File
... John Keegan, American Historian and Author believes that 2,500 Americans died along with 3,000 British and Canadian troops on D-Day ...
... John Keegan, American Historian and Author believes that 2,500 Americans died along with 3,000 British and Canadian troops on D-Day ...
Document
... John Keegan, American Historian and Author believes that 2,500 Americans died along with 3,000 British and Canadian troops on D-Day ...
... John Keegan, American Historian and Author believes that 2,500 Americans died along with 3,000 British and Canadian troops on D-Day ...
World War II, 1939-1945 - APUSH with Mr. Johnson
... United Nations & Universal Declaration of Human Rights ...
... United Nations & Universal Declaration of Human Rights ...
The Road to Revolution – Ch
... Front (West of Germany), North Atlantic naval battles, North Africa, China, Southeast Asia, and the Central Pacific U.S. decided to attack Germany in Europe first, as Germany was far stronger and more crucial than Japan; if U.S. defeated Japan first, Germany could still survive and perhaps be strong ...
... Front (West of Germany), North Atlantic naval battles, North Africa, China, Southeast Asia, and the Central Pacific U.S. decided to attack Germany in Europe first, as Germany was far stronger and more crucial than Japan; if U.S. defeated Japan first, Germany could still survive and perhaps be strong ...
The consequences of the World War II
... the first self-sustaining nuclear chain reaction. The next step was to find and process the uranium needed to manufacture an atomic bomb. On April 28, at a lakeside village in northern Italy, Mussolini was seized by Italian partisans. He had sought to disguise himself in a German Air Force greatcoa ...
... the first self-sustaining nuclear chain reaction. The next step was to find and process the uranium needed to manufacture an atomic bomb. On April 28, at a lakeside village in northern Italy, Mussolini was seized by Italian partisans. He had sought to disguise himself in a German Air Force greatcoa ...
World War II Timeline 1. 1931 Japan Seizes the
... signed the so-called Pact of Steel, formalizing their Axis alliance with military provisions 13. August 1939 Nazi-Soviet Pact 14. September 1, 1939 Poland 15. April 1940 16. May 1940 17. May 6 – June 4, 1940 Dunkirk 18. *June 10, 1940 Italy entered World War II on the Axis side 19. June 22, 1940 20. ...
... signed the so-called Pact of Steel, formalizing their Axis alliance with military provisions 13. August 1939 Nazi-Soviet Pact 14. September 1, 1939 Poland 15. April 1940 16. May 1940 17. May 6 – June 4, 1940 Dunkirk 18. *June 10, 1940 Italy entered World War II on the Axis side 19. June 22, 1940 20. ...
World War II (1942 - 1945)
... decided to open a Western Front by invading Nazi-occupied France Operation Overlord (called D-Day) in June 1944 was the largest land & sea attack in history ...
... decided to open a Western Front by invading Nazi-occupied France Operation Overlord (called D-Day) in June 1944 was the largest land & sea attack in history ...
World War II Vocabulary
... other "undesirables" were sent to either work as slave laborers until they dropped dead from exhaustion, disease, or malnutrition. ...
... other "undesirables" were sent to either work as slave laborers until they dropped dead from exhaustion, disease, or malnutrition. ...
Chapter 8, Lesson 2 The Home Front
... Tuskegee Alabama. They became known as the Tuskegee Airmen. They served proudly over North Africa and Europe. ...
... Tuskegee Alabama. They became known as the Tuskegee Airmen. They served proudly over North Africa and Europe. ...
Chapter 26 Notes
... Hitler, in 1942, ordered a massive increase in armaments production and in the size of the army Hitler's architect, _______________, was made minister for armaments and munitions in 1942 and was able to triple the production between 1942 and 1943 in spite of Allied air raids A total mobilization ...
... Hitler, in 1942, ordered a massive increase in armaments production and in the size of the army Hitler's architect, _______________, was made minister for armaments and munitions in 1942 and was able to triple the production between 1942 and 1943 in spite of Allied air raids A total mobilization ...
