Treaty of Versailles
... (OPA) – fought inflation by freezing prices of most goods. They also set up a system of rationing for goods deemed essential to the military. ...
... (OPA) – fought inflation by freezing prices of most goods. They also set up a system of rationing for goods deemed essential to the military. ...
Major Battles of WWII Notetaker Non
... Germany’s war strategy of using fast airplanes and tanks to win quick victories On ___________________ Hitler attacks and takes over Poland Once Poland is defeated USSR and Germany divide the country and take territory September 3rd __________ and _________ declare war on Germany The Fall of ...
... Germany’s war strategy of using fast airplanes and tanks to win quick victories On ___________________ Hitler attacks and takes over Poland Once Poland is defeated USSR and Germany divide the country and take territory September 3rd __________ and _________ declare war on Germany The Fall of ...
The Homefront
... believe in a certain idea – Used to persuade people to join the forces and to influence how people felt about the war ...
... believe in a certain idea – Used to persuade people to join the forces and to influence how people felt about the war ...
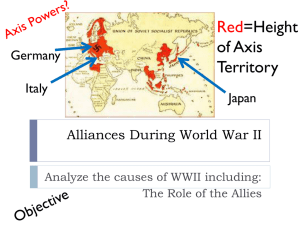
The Role of The Allies-Axis vs. Allies
... The next year, the German army swept across France, soon forcing the French to surrender. Look at the expression of their faces. ...
... The next year, the German army swept across France, soon forcing the French to surrender. Look at the expression of their faces. ...
Origins of World War II
... The U.S. had rejected the Peace of Paris and was caught up in the Depression; Russia was consolidating its revolution; Britain was caught up in the Depression; France alone was left to hold Germany down. Also, Nazi propaganda in the U.S. and Britain portrayed Hitler as the best check on Communist Ru ...
... The U.S. had rejected the Peace of Paris and was caught up in the Depression; Russia was consolidating its revolution; Britain was caught up in the Depression; France alone was left to hold Germany down. Also, Nazi propaganda in the U.S. and Britain portrayed Hitler as the best check on Communist Ru ...
World War II
... space, which meant getting back land that was “wrongfully” taken after WW I and expanding into new ...
... space, which meant getting back land that was “wrongfully” taken after WW I and expanding into new ...
00 Key Terms - 6-4
... in order to inflict maximum damage; done mainly by the British; usually done at night; included civilian targets strategic bombing – tactic of dropping bombs on key political and industrial targets; done mainly by the Americans; usually done during the day; meant to destroy Germany’s capacity to mak ...
... in order to inflict maximum damage; done mainly by the British; usually done at night; included civilian targets strategic bombing – tactic of dropping bombs on key political and industrial targets; done mainly by the Americans; usually done during the day; meant to destroy Germany’s capacity to mak ...
WORLD HISTORY CH. 14: WORLD WAR II AND ITS AFTERMATH
... Why did Japan take over Manchuria (Northern China) in 1931? What was the Rape of Nanjing (see pg. 409)? Which North African country did Italy takeover in 1935? What does appeasement mean? From the chart on pg. 465, what are the 7 reasons why the West (Western Europe, U.S.) appeased Hitler? What agre ...
... Why did Japan take over Manchuria (Northern China) in 1931? What was the Rape of Nanjing (see pg. 409)? Which North African country did Italy takeover in 1935? What does appeasement mean? From the chart on pg. 465, what are the 7 reasons why the West (Western Europe, U.S.) appeased Hitler? What agre ...
Study Guide for World War II Test on May 24th-
... Who was the leader of Japan? What was the $2 billion project that led to the construction of the atomic bomb? Japan invaded this country in 1931? How many Americans were killed in the bombing of Pearl Harbor? Who was the Italian dictator during WWII? What terms means the swift attacks by German forc ...
... Who was the leader of Japan? What was the $2 billion project that led to the construction of the atomic bomb? Japan invaded this country in 1931? How many Americans were killed in the bombing of Pearl Harbor? Who was the Italian dictator during WWII? What terms means the swift attacks by German forc ...
