World War I to Cold War
... – Working Class: industrial workers – Lower Class: small farmers, landless farmers ...
... – Working Class: industrial workers – Lower Class: small farmers, landless farmers ...
PowerPoint - (www.ramsey.k12.nj.us).
... The Allied and Associated Governments affirm and Germany accepts the responsibility of Germany and her allies for causing all the loss and damage to which the Allied and Associated Governments and their nationals have been subjected as a consequence of the war imposed upon them by the aggression of ...
... The Allied and Associated Governments affirm and Germany accepts the responsibility of Germany and her allies for causing all the loss and damage to which the Allied and Associated Governments and their nationals have been subjected as a consequence of the war imposed upon them by the aggression of ...
Outline
... - Germans being fascist to _______________________ and everybody (blue eyes, blonde hair, and German) . fighting over _____________. . Social - ________________________ put themselves on top - Blue eyes, blonde hair . Interaction - total war . Cultural - ______________________ Causes of World War II ...
... - Germans being fascist to _______________________ and everybody (blue eyes, blonde hair, and German) . fighting over _____________. . Social - ________________________ put themselves on top - Blue eyes, blonde hair . Interaction - total war . Cultural - ______________________ Causes of World War II ...
14-2 Part 1 - Cloudfront.net
... idea• of If waryou from neighboring countries was constantly harpedlast upon. He emphasized basketwhich now. headedthe in directions could only carry ruin to it and creat a situation “dangerous to world peace.” He Germany Soviet Union said that we must recognize that while Germany at the time wanted ...
... idea• of If waryou from neighboring countries was constantly harpedlast upon. He emphasized basketwhich now. headedthe in directions could only carry ruin to it and creat a situation “dangerous to world peace.” He Germany Soviet Union said that we must recognize that while Germany at the time wanted ...
Slide 1
... War II ended into two separate parts: West Germany and East Germany. After the war, the western part of Germany was occupied and controlled by U.S., British, and French forces. Eventually, West Germany was set up as an independent, democratic nation with its own government. The eastern part of Germa ...
... War II ended into two separate parts: West Germany and East Germany. After the war, the western part of Germany was occupied and controlled by U.S., British, and French forces. Eventually, West Germany was set up as an independent, democratic nation with its own government. The eastern part of Germa ...
Chapter 23 Notes
... • France thought the treaty was too easy on Germany. • Italy had been on the winning side of the war but was ignored during the peace talks. They had hoped to gain territory. 3. Germany was most affected by the Treaty of Versailles. • Germany gave up control of some of its land, including some impor ...
... • France thought the treaty was too easy on Germany. • Italy had been on the winning side of the war but was ignored during the peace talks. They had hoped to gain territory. 3. Germany was most affected by the Treaty of Versailles. • Germany gave up control of some of its land, including some impor ...
World War II Notes
... he begins rearming Germany and moving troops into areas that he wants breaking the Treaty of Versailles • Lebensraum- “living space” – Austria - annexed peacefully in 1938 – Sudetenland – territory in Czechoslovakia • Given to Germany by Great Britain and France (Appeasement) • He basically invades ...
... he begins rearming Germany and moving troops into areas that he wants breaking the Treaty of Versailles • Lebensraum- “living space” – Austria - annexed peacefully in 1938 – Sudetenland – territory in Czechoslovakia • Given to Germany by Great Britain and France (Appeasement) • He basically invades ...
Tucker
... 8.3. Again breaking the Treaty of Versailles, Hitler continued aggressive movements to gain control of countries in Europe. Again, Britain, France, and the world continued the policy of appeasement and did nothing. 8.4. Hitler made more demands to increase the Third Reich (German Empire) and looked ...
... 8.3. Again breaking the Treaty of Versailles, Hitler continued aggressive movements to gain control of countries in Europe. Again, Britain, France, and the world continued the policy of appeasement and did nothing. 8.4. Hitler made more demands to increase the Third Reich (German Empire) and looked ...
Ch. 24.2 War in Europe Section Objectives: 1. Explain Hitler`s
... The danger of a twofront war was eliminated B. Blitzkrieg in Poland What was the Luftwaffe? The German air force What new tactics did Germany use in attacking Poland? Blitzkrieg, bombing military bases, airfields, railroads, and cities What was a blitzkrieg? A lightning war, attack your enemy as ...
