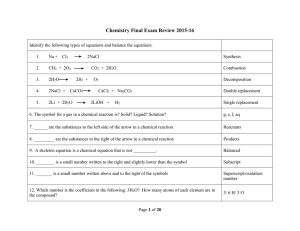
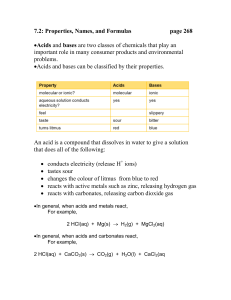
7.2: Properties, Names, and Formulas page 268 •Acids and bases
... 7.2: Properties, Names, and Formulas ...
... 7.2: Properties, Names, and Formulas ...
pH scale. Buffer solutions. Colligative properties of solutions
... Buffer solutions The amount of carbon dioxide in the blood is coupled to the amount present in the lungs. Second, the equilibrium between carbonic acid and bicarbonate ion: H2CO3 (aq) ↔ HCO3− (aq) + H+ (aq), pK = 6.37. These reactions lead to the presence in solution the conjugate pair HCO3−/H2CO3 ...
... Buffer solutions The amount of carbon dioxide in the blood is coupled to the amount present in the lungs. Second, the equilibrium between carbonic acid and bicarbonate ion: H2CO3 (aq) ↔ HCO3− (aq) + H+ (aq), pK = 6.37. These reactions lead to the presence in solution the conjugate pair HCO3−/H2CO3 ...
View Article - Asian Journal of Chemistry
... sodium hydroxide solution. Liquid bromine ( 4.2 mL, 80 mmol) was added dropwise in 2 h when the mixture maintained at 100 - 130 ºC heated by oil bath, excess time was prolonged for reaction until the colour of the reaction mixture turned to light yellow, after that the oil bath was removed and ethyl ...
... sodium hydroxide solution. Liquid bromine ( 4.2 mL, 80 mmol) was added dropwise in 2 h when the mixture maintained at 100 - 130 ºC heated by oil bath, excess time was prolonged for reaction until the colour of the reaction mixture turned to light yellow, after that the oil bath was removed and ethyl ...
Part1. Acid rain formation. 1. Discovery of acid rain.
... In the atmosphere, nitric and sulfuric acids can be formed in two ways: 1) Gas-phase conversion of SO2 to sulfuric acid gas (H2SO4), and NOx to nitric acid gas (HNO3). The gas phase conversion of SO2 requires three steps: SO2 + OH + M -> HSO3 + M HSO3 + O2 -> SO3 + HO2 SO3 + H2O -> H2SO4 The gas pha ...
... In the atmosphere, nitric and sulfuric acids can be formed in two ways: 1) Gas-phase conversion of SO2 to sulfuric acid gas (H2SO4), and NOx to nitric acid gas (HNO3). The gas phase conversion of SO2 requires three steps: SO2 + OH + M -> HSO3 + M HSO3 + O2 -> SO3 + HO2 SO3 + H2O -> H2SO4 The gas pha ...
Technical Data Sheet (E
... E-Phos 660 is a calcium-modified formula which produces fine-grained crystalline coatings on iron and steel with a medium coating weight of 600 mg/ft2. The zinc phosphate coating remains fine-grained regardless of the cleaning method used prior to application. It can be applied by either immersion o ...
... E-Phos 660 is a calcium-modified formula which produces fine-grained crystalline coatings on iron and steel with a medium coating weight of 600 mg/ft2. The zinc phosphate coating remains fine-grained regardless of the cleaning method used prior to application. It can be applied by either immersion o ...
Outline for Unit 1 Solutions, Acid/Base, and Gases
... 1. Write a balanced chemical equation/reaction. 2. Find the moles of a substance in the reaction. 3. Convert the moles of the substance from step 2 to moles of the unknown substance. 4. Find the unknown value. In steps 2 and 4 we are using equations that we have learned to find the moles, or the ...
... 1. Write a balanced chemical equation/reaction. 2. Find the moles of a substance in the reaction. 3. Convert the moles of the substance from step 2 to moles of the unknown substance. 4. Find the unknown value. In steps 2 and 4 we are using equations that we have learned to find the moles, or the ...
selected experiments in organic chemistry
... water (moisture) using chemical drying agents. Such cases are encountered in extraction where the organic phase is in direct contact with the aqueous phase. After separating the layers, traces of water in the organic phase are removed by the addition of a suitable drying agent. One class of drying a ...
... water (moisture) using chemical drying agents. Such cases are encountered in extraction where the organic phase is in direct contact with the aqueous phase. After separating the layers, traces of water in the organic phase are removed by the addition of a suitable drying agent. One class of drying a ...
Test 1 w/answers
... 1. _______ 2. _______ 3. _______ 4. _______ 5. _______ 6. _______ 7. _______ ...
... 1. _______ 2. _______ 3. _______ 4. _______ 5. _______ 6. _______ 7. _______ ...
Characterization of Alcohol Solvents by the Empirical Polarity
... creases parallel to ET(30). The number of data is solvatochromic sensitivity of the corresponding intoo small to propose a reasonably reliable correladicator compound favour ET(30) as compared to Z. tion of the type Z = a • ET(30) -f b, which is reand consequently, (iii) the experimental precision i ...
... creases parallel to ET(30). The number of data is solvatochromic sensitivity of the corresponding intoo small to propose a reasonably reliable correladicator compound favour ET(30) as compared to Z. tion of the type Z = a • ET(30) -f b, which is reand consequently, (iii) the experimental precision i ...
Liquid–liquid extraction

Liquid–liquid extraction (LLE) consists in transferring one (or more) solute(s) contained in a feed solution to another immiscible liquid (solvent). The solvent that is enriched in solute(s) is called extract. The feed solution that is depleted in solute(s) is called raffinate.Liquid–liquid extraction also known as solvent extraction and partitioning, is a method to separate compounds based on their relative solubilities in two different immiscible liquids, usually water and an organic solvent. It is an extraction of a substance from one liquid into another liquid phase. Liquid–liquid extraction is a basic technique in chemical laboratories, where it is performed using a variety of apparatus, from separatory funnels to countercurrent distribution equipment. This type of process is commonly performed after a chemical reaction as part of the work-up.The term partitioning is commonly used to refer to the underlying chemical and physical processes involved in liquid–liquid extraction, but on another reading may be fully synonymous with it. The term solvent extraction can also refer to the separation of a substance from a mixture by preferentially dissolving that substance in a suitable solvent. In that case, a soluble compound is separated from an insoluble compound or a complex matrix.Solvent extraction is used in nuclear reprocessing, ore processing, the production of fine organic compounds, the processing of perfumes, the production of vegetable oils and biodiesel, and other industries.Liquid–liquid extraction is possible in non-aqueous systems: In a system consisting of a molten metal in contact with molten salts, metals can be extracted from one phase to the other. This is related to a mercury electrode where a metal can be reduced, the metal will often then dissolve in the mercury to form an amalgam that modifies its electrochemistry greatly. For example, it is possible for sodium cations to be reduced at a mercury cathode to form sodium amalgam, while at an inert electrode (such as platinum) the sodium cations are not reduced. Instead, water is reduced to hydrogen. A detergent or fine solid can be used to stabilize an emulsion, or third phase.