* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 1- The War in Europe and North Africa - Waverly
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Kriegsmarine wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Military history of the United Kingdom during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Operation Torch wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Military history of Greece during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Italian resistance movement wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
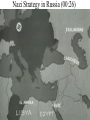
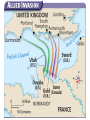
10th American History Unit IV- A Champion of Democracy Chapter 14 – Section 1 The War in Europe and Northern Africa The War in Europe and North Africa The Main Idea After entering World War II, the United States focused first on the war in Europe. Reading Focus • How and why did the Allies fight the Battle of the Atlantic? • What were the key events of the war in the Soviet Union? • What did American forces accomplish in North Africa and Italy? • What were the events and significance of the Allies’ D-Day invasion of France? WWII- A World Conflict Allied Goals1st- Defeat the Germans 2nd- U.S. to postpone the offensive in the Pacific and continue an active defense. How and why did the Allies fight the Battle of the Atlantic? Defeating the Axis Powers depended on control of the seas. The Atlantic needed to be kept safe for shipping so that soldiers and goods could be transported from the United States to the other Allied nations. Germany had a very powerful navy including with new surface ships (including the giant Bismarck) and U-boats. German used new tactics to increase U-boat effectiveness such as the so-called wolf pack. U-boats sent hundreds of ships and tons of supplies to the bottom of the sea. At the same time, the German navy lost few of their boats. The entry of the United States into the war would help turn the tide in the Battle of the Atlantic. Battle for the Atlantic • German Wolf Packs- sinking thousands of tons of Allied shipping each month. • 1942-43 critical, allies need food and supplies. • Radar and Sonar were invented • Use of Ultra (code breaking), Convoys and Destroyers • U.S. Producing more ships and supplies than the Germans could sink. 1942; The Battle of the Atlantic (01:00) England; German U-Boats Hit British Navy; Life in Wartime England (01:37) The Allies Fight the Battle of the Atlantic Allied ships and aircraft • American shipyards began producing new ships at an amazing rate. • The new ships were used to form larger, better-equipped convoys, which cut down on the effectiveness of U-boat attacks. • Allied aircraft protected convoys from the air. Cracking the Enigma • The Allies broke the German code system, which was called the Enigma. • The Allies began to gain vital information about the locations and plans of U-boat formations. • Finally, the Allies had an advantage over the Germans. The Battle of the Atlantic • How and why did the Allies fight the Battle of the Atlantic? • Recall – Why was it so easy for German U-Boats to attack British supply ships at the beginning of World War II? • Identify Cause and Effect – How did America’s entry into the war help turn the tide in the Battle of the Atlantic? • Evaluate – Which do you think was more important in helping the Allies protect shipping lanes, breaking the Enigma code or use of better protected convoys? World War II in the Soviet Union 1. Hitler broke his nonaggression pack with Stalin and invaded the Soviet Union in 1941. – The Soviets then joined the Allies as enemies of the Axis Powers. – At first the Soviets seemed unable to stop the German blitzkrieg; however, the bitterly cold Russian winter proved a great ally. – Still, the Germans held a vast portion of the western Soviet Union and besieged the city of Leningrad. 2. The Germans attacked Stalingrad in August 1942. – The Soviets refused to let Stalingrad fall, and Hitler suffered a stunning defeat in early Feb. 1943. 3. Stalingrad marked the beginning of Germany’s collapse in the Soviet Union. – Soviet forces pushed Germany out of Russia, but lost 12 million soldiers and millions of civilians. Nazi Strategy in Russia (00:26) Operation Barbarosa. • • • • June 22, 1941 – Hitler makes the great blunder- he feels that all battlefields are alike and blitzkrieg always works. He invades Russia Napoleon had learned a hard lesson a hundred years before- Russia is too big, too frozen and would cause the downfall of his empire. Hitler would learn the same lesson. Germans moved quickly and went deep into Russia, but when they got to Moscow the worst winter in 30 years struck. Freezing temps stopped the german advance. Germans are stalemated at Leningrad, Stalingrad and Moscow September 1942; Battle at Stalingrad (01:13) German 6th Army Surrenders - January 31, 1943 (03:09) The War in the Soviet Union • What were the key events of the war in the Soviet Union? • Describe – Why was Stalingrad a major target for the Germans? • Summarize – How did the Russian winter help save the Soviet Union from falling to the Germans? • Develop – What might have happened if the Germans had taken Stalingrad? American Forces in North