... The danger of a twofront war was eliminated B. Blitzkrieg in Poland What was the Luftwaffe? The German air force What new tactics did Germany use in attacking Poland? Blitzkrieg, bombing military bases, airfields, railroads, and cities What was a blitzkrieg? A lightning war, attack your enemy as ...
Mini-Quiz/ Exam Prep Unit 2 (1900-1945), Chapters 25
... Which of these describes why the Big Three Allied leaders met at Yalta in February 1945? (Check all that apply) _____ To convince the Soviet Union to join the war against Japan _____ To mourn Roosevelt’s death from a brain hemorrhage _____ To agree on how to partition and govern Germany after Hitler ...
... Which of these describes why the Big Three Allied leaders met at Yalta in February 1945? (Check all that apply) _____ To convince the Soviet Union to join the war against Japan _____ To mourn Roosevelt’s death from a brain hemorrhage _____ To agree on how to partition and govern Germany after Hitler ...
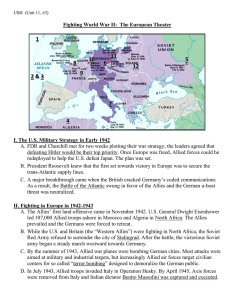
3 Fighting WWII in Europe
... mostly by Jewish organizations in the U.S., the WRB saved approximately 200,000 Jews and 20,000 nonJewish Europeans. The American Public: During World War II, anti-Semitism (anti Jewish feelings) was high. After the violence of Kristallnacht in 1939, 42.3% of Americans believed that the violence in ...
... mostly by Jewish organizations in the U.S., the WRB saved approximately 200,000 Jews and 20,000 nonJewish Europeans. The American Public: During World War II, anti-Semitism (anti Jewish feelings) was high. After the violence of Kristallnacht in 1939, 42.3% of Americans believed that the violence in ...
Chapter 20 Notes
... laws and take intervention or aid Allies but no armed stronger action to the Allies intervention against Germany ...
... laws and take intervention or aid Allies but no armed stronger action to the Allies intervention against Germany ...
The student will demonstrate knowledge of political, economic
... Expansion of production capacities and dominance of the United States in the global economy High protective tariffs Excessive expansion of credit Stock Market Crash (1929) Impact of world depression High unemployment in industrial countries Bank failures and collapse of credit Collapse ...
... Expansion of production capacities and dominance of the United States in the global economy High protective tariffs Excessive expansion of credit Stock Market Crash (1929) Impact of world depression High unemployment in industrial countries Bank failures and collapse of credit Collapse ...
1 Social Science World War II I. THE ROOTS AND CAUSES OF
... b. The Great Depression and National Socialism in Germany c. Key characteristics of National Socialism d. Key events prior to 1938–39 4. Militarism in Japan a. Key events prior to 1937 C. Crises of 1938–39 ...
... b. The Great Depression and National Socialism in Germany c. Key characteristics of National Socialism d. Key events prior to 1938–39 4. Militarism in Japan a. Key events prior to 1937 C. Crises of 1938–39 ...
An Overview of the Nuremberg Trials
... War II. Before Germany surrendered, leaders of the Allied nations began to discuss what should be done to punish Germany. After World War I, the Germans had trade restrictions imposed on them. Land they had taken was restored to the citizens of the original country. Many believed that the punishment ...
... War II. Before Germany surrendered, leaders of the Allied nations began to discuss what should be done to punish Germany. After World War I, the Germans had trade restrictions imposed on them. Land they had taken was restored to the citizens of the original country. Many believed that the punishment ...
... Japanese Attack that brought U.S. into WWII o End the war quickly o Save lives in the long run o Strong resistance of Japanese Minority soldiers not in combat, limited to support roles, officers could only lead other minorities 1. Isolation 1930s: 2. Economic Aid: To England: lend-lease 3. Direct In ...
Document
... Japan, worry about the stronger ones later. • Battle of Guadalcanal (1943) • Allied Victory! ...
