Atoms and Periodic Table Unit Name
... 25 - These are good conductors of heat and electricity. They also have luster and a high density 27 - Metals are considered this if they can be made into wire. 29 - There are this many known quarks? 30 - The attraction that holds atoms close to each other 32 - Group of nitrogenous organic compounds ...
... 25 - These are good conductors of heat and electricity. They also have luster and a high density 27 - Metals are considered this if they can be made into wire. 29 - There are this many known quarks? 30 - The attraction that holds atoms close to each other 32 - Group of nitrogenous organic compounds ...
gallagher chapter 41
... Imagine grinding the coin into fine dust … each speck still has the properties of Cu If you could continue to grind the dust into smaller and smaller Cu dust particles you would eventually come upon a particle of Cu that could no longer be divided and still have the chemical properties of Cu … thi ...
... Imagine grinding the coin into fine dust … each speck still has the properties of Cu If you could continue to grind the dust into smaller and smaller Cu dust particles you would eventually come upon a particle of Cu that could no longer be divided and still have the chemical properties of Cu … thi ...
Atoms, Isotopes and Relative Atomic Masses
... Isotopes of carbon have the same chemical properties. Explain why. ...
... Isotopes of carbon have the same chemical properties. Explain why. ...
Atomic Structure
... Although protons and neutrons are extremely small, theoretical physicists believe that they are composed of yet smaller subnuclear ...
... Although protons and neutrons are extremely small, theoretical physicists believe that they are composed of yet smaller subnuclear ...
Atomic Structure-PRACTICE TEST
... a. neutral, with the number of protons equaling the number of electrons b. neutral, with the number of protons equaling the number of electrons, which is equal to the number of neutrons c. positively charged, with the number of protons exceeding the number of electrons d. negatively charged, with th ...
... a. neutral, with the number of protons equaling the number of electrons b. neutral, with the number of protons equaling the number of electrons, which is equal to the number of neutrons c. positively charged, with the number of protons exceeding the number of electrons d. negatively charged, with th ...
atom
... • Use atomic mass and percent of each isotope to calculate the contribution of each isotope to the weighted average. Atomic mass 35Cl x % abundance = Atomic mass 37Cl x % abundance = • Sum is atomic mass of Cl is ...
... • Use atomic mass and percent of each isotope to calculate the contribution of each isotope to the weighted average. Atomic mass 35Cl x % abundance = Atomic mass 37Cl x % abundance = • Sum is atomic mass of Cl is ...
Elements and Compounds checklist for web
... Explain why internationally recognised symbols are used for elements Research task: What's in a name? • Outline the contributions of Marie Curie, Albert Einstein, Glenn Seaborg and Niels Bohr to our understa ...
... Explain why internationally recognised symbols are used for elements Research task: What's in a name? • Outline the contributions of Marie Curie, Albert Einstein, Glenn Seaborg and Niels Bohr to our understa ...
Teaching/Chemistry/Chemistry Lesson Plans 04
... of the isotopes as they naturally occur - Periodic Table Objective: Describe the origin of the periodic table; Identify the position of groups, periods, and the transition metals in the periodic table o In the mid-1800’s 70 elements had been discovered o Russian Dmitri Mendeleev was the first person ...
... of the isotopes as they naturally occur - Periodic Table Objective: Describe the origin of the periodic table; Identify the position of groups, periods, and the transition metals in the periodic table o In the mid-1800’s 70 elements had been discovered o Russian Dmitri Mendeleev was the first person ...
Vocabulary Review
... e. positively charged particle that exists in the nucleus of an atom f. tiny bits of matter that are the building blocks of an atom Set Two----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1. _____group of elements a. atoms of the same element ...
... e. positively charged particle that exists in the nucleus of an atom f. tiny bits of matter that are the building blocks of an atom Set Two----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1. _____group of elements a. atoms of the same element ...
Valence Electrons
... If the figure represents a cation, an anion, and a neutral atom from the same period, match the letter to correct term. ...
... If the figure represents a cation, an anion, and a neutral atom from the same period, match the letter to correct term. ...
Lesson Overview
... The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called its mass number. Isotopes are identified by their mass numbers; for example, carbon-12, carbon-13, and carbon-14. The weighted average of the masses of an element’s isotopes, in which the abundance of each isotope in nature ...
... The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called its mass number. Isotopes are identified by their mass numbers; for example, carbon-12, carbon-13, and carbon-14. The weighted average of the masses of an element’s isotopes, in which the abundance of each isotope in nature ...
