noble gases
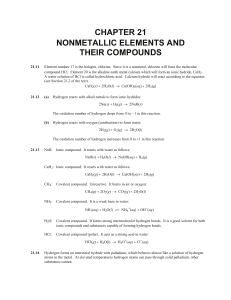
... product formed by the reaction between KI and acidified potassium dichromate solution is a. +4b. +6 c. +2 d. +3 Ans : d K2Cr2O7 is reduced to chromic sulphate, Cr2(SO4)3 in which chromium is in +3 state Vikasana - CET 2012 ...
... product formed by the reaction between KI and acidified potassium dichromate solution is a. +4b. +6 c. +2 d. +3 Ans : d K2Cr2O7 is reduced to chromic sulphate, Cr2(SO4)3 in which chromium is in +3 state Vikasana - CET 2012 ...
PDF - ACS Publications - American Chemical Society
... ABSTRACT: We begin with a brief historical review of the development of our understanding of the normal ordering of nd orbitals of a transition metal interacting with ligands, the most common cases being three below two in an octahedral environment, two below three in tetrahedral coordination, and f ...
... ABSTRACT: We begin with a brief historical review of the development of our understanding of the normal ordering of nd orbitals of a transition metal interacting with ligands, the most common cases being three below two in an octahedral environment, two below three in tetrahedral coordination, and f ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry 4.1
... In a covalent bond, electrons are attracted to two nuclei, but sometimes one nucleus attracts the electrons more strongly than the other. When one nucleus attracts the electrons more strongly, the bonding electrons are located closer to one nucleus than the other. This creates an uneven distribution ...
... In a covalent bond, electrons are attracted to two nuclei, but sometimes one nucleus attracts the electrons more strongly than the other. When one nucleus attracts the electrons more strongly, the bonding electrons are located closer to one nucleus than the other. This creates an uneven distribution ...
Packet 1 - Kentucky Community and Technical College System
... Step 2 Consider the various solids that could form. To do this, simply exchange the anions (or the cations) of the added salts. Step 3 Use the solubility rules to decide whether a solid forms and, if so, to predict the identity of the solid. CHE 170 Packet 4 - 50 ...
... Step 2 Consider the various solids that could form. To do this, simply exchange the anions (or the cations) of the added salts. Step 3 Use the solubility rules to decide whether a solid forms and, if so, to predict the identity of the solid. CHE 170 Packet 4 - 50 ...
МІНІСТЕРСТВО ОХОРОНИ ЗДОРОВ`Я УКРАЇНИ ХАРКІВСЬКИЙ
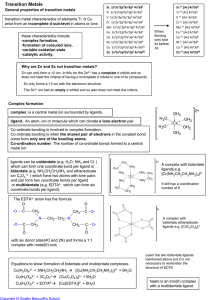
... [Pt(NH3)Cl3], and K2[PtCl4]. Cyclic or chelate (from the Greek word «chele» – claw) complex compounds contain a bi- or polydentate ligand that grips the central atom, as it were, like the claws of a crab. Chelating ligand is attached by two or more donor atoms to the same central metal ion forming a ...
... [Pt(NH3)Cl3], and K2[PtCl4]. Cyclic or chelate (from the Greek word «chele» – claw) complex compounds contain a bi- or polydentate ligand that grips the central atom, as it were, like the claws of a crab. Chelating ligand is attached by two or more donor atoms to the same central metal ion forming a ...
Manganese catalysts in homogeneous oxidation reactions Brinksma
... PS II consists of light harvesting pigments, a water oxidation centre (WOC), and electron transfer components.5 Based on many spectroscopic measurements it has been recognised that a tetranuclear Mn-cluster is the active catalyst for the oxygen evolution, which has been recently confirmed by the cry ...
... PS II consists of light harvesting pigments, a water oxidation centre (WOC), and electron transfer components.5 Based on many spectroscopic measurements it has been recognised that a tetranuclear Mn-cluster is the active catalyst for the oxygen evolution, which has been recently confirmed by the cry ...
Photo-catalytic oxidation of a di-nuclear manganese centre in an
... for BFR was initially produced with two MnII ions bound in the metal binding site [21,23] (Fig. 1a.). Either Mn or Fe metal ions can selectively bind at the active enzymatic site. The BFR protein selfassembles to produce a large spherical-shaped shell, made up of 12 homodimeric units, that enclose a ...
... for BFR was initially produced with two MnII ions bound in the metal binding site [21,23] (Fig. 1a.). Either Mn or Fe metal ions can selectively bind at the active enzymatic site. The BFR protein selfassembles to produce a large spherical-shaped shell, made up of 12 homodimeric units, that enclose a ...
Mineralization of Drugs in Aqueous Medium by Advanced Oxidation
... This procedure is known as anodic oxidation with H2O2 electrogeneration. The electro-Fenton process involves the enhancement of the oxidizing power of the above electrolytic system by adding small amounts of a catalyst like Fe2+, which reacts with electrogenerated H2O2 to yield •OH in solution from ...
... This procedure is known as anodic oxidation with H2O2 electrogeneration. The electro-Fenton process involves the enhancement of the oxidizing power of the above electrolytic system by adding small amounts of a catalyst like Fe2+, which reacts with electrogenerated H2O2 to yield •OH in solution from ...