Oregon State University, Summer 2009 Chemistry 121 Midterm
... a. A combustion reaction is one in which a compound reacts with oxygen to make carbon monoxide and water. b. The Law of Conservation of Matter (Mass) states that the total mass of substances in a chemical reaction does not change. c. In a chemical reaction, the number of atoms of all types remains c ...
... a. A combustion reaction is one in which a compound reacts with oxygen to make carbon monoxide and water. b. The Law of Conservation of Matter (Mass) states that the total mass of substances in a chemical reaction does not change. c. In a chemical reaction, the number of atoms of all types remains c ...
Hierarchically Porous Titania Networks with Controllable
... specific surface areas (up to 71.0 m2 g-1). The photocatalytic performance of the materials was correlated to the anatase:rutile ratio and specific surface area of the materials, with the mixed-phase (rutile content of 15.4%) nanocrystalline titania calcined at 600 °C for 6 h showing the highest pho ...
... specific surface areas (up to 71.0 m2 g-1). The photocatalytic performance of the materials was correlated to the anatase:rutile ratio and specific surface area of the materials, with the mixed-phase (rutile content of 15.4%) nanocrystalline titania calcined at 600 °C for 6 h showing the highest pho ...
No Slide Title
... Zn is oxidized, lost electrons Zn is the reducing agent Cu2+ is reduced, gained electrons ...
... Zn is oxidized, lost electrons Zn is the reducing agent Cu2+ is reduced, gained electrons ...
Mr. Dehne AP Chem Name: ___________ Date: Per#: ___ AP
... 34. Saccharin (C7H5NO3S) is sometimes dispensed in tablet form. Ten tablets with a total mass of 0.5894g were dissolved in water. They were oxidized to convert all of the sulfur to sulfate ion, which was precipitated by adding an excess of barium chloride solution. The mass of BaSO4 obtained was 0.5 ...
... 34. Saccharin (C7H5NO3S) is sometimes dispensed in tablet form. Ten tablets with a total mass of 0.5894g were dissolved in water. They were oxidized to convert all of the sulfur to sulfate ion, which was precipitated by adding an excess of barium chloride solution. The mass of BaSO4 obtained was 0.5 ...
Final Exam - Dawson College
... Limestone, CaCO3, reacts with hydrochloric acid to form calcium chloride, water and carbon dioxide according to the following reaction: CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) How many liters of CO2 gas will be formed at 755 torr and 33.0°C by the reaction of 2.35 g of limestone with an ex ...
... Limestone, CaCO3, reacts with hydrochloric acid to form calcium chloride, water and carbon dioxide according to the following reaction: CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) How many liters of CO2 gas will be formed at 755 torr and 33.0°C by the reaction of 2.35 g of limestone with an ex ...
unit 4 practice
... A. Solutions of weak acids cannot conduct an electric current but solutions of strong acids can conduct an electric current. B. Strong acids can form concentrated solutions but weak acids cannot form co ...
... A. Solutions of weak acids cannot conduct an electric current but solutions of strong acids can conduct an electric current. B. Strong acids can form concentrated solutions but weak acids cannot form co ...
Introduction
... 1) An atom (or molecule) in its elemental state has an oxidation number of 0. 2) An atom in a monatomic ion (Na+, Cl-) has an oxidation number identical to its charge. 3a) Hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1, unless it is combined with a metal, in which case it has an oxidation number of –1. 3b) ...
... 1) An atom (or molecule) in its elemental state has an oxidation number of 0. 2) An atom in a monatomic ion (Na+, Cl-) has an oxidation number identical to its charge. 3a) Hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1, unless it is combined with a metal, in which case it has an oxidation number of –1. 3b) ...
3 - Study Hungary
... B: 2HNO3 + Na2CO3 → 2NaNO3 + H2O + CO2 C: Ba(NO3)2 + Na2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2NaNO3 D: 2HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 → Ca(NO3)2 + 2H2O E: 2HNO3 + 3H2S → 2NO + 3S + 4H2O ...
... B: 2HNO3 + Na2CO3 → 2NaNO3 + H2O + CO2 C: Ba(NO3)2 + Na2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2NaNO3 D: 2HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 → Ca(NO3)2 + 2H2O E: 2HNO3 + 3H2S → 2NO + 3S + 4H2O ...
Review #7: Solutions, Acids and Bases 1. Definitions: a) Solution: a
... i) % W / V: a description of the concentration of a solution. Tells the mass of solute per 100 mL of solution. For example, a 5% W/V solution of sugar would contain 5 g of sugar in 100 mL of solution. j) % W / W: a description of the concentration of a solution. Tells the mass of solute per 100 g of ...