Redox Reactions Test Review
... 9. Define spectator ion. 10. In the equation Ni + 2 HCl NiCl2 + H2 label the following a. Oxidized: b. Reduced: c. Spectator Ion: 11. In the equation Ca2+ + 2 Li Ca + 2 Li+ label the following a. Oxidized: b. Reduced: ...
... 9. Define spectator ion. 10. In the equation Ni + 2 HCl NiCl2 + H2 label the following a. Oxidized: b. Reduced: c. Spectator Ion: 11. In the equation Ca2+ + 2 Li Ca + 2 Li+ label the following a. Oxidized: b. Reduced: ...
Module 4 Trivia Review
... A Semi Conductor is a fancy name for a Metalloid. Semi means half or partial. So semiconductors (metalloids) have electrical conductivity half way between those of a conductor and an insulator (non-metal). Since they are solid and ductile, these metalloids have been found to be indispensable to the ...
... A Semi Conductor is a fancy name for a Metalloid. Semi means half or partial. So semiconductors (metalloids) have electrical conductivity half way between those of a conductor and an insulator (non-metal). Since they are solid and ductile, these metalloids have been found to be indispensable to the ...
DEFINING THE ATOM - Southgate Schools
... Part B True-False Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. ________ 11. The atomic number of an element is the sum of the protons and electrons in an atom of that element. ________ 12. The atomic number of an atom is the total number of protons in ...
... Part B True-False Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. ________ 11. The atomic number of an element is the sum of the protons and electrons in an atom of that element. ________ 12. The atomic number of an atom is the total number of protons in ...
atomic number
... The element nitrogen (N), shown here is liquid form, has an atomic number of 7. How many protons and electrons are in a ...
... The element nitrogen (N), shown here is liquid form, has an atomic number of 7. How many protons and electrons are in a ...
TEST on Atomic Structure
... a. neutral, with the number of protons equaling the number of electrons b. neutral, with the number of protons equaling the number of electrons, which is equal to the number of neutrons c. positively charged, with the number of protons exceeding the number of electrons d. negatively charged, with th ...
... a. neutral, with the number of protons equaling the number of electrons b. neutral, with the number of protons equaling the number of electrons, which is equal to the number of neutrons c. positively charged, with the number of protons exceeding the number of electrons d. negatively charged, with th ...
GEO143_activity_2
... Number of Protons = Atomic Number (Use the large colored marshmallows for protons) Number of Neutrons = Atomic Mass – Atomic Number (Use the large white marshmallows for neutrons) Number of Electrons = Number of Protons (Use the small colored marshmallows for electrons) ...
... Number of Protons = Atomic Number (Use the large colored marshmallows for protons) Number of Neutrons = Atomic Mass – Atomic Number (Use the large white marshmallows for neutrons) Number of Electrons = Number of Protons (Use the small colored marshmallows for electrons) ...
Chapter 23 (Section 3) Pregnancy, Birth, and
... a. (e.g.) chlorine [__] ALWAYS has 17+ __________, but it could have 18 or 20 ___________ b. chlorine-35 [__] with 17+ ____________ and 18 ____________ = ISOTOPE of CHLORINE chlorine-37 [__] with ___+ ___________ and 20 ____________ = __________ of CHLORINE 5. Atomic MASS NUMBER is TOTAL number of ...
... a. (e.g.) chlorine [__] ALWAYS has 17+ __________, but it could have 18 or 20 ___________ b. chlorine-35 [__] with 17+ ____________ and 18 ____________ = ISOTOPE of CHLORINE chlorine-37 [__] with ___+ ___________ and 20 ____________ = __________ of CHLORINE 5. Atomic MASS NUMBER is TOTAL number of ...
Name: ___________ Class: _____ Date: _______________ FALL
... a. ice melts to water. b. paper rips in half. c. sugar is dissolved in a solution. d. an unexpected color change occurs. ____ 11. Which sign does NOT indicate that a chemical change has occurred? a. color change. c. energy absorbed or released. b. dissolving in a solution. d. gas produced. ____ 12. ...
... a. ice melts to water. b. paper rips in half. c. sugar is dissolved in a solution. d. an unexpected color change occurs. ____ 11. Which sign does NOT indicate that a chemical change has occurred? a. color change. c. energy absorbed or released. b. dissolving in a solution. d. gas produced. ____ 12. ...
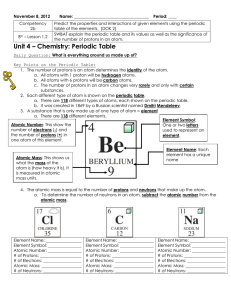
ATOM ATOMIC SYMBOL ATOMIC NUMBER
... (2) 5 pts ‐ Refer to a Periodic Table and the Key below to fill out this table for each element. Turn Lithium atom into an ion and note the information. Turn Beryllium into an isotope and record what you did. ...
