Introduction to electromagnetism - Pierre
... simple experimental setups, and how they evolve and get generalized following new experimental results and richer mathematical formalism ...
... simple experimental setups, and how they evolve and get generalized following new experimental results and richer mathematical formalism ...
B.3 Time dependent quantum mechanics
... In the second example, consider exciting a wave packet consisting of several successive harmonic oscillator eigenstates. They will tend to add up on the left, and cancel on the right (because odd/even quantum number eigenstates switch ‘lobes’ from positive to negative on the right side). The resulti ...
... In the second example, consider exciting a wave packet consisting of several successive harmonic oscillator eigenstates. They will tend to add up on the left, and cancel on the right (because odd/even quantum number eigenstates switch ‘lobes’ from positive to negative on the right side). The resulti ...
Presentation #3
... “The specification of the position and velocity of all the particles present, at some time, and the specification of all the forces acting on the particles.” Then Newton’s (or any other) classical equations of motion allow us to determine the state of the system at any future time. In quantum theory ...
... “The specification of the position and velocity of all the particles present, at some time, and the specification of all the forces acting on the particles.” Then Newton’s (or any other) classical equations of motion allow us to determine the state of the system at any future time. In quantum theory ...
D NAME: 1. Which of the following phenomena could not be expla
... Prove that, given a pair of normalized but not orthogonal functions ψ1 and ψ2, the function ψ3 = ψ2 – Sψ1 is orthogonal to ψ1 if S is the overlap integral of ψ1 and ψ2. Is ψ3 normalized? (Use the back of the page if necessary). ...
... Prove that, given a pair of normalized but not orthogonal functions ψ1 and ψ2, the function ψ3 = ψ2 – Sψ1 is orthogonal to ψ1 if S is the overlap integral of ψ1 and ψ2. Is ψ3 normalized? (Use the back of the page if necessary). ...
6. Quantum Mechanics II
... Homework due next Wednesday Sept. 30th Read Chapters 4 and 5 of Kane Chapter 4: 2, 3, 5, 13, 20 problems Chapter 5: 3, 4, 5, 7, 8 problems ...
... Homework due next Wednesday Sept. 30th Read Chapters 4 and 5 of Kane Chapter 4: 2, 3, 5, 13, 20 problems Chapter 5: 3, 4, 5, 7, 8 problems ...
The Schrödinger equation
... 1. The TDSE is one of the postulates of quantum mechanics. Though the SE cannot be derived, it has been shown to be consistent with all experiments. 2. SE is first order with respect to time (cf. classical wave equation). 3. SE involves the complex number i and so its solutions are essentially compl ...
... 1. The TDSE is one of the postulates of quantum mechanics. Though the SE cannot be derived, it has been shown to be consistent with all experiments. 2. SE is first order with respect to time (cf. classical wave equation). 3. SE involves the complex number i and so its solutions are essentially compl ...
Physics 43 Ch 42 HW# Key
... Bohr’s analysis of the hydrogen atom to show that the allowed radii of the Earth’s orbit are given by where MS is the mass of the Sun, ME is the mass of the Earth, and n is an integer quantum number. (b) Calculate the numerical value of n. (c) Find the distance between the orbit for quantum number n ...
... Bohr’s analysis of the hydrogen atom to show that the allowed radii of the Earth’s orbit are given by where MS is the mass of the Sun, ME is the mass of the Earth, and n is an integer quantum number. (b) Calculate the numerical value of n. (c) Find the distance between the orbit for quantum number n ...
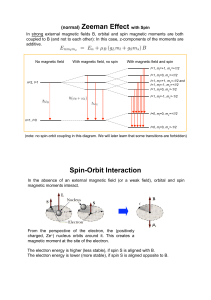
Quantum numbers
... Quantum numbers When solving Schrödinger's equation for the hydrogen model we find wave functions / orbitals. Each orbital is characterized by a series of numbers called Quantum ...
... Quantum numbers When solving Schrödinger's equation for the hydrogen model we find wave functions / orbitals. Each orbital is characterized by a series of numbers called Quantum ...
5.2 The Wave Equation
... function at any time t and position x. Once we have the wave function, our problem is “solved.” In this chapter we will solve Schrödinger's equation for some simple potentials. Let’s get to work… ...
... function at any time t and position x. Once we have the wave function, our problem is “solved.” In this chapter we will solve Schrödinger's equation for some simple potentials. Let’s get to work… ...
MODULE 1
... the quantity in the brackets is recognized as the hamiltonian operator Ĥ The spatial Schrödinger equation above is a special equation. It states that the result of carrying out the (hamiltonian) operation on the wavefunction is the function itself, multiplied by a constant, in this case the energy ...
... the quantity in the brackets is recognized as the hamiltonian operator Ĥ The spatial Schrödinger equation above is a special equation. It states that the result of carrying out the (hamiltonian) operation on the wavefunction is the function itself, multiplied by a constant, in this case the energy ...
Erwin Schrödinger
.jpg?width=300)
Erwin Rudolf Josef Alexander Schrödinger (German: [ˈɛʁviːn ˈʃʁøːdɪŋɐ]; 12 August 1887 – 4 January 1961), sometimes written as Erwin Schrodinger or Erwin Schroedinger, was a Nobel Prize-winning Austrian physicist who developed a number of fundamental results in the field of quantum theory, which formed the basis of wave mechanics: he formulated the wave equation (stationary and time-dependent Schrödinger equation) and revealed the identity of his development of the formalism and matrix mechanics. Schrödinger proposed an original interpretation of the physical meaning of the wave function.In addition, he was the author of many works in various fields of physics: statistical mechanics and thermodynamics, physics of dielectrics, colour theory, electrodynamics, general relativity, and cosmology, and he made several attempts to construct a unified field theory. In his book What Is Life? Schrödinger addressed the problems of genetics, looking at the phenomenon of life from the point of view of physics. He paid great attention to the philosophical aspects of science, ancient and oriental philosophical concepts, ethics, and religion. He also wrote on philosophy and theoretical biology. He is also known for his ""Schrödinger's cat"" thought-experiment.