... Japan, worry about the stronger ones later. • Battle of Guadalcanal (1943) • Allied Victory! ...
War has started!!!!
... • On November 5, 1937, Hitler announced to his advisers his plans to absorb Austria and Czechoslovakia into the Third Reich (ryk), or German Empire. • The Treaty of Versailles prohibited Anschluss (AHN•SHLUS), or a union between Austria and Germany. However, many Austrians supported unity with Germa ...
... • On November 5, 1937, Hitler announced to his advisers his plans to absorb Austria and Czechoslovakia into the Third Reich (ryk), or German Empire. • The Treaty of Versailles prohibited Anschluss (AHN•SHLUS), or a union between Austria and Germany. However, many Austrians supported unity with Germa ...
Comprehensive Info #5 Second World War
... Mussolini deposed and arrested; Italy signs armistice with Allies in Sept Teheran Conference: Western allies agree to open 2nd front on 1 May 1944 Josip Broz Tito sets up provisional Yugoslav partisan government at Jajce (Bosnia) ...
... Mussolini deposed and arrested; Italy signs armistice with Allies in Sept Teheran Conference: Western allies agree to open 2nd front on 1 May 1944 Josip Broz Tito sets up provisional Yugoslav partisan government at Jajce (Bosnia) ...
War and Peace
... agricultural output rose 22 percent Unemployment nearly disappeared Productive capacity and per capita output increased especially dramatically in the South ...
... agricultural output rose 22 percent Unemployment nearly disappeared Productive capacity and per capita output increased especially dramatically in the South ...
World War II
... space, which meant getting back land that was “wrongfully” taken after WW I and expanding into new ...
... space, which meant getting back land that was “wrongfully” taken after WW I and expanding into new ...
History of the Holocaust The Holocaust was the systematic
... believed that Germans were "racially superior" and that the Jews, deemed "inferior," were an alien threat to the so-called German racial community. During the era of the Holocaust, German authorities also targeted other groups because of their perceived "racial inferiority": Roma (Gypsies), the disa ...
... believed that Germans were "racially superior" and that the Jews, deemed "inferior," were an alien threat to the so-called German racial community. During the era of the Holocaust, German authorities also targeted other groups because of their perceived "racial inferiority": Roma (Gypsies), the disa ...
Midterm #1 - Points
... 21. The Atlantic Charter consisted of the nations of, A) Great Britain and the United States, B) Canada and the United States, C) Germany and Japan, D) the Soviet Union and Japan 22. What was the strategy as decided in the Atlantic Charter? A) defeat Japan first, B) Save Great Britain from Italy, C) ...
... 21. The Atlantic Charter consisted of the nations of, A) Great Britain and the United States, B) Canada and the United States, C) Germany and Japan, D) the Soviet Union and Japan 22. What was the strategy as decided in the Atlantic Charter? A) defeat Japan first, B) Save Great Britain from Italy, C) ...
Economy of Nazi Germany

World War I caused economic and manpower losses on Germany led to a decade of economic woes, including hyperinflation in the mid-1920s. Following the Wall Street Crash of 1929, the German economy, like those of many other western nations, suffered the effects of the Great Depression, with unemployment soaring. When Hitler became Chancellor in 1933, he introduced new efforts to improve Germany's economy, including autarky and the development of the German agricultural economy by placing tariffs on agricultural imports.However, these changes—including autarky and nationalization of key industries—had a mixed record. By 1938, unemployment was practically extinct. Wages increased by 10.9% in real terms during this period. However, nationalization and a cutting off of trade meant rationing in key resources like poultry, fruit, and clothing for many Germans.In 1934 Hjalmar Schacht, the Reich Minister of Economics, introduced the Mefo bills, allowing Germany to rearm without spending Reichmarks but instead pay industry with Reichmarks and Mefo bills (Government IOU's) which they could trade with each other. Between 1933 and 1939, the total revenue was 62 billion marks, whereas expenditure (at times made up to 60% by rearmament costs) exceeded 101 billion, thus creating a huge deficit and national debt (reaching 38 billion marks in 1939) coinciding with the Kristallnacht and intensified persecutions of Jews and the outbreak of the war.