Africa and Italy Why was North Africa important? By controlling North Africa, the British could protect shipping on the Mediterranean Sea. They needed the ability to ship oil from the Middle East through the Suez Canal. What was the result of fighting in North Africa? Italy could not drive the British from Egypt. Hitler sent troops under the direction of Erwin Rommel – nicknamed the Desert Fox. After a back-and-forth battle for North Africa, the Allied forces handed the Germans a major defeat at the battle of El Alamein. What happened in Italy? British and American forces invaded Italy in 1943. Sicily, code name “Husky”. The Italian people, sick of war, forced Mussolini from power and the Italian army went home. But, Hitler rushed into Italian mountains to stop the Allies. A bloody standoff. D- Day would not come until Rome fell. The Battle of North Africa (01:02) North African Theater Erwin Rommel- German 1942- Tanks and Blitzkrieg Send to Africa to help the Italians stop the British and take British Oil Fields “Desert Fox”- Outwitting opponentsGreatest German General Also planned the defense of the Atlantic Wall. Later accused of being Anti-Hitler conspirator- forced to take poison. Afrika Korps- Rommel Battle of Tobruk and El Alamein Treaten Oil Fields of Middle East and the Suez Canal North African Theater Bernard Montgomery- British El Alamein- Nov. 4, 1942 Allies defeat the Germans Germans bottled up in Tunisia. U.S. Landing in “Vichy” Algeria“Operation Torch,” November 8, 1942 entailed the largest amphibious invasion in U.S. naval history. 107,000 men. August, 1942; Battle at El Alamein (01:13) Casablanca Conference- Jan. 1943 Jan. 14-24, 1943, World War II meeting of U.S. President Franklin Delano Roosevelt and British Prime Minister Winston Churchill at Casablanca, French Morocco. A joint declaration pledged that the war would end only with the unconditional surrender of the Axis states, and the U.S. to attack Germany 1st. Italy • The Allied invasion of Sicily began on the night of the July 9-10, 1943, and ended August 17 in an Allied victory. The invasion of the island was codenamed Operation Husky and it launched the Italian Campaign. • The Italian Campaign of World War II was the name of Allied operations in and around Italy, from 1943 to the end of the war. It is estimated that between September 1943 and April 1945 some 90,000 Allied and 110,000 German soldiers died in Italy. First Films! Invasion of Italy! (03:37) American Forces in North Africa and Italy • What did American forces accomplish in North Africa and Italy? • Explain – Why was Erwin Rommel sent to North Africa? • Make Inferences – Why did the Italians and Germans want to drive the British out of North Africa? • Make Judgements – Why do you think French soldiers in North Africa joined Allied forces in North Africa? On To Italy • Recall – How did the Italian people respond to the Allied Invasion? • Draw Conclusions – Why are the Tuskegee Airmen remembered.? • Develop – Why is Anzio a significant victory for Allied forces? D-Day: The Invasion of France To end the war as quickly as possible, the Allies planned Operation Overlord—a large invasion of mainland France. The Allies landed at Normandy on June 6, 1944—called D-Day—and began to march on France. The Battle of the Bulge became a symbol of American strength and determination. June 6, 1944: D-Day and Its Aftermath (02:30 ) Amphibious Tanks (DD Tanks) These so-called Duplex Drive tanks of the 741st Armoured Battalion were launched from landing craft four kilometres from the beach. Fitted with large canvas skirts round the upper portion of the vehicle, the DD tanks were designed to float low in the water appearing to the enemy as nothing more menacing than a rubber boat. The entry of this first group into the rough seas proved disastrous. The tanks were intended to operate in seas with a one-foot swell, yet on D-Day the waves rose six feet. High waves The heavy seas swamped 27 DDs, sending them to the sea floor. D-Day: The Invasion of France Operation Overlord • Planned invasion of France from the beaches of Normandy • General Omar Bradley led the American troops. • Good planning and speed were vital. • Americans were concerned about the V1 flying bomb and the V2 rocket. D-Day • June 6, 1944 • Allied force of 3.5 million soldiers • Germans were slow to respond • Estimated 10,000 Allied casualties, including 6,600 Americans • The Allies landed almost 1 million soldiers and 180,000 vehicles. Battle of the Bulge • Surprise offensive by Germans • Key moment came at the Belgium city of Bastogne. • Lieutenant General George S. Patton provided relief for the soldiers at Bastogne. • Symbol of American strength and determination D-Day” The Invasion of France • What were the events and significance of the Allies’ D-Day invasion of France? • Explain – Why were the Germans so slow to respond to the invasion of Normandy? • Evaluate – Why do you think the northern coast of France was selected for D-Day? The Battle of the Bulge and the Fall of the Third Reich (01:23) The Battle of the Bulge • Explain – How did the Battle of the Bulge get its name? • Rank – Which do you think was more important to the Allied victory in Europe D-Day or the Battle of the Bulge