1 Totalitarianism and the Outbreak of World War II
... dictators who demanded loyalty from citizens Fascists did not offer democracy and used one party to rule the nation Unlike Communists, fascists believed people could keep their property ...
... dictators who demanded loyalty from citizens Fascists did not offer democracy and used one party to rule the nation Unlike Communists, fascists believed people could keep their property ...
Ch 16 World War Looms Sec 1 Dictators Threaten World Peace
... 2. Hitler blamed the Jews for Germany’s failure in WWI and for its economic problems following the war 3. Nuremberg Laws – stripped Jews of their civil rights and property if they tried to leave Germany 4. Jews over the age of 6 were required to wear a bright yellow Star of David on their clothing 5 ...
... 2. Hitler blamed the Jews for Germany’s failure in WWI and for its economic problems following the war 3. Nuremberg Laws – stripped Jews of their civil rights and property if they tried to leave Germany 4. Jews over the age of 6 were required to wear a bright yellow Star of David on their clothing 5 ...
9B-Chapter 24 Review Worksheet—ANSWERS
... An agreement reached at a secret meeting in Newfoundland between Churchill and FDR. The agreement said that the United States and Britain 1) would not pursue territorial expansion, 2) affirmed their belief that every nation has the right to choose its own form of government, 3) called for freedom of ...
... An agreement reached at a secret meeting in Newfoundland between Churchill and FDR. The agreement said that the United States and Britain 1) would not pursue territorial expansion, 2) affirmed their belief that every nation has the right to choose its own form of government, 3) called for freedom of ...
World War II
... • Joseph Stalin ordered the killing of anyone who he saw as a threat to his authority (wealthier peasants, government and military leaders) • In 1976, over a million people were executed or died from starvation in Cambodia when Pol Pot forced everyone to move to the countryside. • In 1994, over 80,0 ...
... • Joseph Stalin ordered the killing of anyone who he saw as a threat to his authority (wealthier peasants, government and military leaders) • In 1976, over a million people were executed or died from starvation in Cambodia when Pol Pot forced everyone to move to the countryside. • In 1994, over 80,0 ...
World War II
... without the US directly participating in war B) it limited American involvement in European affairs by only providing advisors to friendly nations C) it curtailed the sale of supplies to all nations involved in conflict D) It assisted Great Britain’s efforts against Germany but did not offer help to ...
... without the US directly participating in war B) it limited American involvement in European affairs by only providing advisors to friendly nations C) it curtailed the sale of supplies to all nations involved in conflict D) It assisted Great Britain’s efforts against Germany but did not offer help to ...
World War II
... The Holocaust was the systematic, bureaucratic, state-sponsored persecution and murder of approximately six million Jews by the Nazi regime and its collaborators. ...
... The Holocaust was the systematic, bureaucratic, state-sponsored persecution and murder of approximately six million Jews by the Nazi regime and its collaborators. ...
(See Neutrality Acts of 1935 and 1937).
... • The Allies fought through Germany’s defense lines at Normandy. • Allied leaders had promised to punish the Nazis for having caused the war. They would not stop until the Nazi regime was destroyed. • German resistance and bad weather slowed the Allies’ advance into France. • German defensive lines, ...
... • The Allies fought through Germany’s defense lines at Normandy. • Allied leaders had promised to punish the Nazis for having caused the war. They would not stop until the Nazi regime was destroyed. • German resistance and bad weather slowed the Allies’ advance into France. • German defensive lines, ...
File
... couldn’t just take over Czechoslovakia. • In September 1938, Hitler demanded that German speakers in Czechoslovakia should be allowed to join his ‘greater Germany.’ War between Germany and Czechoslovakia seemed likely! • Everything depended on the actions of Britain, France and the Soviet Union. ...
... couldn’t just take over Czechoslovakia. • In September 1938, Hitler demanded that German speakers in Czechoslovakia should be allowed to join his ‘greater Germany.’ War between Germany and Czechoslovakia seemed likely! • Everything depended on the actions of Britain, France and the Soviet Union. ...
German victory in Europe by 1941
... the wat, and on 17th September Russia invaded from the east, as agreed in Nazi-Soviet Pact. Since Britain and France could not help, Poland was swiftly defeated when Germany attacked with overwhelming force and speed - "Blitzkrieg". Poland surrendered on 3rd October. There was now a pause, "the Phon ...
