TB_chapter27 without answers
... 6. How did the Nazis attempt to establish a new Order in Europe after their military victories? What were the results of their efforts? 7. Discuss the “Final Solution.” What was it? Who was responsible for it? How did it work? How committed was the entire German war machine to this murderous campaig ...
... 6. How did the Nazis attempt to establish a new Order in Europe after their military victories? What were the results of their efforts? 7. Discuss the “Final Solution.” What was it? Who was responsible for it? How did it work? How committed was the entire German war machine to this murderous campaig ...
Slide 1
... Causes of World War II F) U.S. isolationism – Many Americans believed that the Great Depression was partially caused by U.S. involvement in the First World War. This led many to support an “isolationist” foreign policy that kept the nation out of European affairs. Much like Western European appease ...
... Causes of World War II F) U.S. isolationism – Many Americans believed that the Great Depression was partially caused by U.S. involvement in the First World War. This led many to support an “isolationist” foreign policy that kept the nation out of European affairs. Much like Western European appease ...
WWII
... control of economy during the war • War Production Board: government agency in charge of the economy. Helped factories convert to making military goods • Unemployment went way down, production went way up, Depression over ...
... control of economy during the war • War Production Board: government agency in charge of the economy. Helped factories convert to making military goods • Unemployment went way down, production went way up, Depression over ...
Chapter 7 Notes and Answers
... 6. Describe Canada’s tragic defeat in the Raid on Dieppe during August 1942. Pg 109 More than 6000 Allied soldiers took part, including 4963 Canadians. The raid was a disaster – over 900 Canadians were killed and more than 1900 became POW’s (prisoners of war). 7. Research the Soviet Union’s victory ...
... 6. Describe Canada’s tragic defeat in the Raid on Dieppe during August 1942. Pg 109 More than 6000 Allied soldiers took part, including 4963 Canadians. The raid was a disaster – over 900 Canadians were killed and more than 1900 became POW’s (prisoners of war). 7. Research the Soviet Union’s victory ...
World War Two - Timeline
... Italy surrenders, the Allies. However, the Germans took control of the Italian army, freed Mussolini from imprisonment and set him up as head of a puppet almost government in Northern Italy. This blocked any further Allied advance through Italy. ...
... Italy surrenders, the Allies. However, the Germans took control of the Italian army, freed Mussolini from imprisonment and set him up as head of a puppet almost government in Northern Italy. This blocked any further Allied advance through Italy. ...
World War II
... Persecution of Germany’s Jews Marriage between Jews and other Germans banned German citizenship taken away Kept from voting or holding public office Not allowed to employ non-Jewish Germans Later, banned from owning businesses ...
... Persecution of Germany’s Jews Marriage between Jews and other Germans banned German citizenship taken away Kept from voting or holding public office Not allowed to employ non-Jewish Germans Later, banned from owning businesses ...
1 - Condensed Notes - D-Day to the Bulge
... Nazi leadership throughout Germany with military appointees. b. Four men who had been sitting with Hitler were killed, but the dictator survived the attempt with minor wounds. Stauffenberg, and other conspirators, was executed that evening. The involvement of military officers in the attempt left Hi ...
... Nazi leadership throughout Germany with military appointees. b. Four men who had been sitting with Hitler were killed, but the dictator survived the attempt with minor wounds. Stauffenberg, and other conspirators, was executed that evening. The involvement of military officers in the attempt left Hi ...
WARRING NATIONS - Fort Bend ISD / Homepage
... of Normandy known as D-Day (begins June 6, 1944) to liberate France; • Vichy Regime, led by Pétain in France, falls, eventually leading to ...
... of Normandy known as D-Day (begins June 6, 1944) to liberate France; • Vichy Regime, led by Pétain in France, falls, eventually leading to ...
12. The Course of War
... alliance—from Norway and Finland in the north to Greece in the south and from Poland to France. Britain, the Soviets, a number of insurgent groups, and, finally, America, had before them the long struggle of conquering this Axis “fortress Europe.” ...
... alliance—from Norway and Finland in the north to Greece in the south and from Poland to France. Britain, the Soviets, a number of insurgent groups, and, finally, America, had before them the long struggle of conquering this Axis “fortress Europe.” ...
WWII L2 - Fort Bend ISD / Homepage
... of Normandy known as D-Day (begins June 6, 1944) to liberate France; • Vichy Regime, led by Pétain in France, falls, eventually leading to ...
... of Normandy known as D-Day (begins June 6, 1944) to liberate France; • Vichy Regime, led by Pétain in France, falls, eventually leading to ...
World War II
... France, but he still doesn’t know exactly where the invasion will occur U.S. uses General George Patton and a bunch of fake tanks at Dover to make Hitler believe the invasion will occur at Calais ...
... France, but he still doesn’t know exactly where the invasion will occur U.S. uses General George Patton and a bunch of fake tanks at Dover to make Hitler believe the invasion will occur at Calais ...
WWII
... invades Poland from the East and Soviets invade Poland from the West Sept 27 the Polish capital of Warsaw fell to the Germans. By Oct. 5, 1939 Poland had ...
... invades Poland from the East and Soviets invade Poland from the West Sept 27 the Polish capital of Warsaw fell to the Germans. By Oct. 5, 1939 Poland had ...
HI 224 Final Questions
... Why were the Nazis disappointed by the March 1933 Reichstag elections? How did the Nazis consolidate power after January 1933? What did Gleichschaltung mean? How did the Hitler dictatorship win broad approval in Germany? What was the reality behind the “Röhm Putsch”? What were Hitler’s real aims, an ...
... Why were the Nazis disappointed by the March 1933 Reichstag elections? How did the Nazis consolidate power after January 1933? What did Gleichschaltung mean? How did the Hitler dictatorship win broad approval in Germany? What was the reality behind the “Röhm Putsch”? What were Hitler’s real aims, an ...
