3.3 Yalta and Potsdam Conferences
... split Germany into four zones of occupation, allow free elections in Eastern European countries. The Soviet Union was invited to join the new United Nations, the USSR promised to join the war against Japan when Germany was defeated. ...
... split Germany into four zones of occupation, allow free elections in Eastern European countries. The Soviet Union was invited to join the new United Nations, the USSR promised to join the war against Japan when Germany was defeated. ...
File - AP US History
... Following the fall of France, Americans were confronted with a devil's dilemma. They desired to stay out of the conflict, yet they did not want Britain to be knocked ...
... Following the fall of France, Americans were confronted with a devil's dilemma. They desired to stay out of the conflict, yet they did not want Britain to be knocked ...
The Allies Turn the Tide
... Germans Defeated at Stalingrad A major turning point occurred in the Soviet Union. After their lightning advance in 1941, the Germans were stalled outside Moscow and Leningrad. In 1942, Hitler launched a new offensive. This time, he aimed for the rich oil fields of the south. His troops, however, go ...
... Germans Defeated at Stalingrad A major turning point occurred in the Soviet Union. After their lightning advance in 1941, the Germans were stalled outside Moscow and Leningrad. In 1942, Hitler launched a new offensive. This time, he aimed for the rich oil fields of the south. His troops, however, go ...
Chapter 31 World War 2 and it`s Aftermath REVIEW SHEET
... Chapter 31 World War 2 and it's Aftermath REVIEW SHEET ANSWER. ____ ____ ____ ____ ...
... Chapter 31 World War 2 and it's Aftermath REVIEW SHEET ANSWER. ____ ____ ____ ____ ...
points for discussion
... was locked in a desperate battle against the Nazis on the eastern front, an Allied invasion of Europe was put off in favor of campaigns in Africa and then Italy. The Soviet’s bitterness would haunt the United States in the postwar period. Gradually, the Soviets won the offensive in the east. The Uni ...
... was locked in a desperate battle against the Nazis on the eastern front, an Allied invasion of Europe was put off in favor of campaigns in Africa and then Italy. The Soviet’s bitterness would haunt the United States in the postwar period. Gradually, the Soviets won the offensive in the east. The Uni ...
U - Mr. Havens Class
... Terms: Write your answers on the answer sheet. 1. Proposed by Secretary of State Henry Stimson as early as 1931, this foreign policy tool would allow the United States to ban trade in weapons with aggressor nations as a way to influence world affairs without becoming involved in war. 2. In this inci ...
... Terms: Write your answers on the answer sheet. 1. Proposed by Secretary of State Henry Stimson as early as 1931, this foreign policy tool would allow the United States to ban trade in weapons with aggressor nations as a way to influence world affairs without becoming involved in war. 2. In this inci ...
World War II Homefront Notes
... Many connected this with active involvement of the government. Perhaps this helps to explain why Churchill was replaced by Attlee. Churchill was a conservative who might had reduced government involvement after the war ended; whereas, Attlee was a liberal and more likely to support continued governm ...
... Many connected this with active involvement of the government. Perhaps this helps to explain why Churchill was replaced by Attlee. Churchill was a conservative who might had reduced government involvement after the war ended; whereas, Attlee was a liberal and more likely to support continued governm ...
WWII Begins - Brookwood High School
... • -U.S. can stay out of any War • Neutrality Acts • Roosevelt Favors Allies • American Involvement Grows • March 1941 - Lend-Lease Acts ...
... • -U.S. can stay out of any War • Neutrality Acts • Roosevelt Favors Allies • American Involvement Grows • March 1941 - Lend-Lease Acts ...
Grade 10 History – WWII
... Czechoslovakia was not invited to the negotiations. Czechoslovakia had a military alliance with France and Great Britain. It fled betrayed. In March 1939, Slovakia seceded from Czechoslovakia and became a separate state. ...
... Czechoslovakia was not invited to the negotiations. Czechoslovakia had a military alliance with France and Great Britain. It fled betrayed. In March 1939, Slovakia seceded from Czechoslovakia and became a separate state. ...