... the wat, and on 17th September Russia invaded from the east, as agreed in Nazi-Soviet Pact. Since Britain and France could not help, Poland was swiftly defeated when Germany attacked with overwhelming force and speed - "Blitzkrieg". Poland surrendered on 3rd October. There was now a pause, "the Phon ...
Unit 2 Test Review
... tactics – bombs cities and Britain holds firm • Russia – Hitler changes his sights to longtime enemy Communist Stalin • Battle of Stalingrad – turning point in eastern front war – Russians start to push the German back to Berlin ...
... tactics – bombs cities and Britain holds firm • Russia – Hitler changes his sights to longtime enemy Communist Stalin • Battle of Stalingrad – turning point in eastern front war – Russians start to push the German back to Berlin ...
World War II
... Benito Mussolini of Italy put his Pact of Steel with Hitler into action Italy declared war against France and Britain on June ...
... Benito Mussolini of Italy put his Pact of Steel with Hitler into action Italy declared war against France and Britain on June ...
WWII Project Outline
... the Allies of World War II of Nazi Germany's unconditional surrender of its armed forces. It thus marked the end of World War II in Europe. ...
... the Allies of World War II of Nazi Germany's unconditional surrender of its armed forces. It thus marked the end of World War II in Europe. ...
- Toolbox Pro
... slaughter. Nuclear warfare is indeed inhuman and ought to be banned. By the same token, other forms of warfare, such as the dropping of fire bombs and the shooting of soldiers with cannon and rifles, are likewise uncivilized and should be outlawed…The complaint that so many were killed is answered b ...
... slaughter. Nuclear warfare is indeed inhuman and ought to be banned. By the same token, other forms of warfare, such as the dropping of fire bombs and the shooting of soldiers with cannon and rifles, are likewise uncivilized and should be outlawed…The complaint that so many were killed is answered b ...
Dictators and Warlords
... Japan sees no option but attack. General Tojo ordered a surprise attack on the American naval fleet at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. Dec. 7, 1941 Japanese planes destroy or damage 19 ships, many planes, and kill over 2400 people. It was “a day that will live in infamy.” Dec. 8, 1941, President Roosevelt ask ...
... Japan sees no option but attack. General Tojo ordered a surprise attack on the American naval fleet at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. Dec. 7, 1941 Japanese planes destroy or damage 19 ships, many planes, and kill over 2400 people. It was “a day that will live in infamy.” Dec. 8, 1941, President Roosevelt ask ...
Chapter 26 Notes
... The American people, in the eyes of the Japanese leaders, were _________ ‐‐once divided over participating in the war, America people now took up arms The U.S. joined _______________ nations and Nationalist China in a combined effort to defeat Japan ‐‐believing that the U.S. involvement in the ____ ...
... The American people, in the eyes of the Japanese leaders, were _________ ‐‐once divided over participating in the war, America people now took up arms The U.S. joined _______________ nations and Nationalist China in a combined effort to defeat Japan ‐‐believing that the U.S. involvement in the ____ ...
Chapter 31
... 2. By June 1945 US and Soviets divisive over how to divide Germany a. Hitler kills himself - goes down believing he was betrayed by German people E. The Rise and Fall of the Japanese Empire in the Pacific War 1. 1/3 of Japanese forces fight in China throughout war 2. After Pearl Harbor, Japan takes ...
... 2. By June 1945 US and Soviets divisive over how to divide Germany a. Hitler kills himself - goes down believing he was betrayed by German people E. The Rise and Fall of the Japanese Empire in the Pacific War 1. 1/3 of Japanese forces fight in China throughout war 2. After Pearl Harbor, Japan takes ...
British propaganda during World War II

Britain re-created the World War I Ministry of Information for the duration of World War II to generate propaganda to influence the population towards support for the war effort. A wide range of media was employed aimed at local and overseas audiences. Traditional forms such as newspapers and posters were joined by new media including cinema (film), newsreels and radio. A wide range of themes were addressed, fostering hostility to the enemy, support for allies, and specific pro war projects such as conserving metal and growing vegetables.