World War II Class Notes
... Operation Barbarossa German invasion of the Soviet Union violating Nazi- Soviet Pact -Stalin unprepared for surprise invasion and retreats following a scorched earth policy. German invasion stalled at Leningrad. Millions die in Russian winter including German troops. a. Battle of Stalingrad. Nazi lo ...
... Operation Barbarossa German invasion of the Soviet Union violating Nazi- Soviet Pact -Stalin unprepared for surprise invasion and retreats following a scorched earth policy. German invasion stalled at Leningrad. Millions die in Russian winter including German troops. a. Battle of Stalingrad. Nazi lo ...
Chapter 12 Notes America and World War II Section 1: The Road to
... President Roosevelt established the Fair Employment Practices Commission to combat discrimination in industry. ...
... President Roosevelt established the Fair Employment Practices Commission to combat discrimination in industry. ...
World War II
... • Dr. Kurt von Schuschnigg • Replaced by Dr. Arthur Seyss-Inquart • Austria taken without a shot • Schuschnigg arrested, taken to camps ...
... • Dr. Kurt von Schuschnigg • Replaced by Dr. Arthur Seyss-Inquart • Austria taken without a shot • Schuschnigg arrested, taken to camps ...
world war ii test
... WORLD WAR II TEST: CHAPTERS 19 AND 20 STUDY GUIDE 1. causes of rise in dictatorships after WWI 2. who did Hitler blame for Germany’s WWI defeat? 3. Nye committee decision 4. Axis Powers countries 5. appeasement/its failure 6. Nuremburg Laws 7. SS St. Louis 8. Nazis’ ‘final solution’ 9. ‘Four Freedom ...
... WORLD WAR II TEST: CHAPTERS 19 AND 20 STUDY GUIDE 1. causes of rise in dictatorships after WWI 2. who did Hitler blame for Germany’s WWI defeat? 3. Nye committee decision 4. Axis Powers countries 5. appeasement/its failure 6. Nuremburg Laws 7. SS St. Louis 8. Nazis’ ‘final solution’ 9. ‘Four Freedom ...
Fascism - sunysuffolk.edu
... a. british army trapped, Hitler uses airforce not army b. British escape on huge fleet (300,000 troops) = keeps britain in the war. = air power can not replace soldiers in winning. ...
... a. british army trapped, Hitler uses airforce not army b. British escape on huge fleet (300,000 troops) = keeps britain in the war. = air power can not replace soldiers in winning. ...
UNIT 6 WORLD WAR II AND SOCIAL 50`S Chapter 14 Notes – The
... a. Only Britain, France and U.S. had major input b. Germany was blamed c. Russia, Italy, and Japan (All Allies) felt they were slighted 2. Rise of Totalitarianism a. Theory of gov’t in which a single party or leader controls the economic, social, and cultural lives of its people B. Repression in Sov ...
... a. Only Britain, France and U.S. had major input b. Germany was blamed c. Russia, Italy, and Japan (All Allies) felt they were slighted 2. Rise of Totalitarianism a. Theory of gov’t in which a single party or leader controls the economic, social, and cultural lives of its people B. Repression in Sov ...
World War II - Supplemental 1 - Multi-flow map
... World War I Treaty of Versailles (reparations, war guilt, disarmament) “Dolchstosslegende” (stab–in–back myth, November criminals) Great Depression Failures of the League of Nations (Manchuria, Italy) Rise of Totalitarian Leaders (Hitler, Mussolini, Stalin) ...
... World War I Treaty of Versailles (reparations, war guilt, disarmament) “Dolchstosslegende” (stab–in–back myth, November criminals) Great Depression Failures of the League of Nations (Manchuria, Italy) Rise of Totalitarian Leaders (Hitler, Mussolini, Stalin) ...
WWII Powerpoint - Parkway C-2
... Timeline of German Aggression • 1921 - takes control of the National Socialist Party (a.k.a. the Nazis) • 1923 - attempts Putsch (seizure of government) and fails; lands in jail, where he writes Mein Kampf • 1933 - becomes Germany’s Chancellor – Begins passing restrictive laws for Jews – Germany le ...
... Timeline of German Aggression • 1921 - takes control of the National Socialist Party (a.k.a. the Nazis) • 1923 - attempts Putsch (seizure of government) and fails; lands in jail, where he writes Mein Kampf • 1933 - becomes Germany’s Chancellor – Begins passing restrictive laws for Jews – Germany le ...
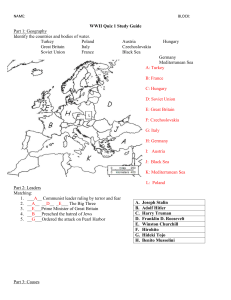
NAME: BLOCK: WWII Quiz 1 Study Guide Part 1: Geography Identify
... They were also resentful towards the Allied powers. Japan felt excluded from the negotiations, and wanted to prove their power. How did post WWI Europe set the stage for WWII? Explain two historical facts learned in class to support your ...