Sample
... 7. Why didn’t Britain attack Germany during Germany’s invasion of Poland? 8. Why was it good for the Allies that Hitler didn’t invade France in 1939? 9. What did Germany want in Norway? ...
... 7. Why didn’t Britain attack Germany during Germany’s invasion of Poland? 8. Why was it good for the Allies that Hitler didn’t invade France in 1939? 9. What did Germany want in Norway? ...
1920`s - WWII Part Two
... During World War II, the United States rapidly mobilized war production, involved citizens in the effort, opened new opportunities to disadvantaged groups while discriminating against others, and ended the New Deal. The Course and End of World War II Between 1942 and 1945, the U.S.-led Allies defeat ...
... During World War II, the United States rapidly mobilized war production, involved citizens in the effort, opened new opportunities to disadvantaged groups while discriminating against others, and ended the New Deal. The Course and End of World War II Between 1942 and 1945, the U.S.-led Allies defeat ...
1939 - 1945 The Second World War
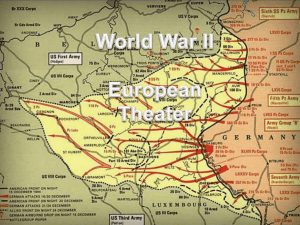
... U.S. troops successfully land on the Normandy beaches of opening a “Second Front” against the Germans. This day is known as D-Day 12 June - The first of Germany's terror weapons, the V1 (doodlebug), falls in Swanscombe in Kent 15 Aug. - Allied forces land in ...
... U.S. troops successfully land on the Normandy beaches of opening a “Second Front” against the Germans. This day is known as D-Day 12 June - The first of Germany's terror weapons, the V1 (doodlebug), falls in Swanscombe in Kent 15 Aug. - Allied forces land in ...
The Allies Win the War
... The Germans thought that the treaty that ended World War I was unfair. (Remember??)The goal of Germany was to avenge itself for this treaty by taking over Europe. They also believed that Germans were a superior people. ...
... The Germans thought that the treaty that ended World War I was unfair. (Remember??)The goal of Germany was to avenge itself for this treaty by taking over Europe. They also believed that Germans were a superior people. ...
America In WWII
... US Navy leapfrogged islands controlled by Japan on its way to Tokyo – “Island Hopping” Major islands of the Marianas fell to U.S. attackers in July and August 1944 From the Marianas, US B-29 bombers could reach Japan ...
... US Navy leapfrogged islands controlled by Japan on its way to Tokyo – “Island Hopping” Major islands of the Marianas fell to U.S. attackers in July and August 1944 From the Marianas, US B-29 bombers could reach Japan ...
The Allies Liberate Europe
... The Battle of Stalingrad • Stalin used the winter to roll in fresh tanks over the frozen ground. • They surrounded the city & cut off German supply lines. The war had turned & the ...
... The Battle of Stalingrad • Stalin used the winter to roll in fresh tanks over the frozen ground. • They surrounded the city & cut off German supply lines. The war had turned & the ...
World War II
... By September, Nazi troops begin major assault on Stalingrad Battle continues for 5 months: February 1943 Germans surrender Russia suffered more casualties than U.S. in entire war Stalin does not forgive Allies for failing to help • Didn’t want to face a winter deep within Russia ...
... By September, Nazi troops begin major assault on Stalingrad Battle continues for 5 months: February 1943 Germans surrender Russia suffered more casualties than U.S. in entire war Stalin does not forgive Allies for failing to help • Didn’t want to face a winter deep within Russia ...
Yalta Big Three Activity Pack Students will be divided into groups to
... He was very paranoid over threats to his control of the Soviet Union and threats of attacks from outside nations. Within the country, purges were staged to eliminate any threats to his power. Information from foreign nations were limited and censored while Soviet secrets were not released. ...
