Nagasaki, Aug. 9, 1945
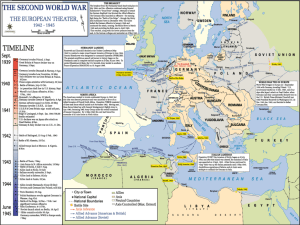
... Tokyo -- would be an “unsinkable aircraft carrier” from which to launch attacks B52s made 2,500 emergency landings here during Tokyo firebombing ...
... Tokyo -- would be an “unsinkable aircraft carrier” from which to launch attacks B52s made 2,500 emergency landings here during Tokyo firebombing ...
World War II — A Selected Chronology
... Mussolini is executed by Italian patriots. Terms for unconditional surrender of Nazis in Italy and part of Austria are signed. U.S.7 th Army takes Munich. Hitler is reported dead; Admiral Doenitz is successor. Soviet troops take Berlin. British recapture Rangoon, Burma. German Army Group G surrender ...
... Mussolini is executed by Italian patriots. Terms for unconditional surrender of Nazis in Italy and part of Austria are signed. U.S.7 th Army takes Munich. Hitler is reported dead; Admiral Doenitz is successor. Soviet troops take Berlin. British recapture Rangoon, Burma. German Army Group G surrender ...
January 1995
... surrender documents. Since he had already done it, Susloparov was recalled home for “strict punishment” which in Stalin’s Soviet Union meant execution. The Soviets made it very clear that a Berlin signing, and only a Berlin signing, would be valid in their eyes. The Soviets had many objections.They ...
... surrender documents. Since he had already done it, Susloparov was recalled home for “strict punishment” which in Stalin’s Soviet Union meant execution. The Soviets made it very clear that a Berlin signing, and only a Berlin signing, would be valid in their eyes. The Soviets had many objections.They ...
WWII
... Should we have switched MacArthur and Patton and let Patton loose given the Japanese atrocities against our troops and civilians? We may have shortened the Pacific war, dropped the bomb earlier but would Japan today be the same? Would MacArthur have more influence over his old aide Eisenhower and be ...
... Should we have switched MacArthur and Patton and let Patton loose given the Japanese atrocities against our troops and civilians? We may have shortened the Pacific war, dropped the bomb earlier but would Japan today be the same? Would MacArthur have more influence over his old aide Eisenhower and be ...
World War II
... “MORE than fourteen years have passed since the unhappy day when the German people, blinded by promises from foes at home and abroad, lost touch with honor and freedom, thereby losing all. Since that day of treachery, the Almighty has withheld his blessing from our people.” Adolf Hitler, February 1, ...
... “MORE than fourteen years have passed since the unhappy day when the German people, blinded by promises from foes at home and abroad, lost touch with honor and freedom, thereby losing all. Since that day of treachery, the Almighty has withheld his blessing from our people.” Adolf Hitler, February 1, ...
CHECK FOR UNDERSTANDING – End of War in the Pacific
... four aircraft carriers, along with more than 230 airplanes and more than 2,000 men. The victory was a major boost to the morale of American forces and allowed the US to shift from defensive position to go on the offense using the island-hopping strategy. Japan’s losses at Midway forced it to shift i ...
... four aircraft carriers, along with more than 230 airplanes and more than 2,000 men. The victory was a major boost to the morale of American forces and allowed the US to shift from defensive position to go on the offense using the island-hopping strategy. Japan’s losses at Midway forced it to shift i ...
WWII outline long - Boone County Schools
... Union and Britain. The politicians' idea was that if Germany was knocked out first (before the Pacific engagements began), then Allied forces could be concentrated on Japan. The Allies Trade Space for Time America's task of WWII was far more complex and hard than during WWI. It had to feed, clothe, ...
... Union and Britain. The politicians' idea was that if Germany was knocked out first (before the Pacific engagements began), then Allied forces could be concentrated on Japan. The Allies Trade Space for Time America's task of WWII was far more complex and hard than during WWI. It had to feed, clothe, ...
Bell Quiz: Pages
... Japan was led by Prime Minister Hideki Tojo and Emperor Hirohito. Goal was to unite East Asia under Japanese rule. U.S. protested Japanese aggression by cutting off trade (oil embargo). December 7, 1941 Japan attacks Pearl Harbor, the largest U.S. naval base in the Pacific. In less than 2 hours, the ...
... Japan was led by Prime Minister Hideki Tojo and Emperor Hirohito. Goal was to unite East Asia under Japanese rule. U.S. protested Japanese aggression by cutting off trade (oil embargo). December 7, 1941 Japan attacks Pearl Harbor, the largest U.S. naval base in the Pacific. In less than 2 hours, the ...
chapt er 17 the unit ed sta tes in ww ii
... Government program that allowed returning WWII vets to go to school paid for by the government ...
... Government program that allowed returning WWII vets to go to school paid for by the government ...