How far did the German people benefit from
... Women were expected to be a home as wife and mother. However, during the Second World War women were needed to work in support of the war effort – this was called a ‘Duty Year’. ...
... Women were expected to be a home as wife and mother. However, during the Second World War women were needed to work in support of the war effort – this was called a ‘Duty Year’. ...
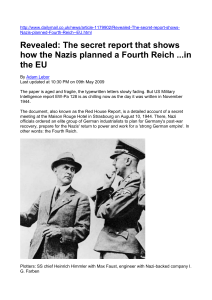
Nazi Fourth Reich - Friends of the Sabbath
... Stage two would see the government allocating large sums to German industrialists to establish a 'secure post-war foundation in foreign countries', while 'existing financial reserves must be placed at the disposal of the party so that a strong German empire can be created after the defeat'. ...
... Stage two would see the government allocating large sums to German industrialists to establish a 'secure post-war foundation in foreign countries', while 'existing financial reserves must be placed at the disposal of the party so that a strong German empire can be created after the defeat'. ...
Militarism
... with Germany and the Soviet Union dividing and annexing the whole of Poland. 10. Blitzkrieg- Literally “lightning war,” the term for Hitler’s invasion strategy of attacking a nation suddenly and with overwhelming force-- Hitler applied the blitzkrieg strategy, with varying degrees of success, to th ...
... with Germany and the Soviet Union dividing and annexing the whole of Poland. 10. Blitzkrieg- Literally “lightning war,” the term for Hitler’s invasion strategy of attacking a nation suddenly and with overwhelming force-- Hitler applied the blitzkrieg strategy, with varying degrees of success, to th ...
Document
... Why did the U.S. ignore Hitler as he rose to power? • We had our own problems to worry about ...
... Why did the U.S. ignore Hitler as he rose to power? • We had our own problems to worry about ...
World War 2 The World at war Again
... ◦ Economic Rights: NONE- all owned by government ◦ Government Rights: Totalitarian/Dictatorship a. One person or party leader Examples: Soviet Union (Russia) Joseph Stalin ...
... ◦ Economic Rights: NONE- all owned by government ◦ Government Rights: Totalitarian/Dictatorship a. One person or party leader Examples: Soviet Union (Russia) Joseph Stalin ...
Study Guide for World War II Test on May 24th-
... What terms means the swift attacks by German forces during WWII? What was the Treaty of Versailles? What term means the extermination of an entire race of people? The alliance of Germany, Italy and Japan during WWII is known as what? Which U.S. president served 12 years including the Great Depressio ...
... What terms means the swift attacks by German forces during WWII? What was the Treaty of Versailles? What term means the extermination of an entire race of people? The alliance of Germany, Italy and Japan during WWII is known as what? Which U.S. president served 12 years including the Great Depressio ...
World War II Many economic and political causes led toward World
... There had been a climate of hatred against Jews in Europe and Russia for centuries. Various instances of genocide have occurred throughout the twentieth century. Genocide is the systematic and purposeful destruction of a racial, political, or cultural group. Elements Leading to the Holocaust: - Tota ...
... There had been a climate of hatred against Jews in Europe and Russia for centuries. Various instances of genocide have occurred throughout the twentieth century. Genocide is the systematic and purposeful destruction of a racial, political, or cultural group. Elements Leading to the Holocaust: - Tota ...
Unit 9 - mrdwyer
... The threat of war persuaded FDR to run for a 3rd term, which broke the precedent set by George Washington. Ran against Republican Wendell Wilkie and what did both candidates say about the war? 4. “Arsenal of democracy” England was running out of money to buy arms and FDR wanted to lend supplie ...
... The threat of war persuaded FDR to run for a 3rd term, which broke the precedent set by George Washington. Ran against Republican Wendell Wilkie and what did both candidates say about the war? 4. “Arsenal of democracy” England was running out of money to buy arms and FDR wanted to lend supplie ...
CH. 5 WWII
... -Allied troops surrounded. - ‘Anything that floats’sent to rescue => ‘A Miracle’ - Morale was boosted even though great losses. ...
... -Allied troops surrounded. - ‘Anything that floats’sent to rescue => ‘A Miracle’ - Morale was boosted even though great losses. ...
Chapter 21-Leading up to War
... • He was cruel, killing over 10 million citizens during his rule (1924-1953) ...
... • He was cruel, killing over 10 million citizens during his rule (1924-1953) ...
Economy of Nazi Germany

World War I caused economic and manpower losses on Germany led to a decade of economic woes, including hyperinflation in the mid-1920s. Following the Wall Street Crash of 1929, the German economy, like those of many other western nations, suffered the effects of the Great Depression, with unemployment soaring. When Hitler became Chancellor in 1933, he introduced new efforts to improve Germany's economy, including autarky and the development of the German agricultural economy by placing tariffs on agricultural imports.However, these changes—including autarky and nationalization of key industries—had a mixed record. By 1938, unemployment was practically extinct. Wages increased by 10.9% in real terms during this period. However, nationalization and a cutting off of trade meant rationing in key resources like poultry, fruit, and clothing for many Germans.In 1934 Hjalmar Schacht, the Reich Minister of Economics, introduced the Mefo bills, allowing Germany to rearm without spending Reichmarks but instead pay industry with Reichmarks and Mefo bills (Government IOU's) which they could trade with each other. Between 1933 and 1939, the total revenue was 62 billion marks, whereas expenditure (at times made up to 60% by rearmament costs) exceeded 101 billion, thus creating a huge deficit and national debt (reaching 38 billion marks in 1939) coinciding with the Kristallnacht and intensified persecutions of Jews and the outbreak of the war.