... (2) 5 pts ‐ Refer to a Periodic Table and the Key below to fill out this table for each element. Turn Lithium atom into an ion and note the information. Turn Beryllium into an isotope and record what you did. ...
Intro to the Periodic Table
... 7. Find the element with the atomic number of 8. a. What is the element name? _________________________ b. What is the element symbol? _________________________ c. How many protons are in one atom of this element? __________________ d. How many electrons are in one atom of this element? ____________ ...
... 7. Find the element with the atomic number of 8. a. What is the element name? _________________________ b. What is the element symbol? _________________________ c. How many protons are in one atom of this element? __________________ d. How many electrons are in one atom of this element? ____________ ...
chemistry chapter 5 notes
... energy is used to produce steam and subsequently, electricity. *A coolant (usually water) is needed. *The water (or carbon) also acts as a moderator. It slows the neutrons down so that they can be captured by the U-235 fuel. *Control rods made of cadmium are present to absorb excess neutrons to slow ...
... energy is used to produce steam and subsequently, electricity. *A coolant (usually water) is needed. *The water (or carbon) also acts as a moderator. It slows the neutrons down so that they can be captured by the U-235 fuel. *Control rods made of cadmium are present to absorb excess neutrons to slow ...
Chapter 4 – Atoms
... Masses of atoms are so small that we define the atomic mass unit (amu) to scale up the numbers. Carbon-12 was chosen as the reference and given a mass value of exactly 12.000 amu. The mass of all other atoms are scaled relative to mass of Carbon-12. The Atomic Mass of an Element in the Periodic Tabl ...
... Masses of atoms are so small that we define the atomic mass unit (amu) to scale up the numbers. Carbon-12 was chosen as the reference and given a mass value of exactly 12.000 amu. The mass of all other atoms are scaled relative to mass of Carbon-12. The Atomic Mass of an Element in the Periodic Tabl ...
Test Review Chapter 1
... ____ 12. Protons and neutrons strongly attract when they a. are moving fast. c. are at high energies. b. are very close together. d. have opposite charges. ____ 13. Protons within a nucleus are attracted to each other by a. nuclear forces. c. their energy levels. b. opposite charges. d. electron rep ...
... ____ 12. Protons and neutrons strongly attract when they a. are moving fast. c. are at high energies. b. are very close together. d. have opposite charges. ____ 13. Protons within a nucleus are attracted to each other by a. nuclear forces. c. their energy levels. b. opposite charges. d. electron rep ...
Recommended Lesson PlansCOMPREHENSIVE SCIENCE
... 1) Identify characteristics of subatomic particles. 2) Compare particle mass and charge. 3) Define mass number, atomic number, and atomic mass. 4) Present chemical symbols. 5) Explain periodic table shorthand. HSTI Resources: 1) Student Handouts: Neutrons, Protons, Electrons; Atomic Structure; Struc ...
... 1) Identify characteristics of subatomic particles. 2) Compare particle mass and charge. 3) Define mass number, atomic number, and atomic mass. 4) Present chemical symbols. 5) Explain periodic table shorthand. HSTI Resources: 1) Student Handouts: Neutrons, Protons, Electrons; Atomic Structure; Struc ...
Neptunium
.png?width=300)
Neptunium is a chemical element with symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactive actinide metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element. Its position in the periodic table just after uranium, named after the planet Uranus, led to it being named after Neptune, the next planet beyond Uranus. A neptunium atom has 93 protons and 93 electrons, of which seven are valence electrons. Neptunium metal is silvery and tarnishes when exposed to air. The element occurs in three allotropic forms and it normally exhibits five oxidation states, ranging from +3 to +7. It is radioactive, pyrophoric, and can accumulate in bones, which makes the handling of neptunium dangerous.Although many false claims of its discovery were made over the years, the element was first synthesized by Edwin McMillan and Philip H. Abelson at the Berkeley Radiation Laboratory in 1940. Since then, most neptunium has been and still is produced by neutron irradiation of uranium in nuclear reactors. The vast majority is generated as a by-product in conventional nuclear power reactors. While neptunium itself has no commercial uses at present, it is widely used as a precursor for the formation of plutonium-238, used in radioisotope thermal generators. Neptunium has also been used in detectors of high-energy neutrons.The most stable isotope of neptunium, neptunium-237, is a by-product of nuclear reactors and plutonium production. It, and the isotope neptunium-239, are also found in trace amounts in uranium ores due to neutron capture reactions and beta decay.