium atom also has neutrons in its nucleus, and different types of sodium atoms exist that have different ...
Synthesis of elements by helium and oxygen building blocks Bohr
... These fusion reactions occur only at the centre of the Sun where the high temperature (~107 K) gives the hydrogen and helium isotopes enough kinetic energy to overcome the long-range repulsive Coulomb force and come within the short-range of the attractive strong nuclear force. The processes descri ...
... These fusion reactions occur only at the centre of the Sun where the high temperature (~107 K) gives the hydrogen and helium isotopes enough kinetic energy to overcome the long-range repulsive Coulomb force and come within the short-range of the attractive strong nuclear force. The processes descri ...
The purpose of this packet is to prepare you for the Biology Course
... Atoms are the foundation of chemistry. They are the basis for everything in the Universe. As you know, matter is composed of atoms. Solids are made of densely packed atoms while gases have atoms that are spread out. We're going to cover basics like atomic structure and bonding between atoms. As you ...
... Atoms are the foundation of chemistry. They are the basis for everything in the Universe. As you know, matter is composed of atoms. Solids are made of densely packed atoms while gases have atoms that are spread out. We're going to cover basics like atomic structure and bonding between atoms. As you ...
1.1 - cloudfront.net
... the number of neutrons. The three isotopes of carbon can be referred to as carbon-12 (126 C), carbon-13 (136 C), and carbon-14 (146 C). Naturally occurring samples of most elements are mixtures of isotopes. Carbon has only three natural isotopes, but some heavier elements have many more. Tin has ten ...
... the number of neutrons. The three isotopes of carbon can be referred to as carbon-12 (126 C), carbon-13 (136 C), and carbon-14 (146 C). Naturally occurring samples of most elements are mixtures of isotopes. Carbon has only three natural isotopes, but some heavier elements have many more. Tin has ten ...
04_Lecture Atoms and Elements
... • Protons and neutrons have similar masses (1 amu), while electrons have a much smaller mass. ...
... • Protons and neutrons have similar masses (1 amu), while electrons have a much smaller mass. ...
Ch 3 Sec 3 Highlighted
... atoms contain 47 protons in their nuclei. Because atoms are neutral, we know from the atomic number that all silver atoms must also contain 47 electrons. Most of the elements consist of mixtures of isotopes. Tin (Sn) has 10 stable isotopes, the most of any element. ...
... atoms contain 47 protons in their nuclei. Because atoms are neutral, we know from the atomic number that all silver atoms must also contain 47 electrons. Most of the elements consist of mixtures of isotopes. Tin (Sn) has 10 stable isotopes, the most of any element. ...
04_Lecture Atoms and Elements
... • Protons and neutrons have similar masses (1 amu), while electrons have a much smaller mass. © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • Protons and neutrons have similar masses (1 amu), while electrons have a much smaller mass. © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Chapter 17 notes
... • Scientists found five quarks and hypothesized that a sixth quark existed. However, it took a team of nearly 450 scientists from around the world several years to find the sixth quark. • The tracks of the sixth quark were hard to detect because only about one billionth of a percent of the proton co ...
... • Scientists found five quarks and hypothesized that a sixth quark existed. However, it took a team of nearly 450 scientists from around the world several years to find the sixth quark. • The tracks of the sixth quark were hard to detect because only about one billionth of a percent of the proton co ...
Masses of Atoms - Pelham City Schools
... • Scientists found five quarks and hypothesized that a sixth quark existed. However, it took a team of nearly 450 scientists from around the world several years to find the sixth quark. • The tracks of the sixth quark were hard to detect because only about one billionth of a percent of the proton co ...
... • Scientists found five quarks and hypothesized that a sixth quark existed. However, it took a team of nearly 450 scientists from around the world several years to find the sixth quark. • The tracks of the sixth quark were hard to detect because only about one billionth of a percent of the proton co ...
periodic table - Cloudfront.net
... • Scientists found five quarks and hypothesized that a sixth quark existed. However, it took a team of nearly 450 scientists from around the world several years to find the sixth quark. • The tracks of the sixth quark were hard to detect because only about one billionth of a percent of the proton co ...
... • Scientists found five quarks and hypothesized that a sixth quark existed. However, it took a team of nearly 450 scientists from around the world several years to find the sixth quark. • The tracks of the sixth quark were hard to detect because only about one billionth of a percent of the proton co ...
File
... 20. Element whose atoms lose electrons in chemical reactions to become positive ions. 21. Groups 3-12 on the periodic table. 22. Scientist who performed the gold foil experiment, and concluded that an atom must be composed of mostly empty space with a small, dense, positively-charged nucleus. 23. An ...
... 20. Element whose atoms lose electrons in chemical reactions to become positive ions. 21. Groups 3-12 on the periodic table. 22. Scientist who performed the gold foil experiment, and concluded that an atom must be composed of mostly empty space with a small, dense, positively-charged nucleus. 23. An ...
periodic table
... • The electron cloud is 100,000 times larger than the diameter of the nucleus. • In contrast, each electron in the cloud is much smaller than a single proton. • Because an electron’s mass is small and the electron is moving so quickly around the nucleus, it is impossible to describe its exact locati ...
... • The electron cloud is 100,000 times larger than the diameter of the nucleus. • In contrast, each electron in the cloud is much smaller than a single proton. • Because an electron’s mass is small and the electron is moving so quickly around the nucleus, it is impossible to describe its exact locati ...
4.1 Experiencing Atoms at Tiburon 4.1 Experiencing Atoms
... masses of the isotopes to compute the atomic mass according to the atomic mass definition ...
... masses of the isotopes to compute the atomic mass according to the atomic mass definition ...