Grade 10 History WWII Battles
... Protection of sea lanes to ensure troops, supplies, equipment available to allies If supplies cut off to allies, outcome of war could be different Battle of Hong Kong Operation Hana Suka- Flowers in Bloom; station in Hong Kong Allies lose military base to support war efforts in Pacific Def ...
... Protection of sea lanes to ensure troops, supplies, equipment available to allies If supplies cut off to allies, outcome of war could be different Battle of Hong Kong Operation Hana Suka- Flowers in Bloom; station in Hong Kong Allies lose military base to support war efforts in Pacific Def ...
WWII P2
... Germany stuck on Eastern Front (Near Soviet Union) Stalingrad major Soviet industrial center, Germany needs the resources because it’s low on oil & machinery Nov. 1942-Feb. 1943 Hitler tried to take Stalingrad, burned city Soviets retaliated, fighting back in -44 weather Turning point of the ...
... Germany stuck on Eastern Front (Near Soviet Union) Stalingrad major Soviet industrial center, Germany needs the resources because it’s low on oil & machinery Nov. 1942-Feb. 1943 Hitler tried to take Stalingrad, burned city Soviets retaliated, fighting back in -44 weather Turning point of the ...
World War II (1939
... moved to the interior; away from the coast • Japanese farms/businesses bought for far less value ...
... moved to the interior; away from the coast • Japanese farms/businesses bought for far less value ...
World War II Notes
... try the people responsible for the war. – Many are executed and jailed for war crimes. ...
... try the people responsible for the war. – Many are executed and jailed for war crimes. ...
World War II - Inside Out.net
... English Channel from England to Normandy – the largest invasion by sea in military history. Almost 7,000 vessels were involved, supported by 12,000 aircraft. The battle in Normandy lasted for more than two months, ending with the liberation of Paris. World War II took place between 1939 and 1945, an ...
... English Channel from England to Normandy – the largest invasion by sea in military history. Almost 7,000 vessels were involved, supported by 12,000 aircraft. The battle in Normandy lasted for more than two months, ending with the liberation of Paris. World War II took place between 1939 and 1945, an ...
Chapter 25
... We knew the world would not be the same. A few people laughed, a few people cried, most people were silent. I remembered the line from the Hindu scripture, the Bhagavad-Gita. Vishnu is trying to persuade the Prince that he should do his duty and to impress him takes on his multi-armed form and says ...
... We knew the world would not be the same. A few people laughed, a few people cried, most people were silent. I remembered the line from the Hindu scripture, the Bhagavad-Gita. Vishnu is trying to persuade the Prince that he should do his duty and to impress him takes on his multi-armed form and says ...
World War II - Inside Out.net
... English Channel from England to Normandy – the largest invasion by sea in military history. Almost 7,000 vessels were involved, supported by 12,000 aircraft. The battle in Normandy lasted for more than two months, ending with the liberation of Paris. World War II took place between 1939 and 1945, an ...
... English Channel from England to Normandy – the largest invasion by sea in military history. Almost 7,000 vessels were involved, supported by 12,000 aircraft. The battle in Normandy lasted for more than two months, ending with the liberation of Paris. World War II took place between 1939 and 1945, an ...
1941
... Force. The Allies had 3 million men, 16 million tons of weapons and supplies, 9,000 boats of various sizes, and 11,000 aircraft. Eisenhower’s men landed on the Normandy coast of France on “D-Day,” June 6, 1944. In the months that followed, the Allies drove through France, Belgium, and The Netherland ...
... Force. The Allies had 3 million men, 16 million tons of weapons and supplies, 9,000 boats of various sizes, and 11,000 aircraft. Eisenhower’s men landed on the Normandy coast of France on “D-Day,” June 6, 1944. In the months that followed, the Allies drove through France, Belgium, and The Netherland ...