... i) % W / V: a description of the concentration of a solution. Tells the mass of solute per 100 mL of solution. For example, a 5% W/V solution of sugar would contain 5 g of sugar in 100 mL of solution. j) % W / W: a description of the concentration of a solution. Tells the mass of solute per 100 g of ...
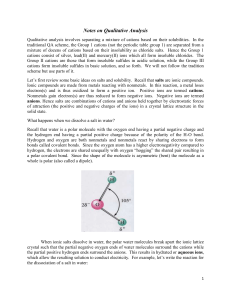
Notes on QA - Scarsdale Public Schools
... Qualitative analysis involves separating a mixture of cations based on their solubilities. In the traditional QA scheme, the Group 1 cations (not the periodic table group 1) are separated from a mixture of dozens of cations based on their insolubility as chloride salts. Hence the Group 1 cations con ...
... Qualitative analysis involves separating a mixture of cations based on their solubilities. In the traditional QA scheme, the Group 1 cations (not the periodic table group 1) are separated from a mixture of dozens of cations based on their insolubility as chloride salts. Hence the Group 1 cations con ...
LN_atoms_etc
... Modern View of Atomic Structure Experiments by Thomson and Millikan confirmed the existence of electrons as the negatively charged particles within an atom. Electrons have a charge of e = 1.6021773 10–19 C and a mass of 9.109390 10–31 kg. Later experiments by Rutherford determined that at the ce ...
... Modern View of Atomic Structure Experiments by Thomson and Millikan confirmed the existence of electrons as the negatively charged particles within an atom. Electrons have a charge of e = 1.6021773 10–19 C and a mass of 9.109390 10–31 kg. Later experiments by Rutherford determined that at the ce ...
cbse class – x science solutions
... electronic structure. (v) What would be the ratio of number of combining atoms in a compound formed by the combination of element A with carbon? (vi) Which one of the given elements is likely to have the smallest atomic radius? (i) The element A combines with chlorine is form an acid and its oxide i ...
... electronic structure. (v) What would be the ratio of number of combining atoms in a compound formed by the combination of element A with carbon? (vi) Which one of the given elements is likely to have the smallest atomic radius? (i) The element A combines with chlorine is form an acid and its oxide i ...
A2 2, Analytical, Transition Metals, Electrochemistry and
... breathing carbon monoxide can result in death. ...
... breathing carbon monoxide can result in death. ...
Experimental and Simulation Results for the Removal of H2S from
... models represent a higher fidelity, more realistic modeling approach and the simulation results are more accurate than those attainable from the equilibrium-stage models [6]. In order to develop a rigorous and thermodynamically consistent simulation, the generalized electrolyte NonRandom Two-Liquid ...
... models represent a higher fidelity, more realistic modeling approach and the simulation results are more accurate than those attainable from the equilibrium-stage models [6]. In order to develop a rigorous and thermodynamically consistent simulation, the generalized electrolyte NonRandom Two-Liquid ...
Liquid–liquid extraction

Liquid–liquid extraction (LLE) consists in transferring one (or more) solute(s) contained in a feed solution to another immiscible liquid (solvent). The solvent that is enriched in solute(s) is called extract. The feed solution that is depleted in solute(s) is called raffinate.Liquid–liquid extraction also known as solvent extraction and partitioning, is a method to separate compounds based on their relative solubilities in two different immiscible liquids, usually water and an organic solvent. It is an extraction of a substance from one liquid into another liquid phase. Liquid–liquid extraction is a basic technique in chemical laboratories, where it is performed using a variety of apparatus, from separatory funnels to countercurrent distribution equipment. This type of process is commonly performed after a chemical reaction as part of the work-up.The term partitioning is commonly used to refer to the underlying chemical and physical processes involved in liquid–liquid extraction, but on another reading may be fully synonymous with it. The term solvent extraction can also refer to the separation of a substance from a mixture by preferentially dissolving that substance in a suitable solvent. In that case, a soluble compound is separated from an insoluble compound or a complex matrix.Solvent extraction is used in nuclear reprocessing, ore processing, the production of fine organic compounds, the processing of perfumes, the production of vegetable oils and biodiesel, and other industries.Liquid–liquid extraction is possible in non-aqueous systems: In a system consisting of a molten metal in contact with molten salts, metals can be extracted from one phase to the other. This is related to a mercury electrode where a metal can be reduced, the metal will often then dissolve in the mercury to form an amalgam that modifies its electrochemistry greatly. For example, it is possible for sodium cations to be reduced at a mercury cathode to form sodium amalgam, while at an inert electrode (such as platinum) the sodium cations are not reduced. Instead, water is reduced to hydrogen. A detergent or fine solid can be used to stabilize an emulsion, or third phase.