... He was very paranoid over threats to his control of the Soviet Union and threats of attacks from outside nations. Within the country, purges were staged to eliminate any threats to his power. Information from foreign nations were limited and censored while Soviet secrets were not released. ...
Allied Strategy in World War II
... • Attacks in North Africa and Italy 1942–1943 brought some Allied success. • War in Pacific (U.S. vs. Japan) would not be first priority until victory in Europe. ...
... • Attacks in North Africa and Italy 1942–1943 brought some Allied success. • War in Pacific (U.S. vs. Japan) would not be first priority until victory in Europe. ...
WWII Presentation
... Freedom of trade The right of people to choose their own government Called for the final destruction of Nazi Tyranny ...
... Freedom of trade The right of people to choose their own government Called for the final destruction of Nazi Tyranny ...
textbook 569-577 - San Leandro Unified School District
... the two leaders agreed to accept only the unconditional surrender of the Axis powers. That is, enemy nations would have to accept whatever terms of peace the Allies dictated. The two leaders also discussed where to strike next. The Americans argued that the best approach to victory was to assemble a ...
... the two leaders agreed to accept only the unconditional surrender of the Axis powers. That is, enemy nations would have to accept whatever terms of peace the Allies dictated. The two leaders also discussed where to strike next. The Americans argued that the best approach to victory was to assemble a ...
World War II Test
... 37. Two days after Hitler’s invasion of _________, Britain and France declared war on Germany, officially beginning World War Two. a. Austria b. Poland c. France d. Slovakia 38. During WWII, this Allied country quickly fell to Nazi Germany. a. The United States b. France c. Great Britain d. Ireland ...
... 37. Two days after Hitler’s invasion of _________, Britain and France declared war on Germany, officially beginning World War Two. a. Austria b. Poland c. France d. Slovakia 38. During WWII, this Allied country quickly fell to Nazi Germany. a. The United States b. France c. Great Britain d. Ireland ...
Globalization
... By late 1940, Britain was in financial trouble from fighting Germany all alone. FDR asked Congress to increase spending to provide needed munitions and supplies to the British through loans or leases (to be paid back or not at a later ...
... By late 1940, Britain was in financial trouble from fighting Germany all alone. FDR asked Congress to increase spending to provide needed munitions and supplies to the British through loans or leases (to be paid back or not at a later ...
Canada and World War Two
... People here began to believe that joining Canada would be good-they were bankrupt and needed ...
... People here began to believe that joining Canada would be good-they were bankrupt and needed ...
War in Europe and Africa
... created by the Nazis during WWII – this number does not include the ghettos. • Largest and most famous camps: ...
... created by the Nazis during WWII – this number does not include the ghettos. • Largest and most famous camps: ...
Allies of World War II

The Allies of World War II, called the United Nations from the 1 January 1942 declaration, were the countries that opposed the Axis powers together during the Second World War (1939–1945). The Allies promoted the alliance as seeking to stop German, Japanese and Italian aggression.The anti-German coalition at the start of the war (1 September 1939) consisted of France, Poland and Great Britain, soon to be joined by the British Commonwealth (Canada, Australia, New Zealand and South Africa). Poland was a minor factor after its defeat in 1939; France was a minor factor after its defeat in 1940. After first having cooperated with Germany in partitioning Poland whilst remaining neutral in the Allied-Axis conflict, the Soviet Union perforce joined the Allies in June 1941 after being invaded by Germany. The United States provided war material and money all along, and officially joined in December 1941 after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor. As of 1942, the ""Big Three"" leaders of the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union, and the United States controlled Allied policy; relations between the UK and the U.S. were especially close. China had been already at war with Japan since 1937 but officially joined the Allies in 1941. The Big Three and China were referred as a ""trusteeship of the powerful"", then were recognized as the Allied ""Big Four"" in Declaration by United Nations and later the ""Four Policemen"" of ""United Nations"" for the Allies. Other key Allies included British India, the Netherlands, and Yugoslavia as well as Free France; there were numerous others. Together they called themselves the ""United Nations"" and in 1945 created the modern UN.