Chapter 16
... against Hitler – Soviet forces were dying by the millions (20 million by war’s end) – Americans were eager to comply, but the British, remembering WWI, were reluctant. – Instead of a frontal European assault, the British devised an invasion through North Africa, so that the Allies could cut Hitler’s ...
... against Hitler – Soviet forces were dying by the millions (20 million by war’s end) – Americans were eager to comply, but the British, remembering WWI, were reluctant. – Instead of a frontal European assault, the British devised an invasion through North Africa, so that the Allies could cut Hitler’s ...
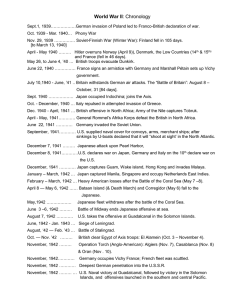
WW II - Chronology - Mira Costa High School
... Nov. 29, 1939 …………… Soviet-Finnish War (Winter War): Finland fell in 105 days. [to March 13, 1940] April - May 1940 ……… Hitler overruns Norway (April 9)), Denmark, the Low Countries (14th & 15th) and France (fell in 46 days). May 26, to June 4, ’40 … British troops evacuate Dunkirk. June 22, 1940 …… ...
... Nov. 29, 1939 …………… Soviet-Finnish War (Winter War): Finland fell in 105 days. [to March 13, 1940] April - May 1940 ……… Hitler overruns Norway (April 9)), Denmark, the Low Countries (14th & 15th) and France (fell in 46 days). May 26, to June 4, ’40 … British troops evacuate Dunkirk. June 22, 1940 …… ...
Chapter 17
... 12. Churchill compared postwar Soviet policy in Eastern Europe to a. liberation. b. nuclear age. c. second front. d. iron curtain. 13. Harry S. Truman authorized dropping the atomic bomb on Japan because a. he wanted to see if it would work. b. he thought an invasion would kill too many U.S. troops. ...
... 12. Churchill compared postwar Soviet policy in Eastern Europe to a. liberation. b. nuclear age. c. second front. d. iron curtain. 13. Harry S. Truman authorized dropping the atomic bomb on Japan because a. he wanted to see if it would work. b. he thought an invasion would kill too many U.S. troops. ...
Chapter 22 Power Point
... Russians defeat the Germans after months of fierce fighting. Russians began receiving supplies from the other Allies through Iran, which helped them greatly. ...
... Russians defeat the Germans after months of fierce fighting. Russians began receiving supplies from the other Allies through Iran, which helped them greatly. ...
WHChapter_28
... The Afrika Korps was the Axis force in North Africa. By late 1942, the Allies started to take control. The Battle of El Alamein in Egypt started to turn the tide in North Africa. The Allies took advantage of Rommel’s supply problems. By 1943, the Americans had joined the British and finally defe ...
... The Afrika Korps was the Axis force in North Africa. By late 1942, the Allies started to take control. The Battle of El Alamein in Egypt started to turn the tide in North Africa. The Allies took advantage of Rommel’s supply problems. By 1943, the Americans had joined the British and finally defe ...
Home front during World War II

The home front covers the activities of the civilians in a nation at war. World War II was a total war; homeland production became even more invaluable to both the Allied and Axis powers. Life on the home front during World War II was a significant part of the war effort for all participants and had a major impact on the outcome of the war. Governments became involved with new issues such as rationing, manpower allocation, home defense, evacuation in the face of air raids, and response to occupation by an enemy power. The morale and psychology of the people responded to leadership and propaganda. Typically women were mobilized to an unprecedented degree.All of the powers involved had learned from their experiences good and bad on the home front during World War I. Their success in mobilizing economic output was a major factor in supporting combat operations. Among morale-boosting activities that also benefited combat efforts, the home front engaged in a variety of scrap drives for materials crucial to the war effort such as metal, rubber, and rags.