File - Mr. Cardinal
... they have in society (like cleaning human waste). It is also believed that they, in some way, lived a vile, unacceptable previous life. • escape from caste is not possible until death. Fidelity to dharma (duty) demands that a person submit willingly to the social status, occupation, eating habits, d ...
... they have in society (like cleaning human waste). It is also believed that they, in some way, lived a vile, unacceptable previous life. • escape from caste is not possible until death. Fidelity to dharma (duty) demands that a person submit willingly to the social status, occupation, eating habits, d ...
Chapter 19 section 2 Origins of Hinduism Power Point Notes
... • More than 900 million people in India practice Hinduism today! • According to the traditional Hindu view of reincarnation, a person who has died is reborn in a new physical form. – The type of form depends upon his or her karma, the effects that good or bad actions have on a person’s soul. – Evil ...
... • More than 900 million people in India practice Hinduism today! • According to the traditional Hindu view of reincarnation, a person who has died is reborn in a new physical form. – The type of form depends upon his or her karma, the effects that good or bad actions have on a person’s soul. – Evil ...
Hinduism - WordPress.com
... developmenmt of devotional and poetic literature in Sanskrit and Tantric literature - The modern period (~ 150CE to present) includes the fall of two great empires the Mughal and the British, and the origin of India as an independent nation in 1947. 3. Basic philosophy Hinduism is a complex religion ...
... developmenmt of devotional and poetic literature in Sanskrit and Tantric literature - The modern period (~ 150CE to present) includes the fall of two great empires the Mughal and the British, and the origin of India as an independent nation in 1947. 3. Basic philosophy Hinduism is a complex religion ...
- DakshaLegal
... Vedism, the religion of the ancient Indo-European peoples who settled in India in the last centuries of the 2nd millennium B.C. Because it integrates a large variety of heterogeneous elements, Hinduism constitutes a very complex but largely continuous whole, and since it covers the whole of life, it ...
... Vedism, the religion of the ancient Indo-European peoples who settled in India in the last centuries of the 2nd millennium B.C. Because it integrates a large variety of heterogeneous elements, Hinduism constitutes a very complex but largely continuous whole, and since it covers the whole of life, it ...
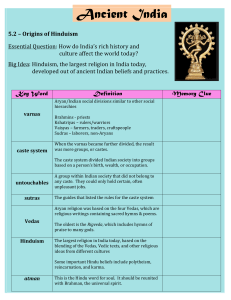
Ancient India 5.2
... Rules became stricter, and each varna was divided into even more castes, or _________________. This caste system divided Indian society into groups based on a person’s ________________, ________________, or ...
... Rules became stricter, and each varna was divided into even more castes, or _________________. This caste system divided Indian society into groups based on a person’s ________________, ________________, or ...
Hinduism
... Hinduism, which is collectively referred to as "Shastras", are essentially a collection of spiritual laws discovered by different saints and sages at different points in its long history. The Two types of sacred writings comprise the Hindu scriptures: "Shruti" (heard) and "Smriti" (memorized). They ...
... Hinduism, which is collectively referred to as "Shastras", are essentially a collection of spiritual laws discovered by different saints and sages at different points in its long history. The Two types of sacred writings comprise the Hindu scriptures: "Shruti" (heard) and "Smriti" (memorized). They ...
Lon Fuller and the Inner Morality of Law
... What I have tried to do is to discern and articulate the natural laws of a particular kind of human undertaking, which I have described as "the enterprise of subjecting human conduct to the governance of rules." These natural laws have nothing to do with any "brooding omnipresence in the skies." Nor ...
... What I have tried to do is to discern and articulate the natural laws of a particular kind of human undertaking, which I have described as "the enterprise of subjecting human conduct to the governance of rules." These natural laws have nothing to do with any "brooding omnipresence in the skies." Nor ...
Intro to Hinduism
... truth, hospitality, respect for family (especially their elders). “What matters most for Hindus is not what people believe and how they express it, but that they believe in an order greater than the human mind can fathom or spirit can dominate.” Renard, p 7 Hindus may be polytheistic, monotheistic, ...