Chapter 4 Atoms and Elements
... masses of the isotopes to compute the atomic mass according to the atomic mass definition ...
... masses of the isotopes to compute the atomic mass according to the atomic mass definition ...
19 Chapter
... • Scientists found five quarks and hypothesized that a sixth quark existed. However, it took a team of nearly 450 scientists from around the world several years to find the sixth quark. • The tracks of the sixth quark were hard to detect because only about one billionth of a percent of the proton co ...
... • Scientists found five quarks and hypothesized that a sixth quark existed. However, it took a team of nearly 450 scientists from around the world several years to find the sixth quark. • The tracks of the sixth quark were hard to detect because only about one billionth of a percent of the proton co ...
4 ATOMIC STRUCTURE NOTES __ /__ pts 1 1
... Part B True-False Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. ________ 11. The atomic number of an element is the sum of the protons and electrons in an atom of that element. ________ 12. The atomic number of an atom is the total number of protons in ...
... Part B True-False Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. ________ 11. The atomic number of an element is the sum of the protons and electrons in an atom of that element. ________ 12. The atomic number of an atom is the total number of protons in ...
Chapter 4 Early Atomic Theory
... If two elements form more that one compound, the ratio of the second element that combines with 1 gram of the first element in each is a simple whole number. • In hydrogen peroxide 32.0 g oxygen reacts with 2.0 g hydrogen (H2O2) O:H = 16:1 • Ratio of the masses of oxygen in hydrogen peroxide and wat ...
... If two elements form more that one compound, the ratio of the second element that combines with 1 gram of the first element in each is a simple whole number. • In hydrogen peroxide 32.0 g oxygen reacts with 2.0 g hydrogen (H2O2) O:H = 16:1 • Ratio of the masses of oxygen in hydrogen peroxide and wat ...
File
... matter and how matter changes. In chemistry, a substance is a single kind of matter that is pure. Every form of matter has two kinds of properties - physical and chemical properties. A physical property is observed without changing a substance into another substance. Examples of physical properties ...
... matter and how matter changes. In chemistry, a substance is a single kind of matter that is pure. Every form of matter has two kinds of properties - physical and chemical properties. A physical property is observed without changing a substance into another substance. Examples of physical properties ...
Chapter 1 (Matter and Measurement) Objectives
... Understand that regular, repeatable patterns occur in the periodic table Appreciate that these patterns sometimes have notable exceptions Explain how the periodic law can be used to predict physical and chemical properties of elements Recall and understand that the noble gases have full outer shells ...
... Understand that regular, repeatable patterns occur in the periodic table Appreciate that these patterns sometimes have notable exceptions Explain how the periodic law can be used to predict physical and chemical properties of elements Recall and understand that the noble gases have full outer shells ...
Chapter 17 Resource: Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... isotopes. Terms may be used more than once. six number electrons isotopes electron cloud neutron(s) proton(s) mass quarks six protons The electron has very little mass compared to the 1. ________________ or many 3. ________________ and 4. ________________ it has. The sum of the protons and neutrons ...
... isotopes. Terms may be used more than once. six number electrons isotopes electron cloud neutron(s) proton(s) mass quarks six protons The electron has very little mass compared to the 1. ________________ or many 3. ________________ and 4. ________________ it has. The sum of the protons and neutrons ...
Unit 2 Complete 2016 2017
... 14)______________________ A positively charged particle. 15)______________________ Chemical compounds have the same elements in exactly the same ratios. 16)______________________ This English scientist is credited with discovering the neutron. 17)______________________ It represents the number of pr ...
... 14)______________________ A positively charged particle. 15)______________________ Chemical compounds have the same elements in exactly the same ratios. 16)______________________ This English scientist is credited with discovering the neutron. 17)______________________ It represents the number of pr ...
ATOMIC STRUacad test
... 16. Dalton’s atomic theory helped to explain the law of conservation of mass because it stated that atoms: A. could not combine C. could not be created or destroyed B. all have the same mass D. are invisible 17. The law of multiple proportions was proposed by A. Avogadro B. Rutherford C. Thomson D. ...
... 16. Dalton’s atomic theory helped to explain the law of conservation of mass because it stated that atoms: A. could not combine C. could not be created or destroyed B. all have the same mass D. are invisible 17. The law of multiple proportions was proposed by A. Avogadro B. Rutherford C. Thomson D. ...
Neptunium
.png?width=300)
Neptunium is a chemical element with symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactive actinide metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element. Its position in the periodic table just after uranium, named after the planet Uranus, led to it being named after Neptune, the next planet beyond Uranus. A neptunium atom has 93 protons and 93 electrons, of which seven are valence electrons. Neptunium metal is silvery and tarnishes when exposed to air. The element occurs in three allotropic forms and it normally exhibits five oxidation states, ranging from +3 to +7. It is radioactive, pyrophoric, and can accumulate in bones, which makes the handling of neptunium dangerous.Although many false claims of its discovery were made over the years, the element was first synthesized by Edwin McMillan and Philip H. Abelson at the Berkeley Radiation Laboratory in 1940. Since then, most neptunium has been and still is produced by neutron irradiation of uranium in nuclear reactors. The vast majority is generated as a by-product in conventional nuclear power reactors. While neptunium itself has no commercial uses at present, it is widely used as a precursor for the formation of plutonium-238, used in radioisotope thermal generators. Neptunium has also been used in detectors of high-energy neutrons.The most stable isotope of neptunium, neptunium-237, is a by-product of nuclear reactors and plutonium production. It, and the isotope neptunium-239, are also found in trace amounts in uranium ores due to neutron capture reactions and beta decay.