PART ONE: First Things First: Beginnings in
... d. Within six months, Hitler’s forces had overrun the rest of Czechoslovakia and were threatening to march into Poland. e. In August 1939, Hitler signed a nonaggression pact with the Soviet Union, which assured Germany it would not have to wage war on two fronts at once. f. On September 1, 1939, Ger ...
... d. Within six months, Hitler’s forces had overrun the rest of Czechoslovakia and were threatening to march into Poland. e. In August 1939, Hitler signed a nonaggression pact with the Soviet Union, which assured Germany it would not have to wage war on two fronts at once. f. On September 1, 1939, Ger ...
Once More, the Road to War
... Spring 1942, the US has a string of victories against Japan in the pacific Summer 1942, the Battle of Stalingrad raged for months, with the Russians eventually prevailing. The Germans lost an entire army November 1942, an Allied forced landed in French North Africa, defeating German forces there. Ju ...
... Spring 1942, the US has a string of victories against Japan in the pacific Summer 1942, the Battle of Stalingrad raged for months, with the Russians eventually prevailing. The Germans lost an entire army November 1942, an Allied forced landed in French North Africa, defeating German forces there. Ju ...
HI136 The History of Germany Lecture 14
... Article II. In the event of a territorial and political rearrangement of the areas belonging to the Polish state, the spheres of influence of Germany and the U.S.S.R. shall be bounded approximately by the line of the rivers Narev, Vistula and San. The question of whether the interests of both partie ...
... Article II. In the event of a territorial and political rearrangement of the areas belonging to the Polish state, the spheres of influence of Germany and the U.S.S.R. shall be bounded approximately by the line of the rivers Narev, Vistula and San. The question of whether the interests of both partie ...
Intro WWII Forum Lecture
... Why? (underlying causes of WWII) 2. World-wide Depression 2) Hitler provided scapegoats for Germany’s problems ...
... Why? (underlying causes of WWII) 2. World-wide Depression 2) Hitler provided scapegoats for Germany’s problems ...
World War II (1939
... materials) to Japan after they took French territory in Asia -made the Japanese mad – planned an attack Pearl Harbor – Am.’s largest naval base – in Hawaii – Japan chose to attack it – 4,000 ...
... materials) to Japan after they took French territory in Asia -made the Japanese mad – planned an attack Pearl Harbor – Am.’s largest naval base – in Hawaii – Japan chose to attack it – 4,000 ...
End of War-Triumph and Tragedy
... The War’s Aftermath After the war, people around the world came to realize the full extent of the Holocaust. The Allies put many Axis leaders on trial for “crimes against humanity.” Western Allies also built new governments in Germany and Japan that would give more power to the people. ...
... The War’s Aftermath After the war, people around the world came to realize the full extent of the Holocaust. The Allies put many Axis leaders on trial for “crimes against humanity.” Western Allies also built new governments in Germany and Japan that would give more power to the people. ...
... The U.S. Government responded to Britain's peril as well with passage of the Lend-Lease Act in March 1941. Almost immediately, quantities of "U.S. Rifle, Cal. .30, M1" were on their way across the Atlantic. Winston Churchill wrote: "When the ships from America approached our shores with their pricel ...
Unit 9 Study Guide working doc BNa-2dp1bb2
... a. “A day that will live in infamy…” b. December 7. 1941 Battle of the Bulge – Why is this important? a. The FINAL German Offensive. Marks the turning of the tide on the Western Front. Begins the Allied advance to Berlin. b. Stalingrad - The FINAL German Offensive. Marks the turning of the tide on t ...
... a. “A day that will live in infamy…” b. December 7. 1941 Battle of the Bulge – Why is this important? a. The FINAL German Offensive. Marks the turning of the tide on the Western Front. Begins the Allied advance to Berlin. b. Stalingrad - The FINAL German Offensive. Marks the turning of the tide on t ...
Section 1- The War in Europe and North Africa - Waverly
... entailed the largest amphibious invasion in U.S. naval history. 107,000 men. ...
... entailed the largest amphibious invasion in U.S. naval history. 107,000 men. ...
A second global conflict and the end of the European World
... • But the Japanese were fascists who wanted to create their own imperial empire in Asia. They soon proved to be far worse than European rulers. They ruled with an iron first and tortured and killed anyone who was even suspected of disagreeing with their rule. They also forced peasants and workers in ...
... • But the Japanese were fascists who wanted to create their own imperial empire in Asia. They soon proved to be far worse than European rulers. They ruled with an iron first and tortured and killed anyone who was even suspected of disagreeing with their rule. They also forced peasants and workers in ...
APUSH World War II Notes Part A
... Japan wanted to control the Pacific (Japanese Empire) Invasion of Manchuria (1931) Invasion of China (1937) League of Nations “inaction” Pearl Harbor (Dec. 7, 1941) who planned it? What was the goal? did we know ahead of time? ...