... truth, hospitality, respect for family (especially their elders). “What matters most for Hindus is not what people believe and how they express it, but that they believe in an order greater than the human mind can fathom or spirit can dominate.” Renard, p 7 Hindus may be polytheistic, monotheistic, ...
Document
... divine source • By providing a basis for a moral life in this world, karma and dharma penetrate the earthly spiritual significance ...
... divine source • By providing a basis for a moral life in this world, karma and dharma penetrate the earthly spiritual significance ...
What is Hinduism? Hinduism is quite different from other world
... Hinduism, the soul does not stay in one body. The soul first enters the body of something simple, not human. You might be a bug in your first life! As your soul evolves, it enters more and more complex life forms (here kitty, kitty). Eventually, the soul enters a human body. Then the law of karma ki ...
... Hinduism, the soul does not stay in one body. The soul first enters the body of something simple, not human. You might be a bug in your first life! As your soul evolves, it enters more and more complex life forms (here kitty, kitty). Eventually, the soul enters a human body. Then the law of karma ki ...
hinduismUWO
... karma (literally ``action'') states that no sin ever goes unpunished and no virtue remains unrewarded; if people do not receive punishment or reward in this life, they will in some succeeding life. By their behavior people determine whether their rebirth will be in a higher station or lower; rebirth ...
... karma (literally ``action'') states that no sin ever goes unpunished and no virtue remains unrewarded; if people do not receive punishment or reward in this life, they will in some succeeding life. By their behavior people determine whether their rebirth will be in a higher station or lower; rebirth ...
the nature of Hinduism - Interreligious Insight
... in general. Peoples following the great religions call God by different names. Names are symbols; they are more durable than “graven images”. To understand their significance, we should get to their meaning, namely the truth indicated by the names. To choose a different name for praise and adoration ...
... in general. Peoples following the great religions call God by different names. Names are symbols; they are more durable than “graven images”. To understand their significance, we should get to their meaning, namely the truth indicated by the names. To choose a different name for praise and adoration ...
gcse religion hinduism
... society),Vaishyas (traders and merchants) and Shudras (a variety of jobs, serving the needs of the other three varnas). The word 'caste' refers to the sub-divisions within each varna. One group of Hindus consider themselves as being outside the varna system (‘Dalits’ from Sanskrit, meaning 'suppress ...
... society),Vaishyas (traders and merchants) and Shudras (a variety of jobs, serving the needs of the other three varnas). The word 'caste' refers to the sub-divisions within each varna. One group of Hindus consider themselves as being outside the varna system (‘Dalits’ from Sanskrit, meaning 'suppress ...
2017 Hinduism PowerPoint Lecture
... essence in human is the same as that in an ant, the same as that in a gnat, the same as that in an elephant…indeed the same as that in the whole universe.” ...
... essence in human is the same as that in an ant, the same as that in a gnat, the same as that in an elephant…indeed the same as that in the whole universe.” ...
The Owl and the Pussy-cat - University of Wisconsin Law School
... There is some evidence that a fourth version is emerging but some question whether it is a real change from the third, neo-liberal model. For discussions of this issue and detailed accounts of the history of law and development see generally Trubek and Santos, eds., The New Law and Economic Developm ...
... There is some evidence that a fourth version is emerging but some question whether it is a real change from the third, neo-liberal model. For discussions of this issue and detailed accounts of the history of law and development see generally Trubek and Santos, eds., The New Law and Economic Developm ...
Sacred Stories of Hinduism
... – Duty is laid upon a person at birth and by birth. – Chaos will develop if individuals take it upon themselves to reject the divinely ordained order of things – the fate of the combatants has been decided and Arjuna is merely the mediator. ...