... They were also resentful towards the Allied powers. Japan felt excluded from the negotiations, and wanted to prove their power. How did post WWI Europe set the stage for WWII? Explain two historical facts learned in class to support your ...
chapter outline
... as a man of peace, Hitler claimed that the Treaty of Versailles was unfair; and when he stated that Germany would rearm and when German troops occupied the demilitarized Rhineland, there was little reaction by Britain and France. Criticized for invading Ethiopia, Mussolini joined Hitler in forming t ...
... as a man of peace, Hitler claimed that the Treaty of Versailles was unfair; and when he stated that Germany would rearm and when German troops occupied the demilitarized Rhineland, there was little reaction by Britain and France. Criticized for invading Ethiopia, Mussolini joined Hitler in forming t ...
Hitler and the Rise of Germany
... 1920s- Good times for most countries (U.S.A). 1930s- Worldwide economic depression. Result- Many people turned to Fascism. Fascism- political system that stresses nationalism, dictatorship, and military/economic strength of the state above individual rights. Japan-Run by warlike generals who want la ...
... 1920s- Good times for most countries (U.S.A). 1930s- Worldwide economic depression. Result- Many people turned to Fascism. Fascism- political system that stresses nationalism, dictatorship, and military/economic strength of the state above individual rights. Japan-Run by warlike generals who want la ...
WW2 Vocab answer
... Code name for the re-taking of mainland Europe (d-day and onward into France) by the Allied troops Secretive term used by the Germans about their decision of how to eliminate the Jewish population from Europe. Largest tank battle in history. Although both sides suffered huge losses, it was a victory ...
... Code name for the re-taking of mainland Europe (d-day and onward into France) by the Allied troops Secretive term used by the Germans about their decision of how to eliminate the Jewish population from Europe. Largest tank battle in history. Although both sides suffered huge losses, it was a victory ...
World War II
... World wide Depression Germany’s high World War I debt (remember Treaty of Versailles and reparations) High inflation – the value of money goes down over time. Massive unemployment ...
... World wide Depression Germany’s high World War I debt (remember Treaty of Versailles and reparations) High inflation – the value of money goes down over time. Massive unemployment ...
Chapter 16
... establishment of a communist state, officially called the Soviet Union. • Joseph Stalin took control of the country after the death of Lenin. • Stalin abolished private owned farms and set up collectives, or large government owned farms. • Stalin established a series of “five year plans” to direct i ...
... establishment of a communist state, officially called the Soviet Union. • Joseph Stalin took control of the country after the death of Lenin. • Stalin abolished private owned farms and set up collectives, or large government owned farms. • Stalin established a series of “five year plans” to direct i ...
Why Italy?
... -1934 he became the Fuhrer of Germany (only 15% of the population claimed to be Nazi )and began to ignore the treaty of Versailles – began to rebuild his military – 1934 he supported the Franco forces in the Spanish Civil War --- this was a testing ground or the Germany tactics the BLITZ 1936 re too ...
... -1934 he became the Fuhrer of Germany (only 15% of the population claimed to be Nazi )and began to ignore the treaty of Versailles – began to rebuild his military – 1934 he supported the Franco forces in the Spanish Civil War --- this was a testing ground or the Germany tactics the BLITZ 1936 re too ...
World War II Notes
... Poland by Germany on September 1st, 1939. • The Germans used a method known as blitzkrieg or lightning war when invading Poland. • As a result, France and Great Britain declared war on Germany. • The Soviet Union also invaded Poland and the Baltic nations of Latvia, Lithuania, Estonia. • Germany inv ...
... Poland by Germany on September 1st, 1939. • The Germans used a method known as blitzkrieg or lightning war when invading Poland. • As a result, France and Great Britain declared war on Germany. • The Soviet Union also invaded Poland and the Baltic nations of Latvia, Lithuania, Estonia. • Germany inv ...
Chapter 34 PowerPoint
... United States Congress in the 1930s, in response to the growing turmoil in Europe and Asia that eventually led to World War II. They were spurred by the growth in isolationism and non-interventionism in the US following its costly involvement in World War I, and sought to ensure that the US would no ...
... United States Congress in the 1930s, in response to the growing turmoil in Europe and Asia that eventually led to World War II. They were spurred by the growth in isolationism and non-interventionism in the US following its costly involvement in World War I, and sought to ensure that the US would no ...
Onset of World War II
... lost in World War I. • Stalin signs nonaggression pact in August, 1939. – Hitler promised Stalin territory, including half of Poland. ...
... lost in World War I. • Stalin signs nonaggression pact in August, 1939. – Hitler promised Stalin territory, including half of Poland. ...
Class Rules - Denton ISD
... 1935-1936 Germany remilitarizes Hitler announced the formation of a German air force and compulsory military service. In 1936, he sent troops into the Rhineland, a German region on the border with France. These actions all challenged the Treaty of Versailles. 1935 Italy invades Ethiopia The Italian ...
... 1935-1936 Germany remilitarizes Hitler announced the formation of a German air force and compulsory military service. In 1936, he sent troops into the Rhineland, a German region on the border with France. These actions all challenged the Treaty of Versailles. 1935 Italy invades Ethiopia The Italian ...