... Japan wanted to control the Pacific (Japanese Empire) Invasion of Manchuria (1931) Invasion of China (1937) League of Nations “inaction” Pearl Harbor (Dec. 7, 1941) who planned it? What was the goal? did we know ahead of time? ...
3. What was World War II?
... A. Treaty of Versailles Failed B. Germany blamed and therefore was angry C. Economic Depression D. People were desperate for help E. German invaded Poland after having taken over Austria and Czechoslovakia ...
... A. Treaty of Versailles Failed B. Germany blamed and therefore was angry C. Economic Depression D. People were desperate for help E. German invaded Poland after having taken over Austria and Czechoslovakia ...
The End of WWI
... League of Nations was established Estonia, Finland, Latvia, Lithuania, Czechoslovakia, and Yugoslavia became their own countries Central Powers turned their colonies over to League of Nations who assigned them to the other European Countries Wilson reluctantly agreed to it hoping that while the othe ...
... League of Nations was established Estonia, Finland, Latvia, Lithuania, Czechoslovakia, and Yugoslavia became their own countries Central Powers turned their colonies over to League of Nations who assigned them to the other European Countries Wilson reluctantly agreed to it hoping that while the othe ...
WWII PowerPoint - Aurora City Schools
... airplanes and tanks, followed by massive infantry forces to take enemy by surprise. • Effective in Poland. • September 1, 1939. Hitler invades Poland after the Nazi-Soviet NonAggression Pact is signed. • This is the spark that begins WWII • France and Great Britain finally realized that Hitler could ...
... airplanes and tanks, followed by massive infantry forces to take enemy by surprise. • Effective in Poland. • September 1, 1939. Hitler invades Poland after the Nazi-Soviet NonAggression Pact is signed. • This is the spark that begins WWII • France and Great Britain finally realized that Hitler could ...
World War II
... 2. The Allies landed at Normandy on June 6, 1944—called D-Day—and began to march on France. 3. The Battle of the Bulge became a symbol of American strength and determination. ...
... 2. The Allies landed at Normandy on June 6, 1944—called D-Day—and began to march on France. 3. The Battle of the Bulge became a symbol of American strength and determination. ...
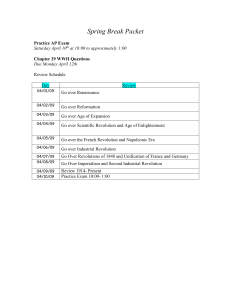
Spring Break Packet Chapter 29 WWI Questions
... genocidal practices during World War II [see doc. on page 1079]? ...
... genocidal practices during World War II [see doc. on page 1079]? ...
Section 2 Objectives
... Americans, and Asian Americans. B. Unemployment decreased, women took jobs outside of the home. C. The media issued propaganda to stress the alliance between the United States and the Soviet Union D. The convoy system was used to accelerate ship building. Main Idea: Allied forces, led by the United ...
... Americans, and Asian Americans. B. Unemployment decreased, women took jobs outside of the home. C. The media issued propaganda to stress the alliance between the United States and the Soviet Union D. The convoy system was used to accelerate ship building. Main Idea: Allied forces, led by the United ...
1. Historical terms
... -The Allies: in this section Britain and France. -The Nazi-Soviet Non-Aggresion Pact: an agreement between Hitler and Stalin that they won't attack each other; an agreement that they would invade Poland together and divide it in two. -Lebensraum: the German word for 'living space'. 2. English words ...
... -The Allies: in this section Britain and France. -The Nazi-Soviet Non-Aggresion Pact: an agreement between Hitler and Stalin that they won't attack each other; an agreement that they would invade Poland together and divide it in two. -Lebensraum: the German word for 'living space'. 2. English words ...
Allies of World War II

The Allies of World War II, called the United Nations from the 1 January 1942 declaration, were the countries that opposed the Axis powers together during the Second World War (1939–1945). The Allies promoted the alliance as seeking to stop German, Japanese and Italian aggression.The anti-German coalition at the start of the war (1 September 1939) consisted of France, Poland and Great Britain, soon to be joined by the British Commonwealth (Canada, Australia, New Zealand and South Africa). Poland was a minor factor after its defeat in 1939; France was a minor factor after its defeat in 1940. After first having cooperated with Germany in partitioning Poland whilst remaining neutral in the Allied-Axis conflict, the Soviet Union perforce joined the Allies in June 1941 after being invaded by Germany. The United States provided war material and money all along, and officially joined in December 1941 after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor. As of 1942, the ""Big Three"" leaders of the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union, and the United States controlled Allied policy; relations between the UK and the U.S. were especially close. China had been already at war with Japan since 1937 but officially joined the Allies in 1941. The Big Three and China were referred as a ""trusteeship of the powerful"", then were recognized as the Allied ""Big Four"" in Declaration by United Nations and later the ""Four Policemen"" of ""United Nations"" for the Allies. Other key Allies included British India, the Netherlands, and Yugoslavia as well as Free France; there were numerous others. Together they called themselves the ""United Nations"" and in 1945 created the modern UN.