... – Duty is laid upon a person at birth and by birth. – Chaos will develop if individuals take it upon themselves to reject the divinely ordained order of things – the fate of the combatants has been decided and Arjuna is merely the mediator. ...
hinduism - Library Video Company
... What are the Vedas? What role do they play in Hinduism today? What is reincarnation? What were Buddhism and Jainism reacting against within the Hindu faith? What is the caste system? In the period from 500 B.C.E. to 800 C.E., how did the Hindus deal with the challenges of the Buddhists and the Jains ...
... What are the Vedas? What role do they play in Hinduism today? What is reincarnation? What were Buddhism and Jainism reacting against within the Hindu faith? What is the caste system? In the period from 500 B.C.E. to 800 C.E., how did the Hindus deal with the challenges of the Buddhists and the Jains ...
What do Hindus believe - Social Studies Team @ Paul
... Hinduism is practiced by more than 80% of India's population. The word "Hindu" comes from the name of the river Indus, which flows 1800 miles from Tibet through Kashmir and Pakistan to the sea. Hinduism has no founder, it developed out of Brahminism. Hinduism is the oldest religion, it may date to p ...
... Hinduism is practiced by more than 80% of India's population. The word "Hindu" comes from the name of the river Indus, which flows 1800 miles from Tibet through Kashmir and Pakistan to the sea. Hinduism has no founder, it developed out of Brahminism. Hinduism is the oldest religion, it may date to p ...
Chp. 1.2 “Origins of Hinduism” pgs. 22
... Aryan priests were called Brahmins, so their religion is often called Brahmanism Aryan religion based on Veda, which contain sacred hymns and poems. o oldest of the Veda, the Rigveda (c1000BC) includes hymns of praise to many gods Verdic texts – thoughts about the Vedas o One collection describes re ...
... Aryan priests were called Brahmins, so their religion is often called Brahmanism Aryan religion based on Veda, which contain sacred hymns and poems. o oldest of the Veda, the Rigveda (c1000BC) includes hymns of praise to many gods Verdic texts – thoughts about the Vedas o One collection describes re ...
Chapter 15: Learning About World Religions: Hinduism
... they do, and even what they eat. It has inspired great art and literature. A n d it has helped determine the status of people i n Indian society. One of the basic beliefs of Hinduism and some other Indian religions is dharma. Dharma refers to law, duty, and obligation. To follow one's dharma means t ...
... they do, and even what they eat. It has inspired great art and literature. A n d it has helped determine the status of people i n Indian society. One of the basic beliefs of Hinduism and some other Indian religions is dharma. Dharma refers to law, duty, and obligation. To follow one's dharma means t ...
Ch_15Hinduism - Chaparral Middle School
... Many holidays, such as Divali, honor various deities ...
... Many holidays, such as Divali, honor various deities ...
Introduction to Hinduism
... Every action produces a Justified effect based on its moral worthiness. Karma determines all the particular circumstances and Situations of one’s life. ...
... Every action produces a Justified effect based on its moral worthiness. Karma determines all the particular circumstances and Situations of one’s life. ...
Hinduism: World Civilizations Jefferson High School: 2012
... the Upanishads, they have become a more “personal” document – they are used by some Hindu believers. The Upanishads (to end/conclude): (800 B.C. – 300 B.C.) The equivalent to the Christian New Testament, are a series of stories called the Upanishads. These stories expound the idea that behind the ma ...
... the Upanishads, they have become a more “personal” document – they are used by some Hindu believers. The Upanishads (to end/conclude): (800 B.C. – 300 B.C.) The equivalent to the Christian New Testament, are a series of stories called the Upanishads. These stories expound the idea that behind the ma ...
Learning About World Religions: Hinduism
... to generation, before India had a written form of Sanskrit. Centuries later, this understanding spread to other parts of Asia, particularly Southeast Asia, where its influence is still present today in countries such as Indonesia, Cambodia, Thailand, and Vietnam. Vedic culture includes rituals and s ...
... to generation, before India had a written form of Sanskrit. Centuries later, this understanding spread to other parts of Asia, particularly Southeast Asia, where its influence is still present today in countries such as Indonesia, Cambodia, Thailand, and Vietnam. Vedic culture includes rituals and s ...