Lesson Plan 1 PowerPoint
... Appeasement means giving in to someone provided their demands are seen as reasonable In the 1930’s, politicians in both Britain and France felt that Germany was being treated unfairly by the Treaty of Versailles German was given permission to re-arm the Rhineland with German troops In 1937, at the h ...
... Appeasement means giving in to someone provided their demands are seen as reasonable In the 1930’s, politicians in both Britain and France felt that Germany was being treated unfairly by the Treaty of Versailles German was given permission to re-arm the Rhineland with German troops In 1937, at the h ...
The Global conflict Axis Advances
... on Germany,” predicted a confident French general on the eve of WWII. He could not have been more wrong. WWII, the costliest war in history, lasted six years form 1939-1945. Axis powers Included Germany, Italy, and Japan, against the Allied powers, which eventually included Britain, France, the Sovi ...
... on Germany,” predicted a confident French general on the eve of WWII. He could not have been more wrong. WWII, the costliest war in history, lasted six years form 1939-1945. Axis powers Included Germany, Italy, and Japan, against the Allied powers, which eventually included Britain, France, the Sovi ...
operation sealion
... • Casablanca Conference- January, 1943 FDR and Churchill announced that they would only accept unconditional surrender from their enemies • May, 1943- Allies controlled N. Africa ...
... • Casablanca Conference- January, 1943 FDR and Churchill announced that they would only accept unconditional surrender from their enemies • May, 1943- Allies controlled N. Africa ...
World War II
... Poland defeated in about a month; partition occurred when USSR attacked from east ...
... Poland defeated in about a month; partition occurred when USSR attacked from east ...
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany or the Third Reich (German: Drittes Reich) are common English names for the period of history in Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a dictatorship under the control of Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP). Under Hitler's rule, Germany was transformed into a fascist totalitarian state which controlled nearly all aspects of life. The official name of the state was the Deutsches Reich (German Reich) from 1933 to 1943 and Großdeutsches Reich (Greater German Reich) from 1943 to 1945. Nazi Germany ceased to exist after the Allied Forces defeated Germany in May 1945, ending World War II in Europe.Hitler was appointed Chancellor of Germany by the President of the Weimar Republic Paul von Hindenburg on 30 January 1933. The Nazi Party then began to eliminate all political opposition and consolidate its power. Hindenburg died on 2 August 1934, and Hitler became dictator of Germany by merging the powers and offices of the Chancellery and Presidency. A national referendum held 19 August 1934 confirmed Hitler as sole Führer (leader) of Germany. All power was centralised in Hitler's hands, and his word became above all laws. The government was not a coordinated, co-operating body, but a collection of factions struggling for power and Hitler's favour. In the midst of the Great Depression, the Nazis restored economic stability and ended mass unemployment using heavy military spending and a mixed economy. Extensive public works were undertaken, including the construction of Autobahns (high speed highways). The return to economic stability boosted the regime's popularity.Racism, especially antisemitism, was a central feature of the regime. The Germanic peoples (the Nordic race) were considered the purest of the Aryan race, and were therefore the master race. Millions of Jews and others deemed undesirable were persecuted and murdered in the Holocaust. Opposition to Hitler's rule was ruthlessly suppressed. Members of the liberal, socialist, and communist opposition were killed, imprisoned, or exiled. The Christian churches were also oppressed, with many leaders imprisoned. Education focused on racial biology, population policy, and fitness for military service. Career and educational opportunities for women were curtailed. Recreation and tourism were organised via the Strength Through Joy program, and the 1936 Summer Olympics showcased the Third Reich on the international stage. Propaganda minister Joseph Goebbels made effective use of film, mass rallies, and Hitler's hypnotising oratory to control public opinion. The government controlled artistic expression, promoting specific art forms and banning or discouraging others.Nazi Germany made increasingly aggressive territorial demands, threatening war if they were not met. It seized Austria and Czechoslovakia in 1938 and 1939. Hitler made a pact with Joseph Stalin and invaded Poland in September 1939, launching World War II in Europe. In alliance with Italy and smaller Axis powers, Germany conquered most of Europe by 1940 and threatened Great Britain. Reichskommissariats took control of conquered areas, and a German administration was established in what was left of Poland. Jews and others deemed undesirable were imprisoned and murdered in Nazi concentration camps and extermination camps. The implementation of the regime's racial policies culminated in the mass murder of Jews and other minorities in the Holocaust. Following the German invasion of the Soviet Union in 1941, the tide turned against the Nazis, who suffered major military defeats in 1943. Large-scale aerial bombing of Germany escalated in 1944, and the Nazis retreated from Eastern and Southern Europe. Following the Allied invasion of France, Germany was conquered by the Soviets from the east and the other Allied powers from the west and surrendered within a year. Hitler's refusal to admit defeat led to massive destruction of German infrastructure and additional war-related deaths in the closing months of the war. The victorious Allies initiated a policy of denazification and put many of the surviving Nazi leadership on trial for war crimes at the Nuremberg trials.