Battle of the Bulge
... Truman now had to decide how to end the war – should the US mount an invasion of Japan, which would cost an estimated 1 million American lives or should it use the new atomic bomb, which would kill an unknown number of Japanese civilians and whose after-effects were still unknown? ...
... Truman now had to decide how to end the war – should the US mount an invasion of Japan, which would cost an estimated 1 million American lives or should it use the new atomic bomb, which would kill an unknown number of Japanese civilians and whose after-effects were still unknown? ...
World War II The Road to Victory in Europe
... concentrate on Europe before trying to win the war in the Pacific. • They want unconditional surrender. ...
... concentrate on Europe before trying to win the war in the Pacific. • They want unconditional surrender. ...
World War II Quiz 3 - Social Studies With A Smile
... 12. How did discrimination affect life on the home front in World War II? a. Japanese immigrants and native-born Americans of Japanese descent were rounded up and held in internment camps. b. Job discrimination against African Americans was ended in industries that had government contracts to produc ...
... 12. How did discrimination affect life on the home front in World War II? a. Japanese immigrants and native-born Americans of Japanese descent were rounded up and held in internment camps. b. Job discrimination against African Americans was ended in industries that had government contracts to produc ...
unit 8 pacific theater cornell notes
... 23. August 9, 1945: Atomic bomb is dropped on ________________________ 24. Japan surrenders to Allied Forces on the USS __________________after the second bomb was dropped on Nagasaki: August 14th–______________Day The Occupation of Japan 25. Japan was occupied by U.S. forces under the command of Ge ...
... 23. August 9, 1945: Atomic bomb is dropped on ________________________ 24. Japan surrenders to Allied Forces on the USS __________________after the second bomb was dropped on Nagasaki: August 14th–______________Day The Occupation of Japan 25. Japan was occupied by U.S. forces under the command of Ge ...
WWII the Tide Turns
... • 176,000 allied troops landed on Omaha, Utah, Gold, Sword and Juno beaches marking the largest amphibious assault in history ...
... • 176,000 allied troops landed on Omaha, Utah, Gold, Sword and Juno beaches marking the largest amphibious assault in history ...
CHC2P1 Review Package
... When did the Americans join WWII? What happened that made them join? The Japanese Internment in Canada was made possible by the __________________ Act. The Japanese-Canadians had their __________________________ taken away, were fingerprinted and _____________________ and eventually were put into in ...
... When did the Americans join WWII? What happened that made them join? The Japanese Internment in Canada was made possible by the __________________ Act. The Japanese-Canadians had their __________________________ taken away, were fingerprinted and _____________________ and eventually were put into in ...
War in the Pacific
... an atomic bomb on the city of Hiroshima. The bomb destroyed 4 square miles and instantly killed more than 70,000 people. In the months to follow, many more Japanese died from radiation. After Hiroshima, Truman warned the Japanese again. He said that if they did not surrender they could expect a “Rai ...
... an atomic bomb on the city of Hiroshima. The bomb destroyed 4 square miles and instantly killed more than 70,000 people. In the months to follow, many more Japanese died from radiation. After Hiroshima, Truman warned the Japanese again. He said that if they did not surrender they could expect a “Rai ...
7 Future American Presidents Served in World War II
... US provides upwards of $12 billion in aid to rebuild Western Europe’s infrastructure and industrial base. ...
... US provides upwards of $12 billion in aid to rebuild Western Europe’s infrastructure and industrial base. ...
Victory in Europe and the Pacific
... The Americans gradually moved north and were able to blockade Japan Bombers pounded Japanese cities and industries At the same time, the British pushed Japanese forces back into the jungles of Burma and Malaya ...
... The Americans gradually moved north and were able to blockade Japan Bombers pounded Japanese cities and industries At the same time, the British pushed Japanese forces back into the jungles of Burma and Malaya ...
Chapter 16
... Philippines. Although the United States Army and Filipino defense forces had battled to keep the Japanese out of the island chain, they had not been successful. Thousands of Allied civilian men, women, and children were being held in prison camps throughout the islands, and American and Filipino sol ...
... Philippines. Although the United States Army and Filipino defense forces had battled to keep the Japanese out of the island chain, they had not been successful. Thousands of Allied civilian men, women, and children were being held in prison camps throughout the islands, and American and Filipino sol ...
The End of WWII in Europe and the Aftermath
... The Nazis killed over 14 million people in their labor and death camps. They murdered six million Jews. London, Berlin, Dresden, and Tokyo were heavily bombed with high civilian casualties. Millions of Chinese civilians were murdered by the Japanese. The Atomic bomb killed over 250,000 civilians in ...
... The Nazis killed over 14 million people in their labor and death camps. They murdered six million Jews. London, Berlin, Dresden, and Tokyo were heavily bombed with high civilian casualties. Millions of Chinese civilians were murdered by the Japanese. The Atomic bomb killed over 250,000 civilians in ...
Winning World War II
... targets, but it did give the American people something to celebrate and worried Japan’s leaders. ...
... targets, but it did give the American people something to celebrate and worried Japan’s leaders. ...