Contributions to the chemistry of group 15 and 16 hypervalent
... The organometallic bismuth compounds can increase their valence by extended bonding. For organobismuth compounds, several hypercoordinated systems were already reported in the literature. Organometallic compounds of type 8-Bi-3 6 present themselves as generally having a trigonal pyramidal structure. ...
... The organometallic bismuth compounds can increase their valence by extended bonding. For organobismuth compounds, several hypercoordinated systems were already reported in the literature. Organometallic compounds of type 8-Bi-3 6 present themselves as generally having a trigonal pyramidal structure. ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... B Proteins are long chains (polymers) of amino acids. Their properties depend on their shape. This shape comes from the order of the amino acids and the way the protein “folds up” as it is formed. Hydrogen bonding plays a huge role in how a protein folds up to give it a shape. When a protein is heat ...
... B Proteins are long chains (polymers) of amino acids. Their properties depend on their shape. This shape comes from the order of the amino acids and the way the protein “folds up” as it is formed. Hydrogen bonding plays a huge role in how a protein folds up to give it a shape. When a protein is heat ...
Ch 4 Student.pptx
... • Limiting Reactant – reactant that is completely consumed and limits amount of product • Reactant in excess – reactant present in greater quantity than limiting reactant • Theoretical Yield – amount of product made based on consumption of all the limiting reactant • Actual Yield – amount of pro ...
... • Limiting Reactant – reactant that is completely consumed and limits amount of product • Reactant in excess – reactant present in greater quantity than limiting reactant • Theoretical Yield – amount of product made based on consumption of all the limiting reactant • Actual Yield – amount of pro ...
Acrobat - chemmybear.com
... However, [HA] > [A− ] (more of the acid), ∴ [H+ ] is a little larger than 3.0 x 10-6 . Ans: 6.0 x 10-6 D All compounds are 1:1 ∴ Ksp ∝ solubility [“∝” means “is proportional to”]; smallest to largest Ksp C Oxidation means an increase in oxidation #. Cr3+ → CrO 42- is an increase from (+3) → (+6) B T ...
... However, [HA] > [A− ] (more of the acid), ∴ [H+ ] is a little larger than 3.0 x 10-6 . Ans: 6.0 x 10-6 D All compounds are 1:1 ∴ Ksp ∝ solubility [“∝” means “is proportional to”]; smallest to largest Ksp C Oxidation means an increase in oxidation #. Cr3+ → CrO 42- is an increase from (+3) → (+6) B T ...
w_4-3 Chemistry of Nitrogen Compounds
... The decomposition of the monochloro derivative is first order with a half–life of 46 min at 25°C over the pH range 5–9. The apparent activation energy is 26.6 Kcal. The acetaldehyde formed will be oxidized by free chlorine to acetic acid (CH3CHO + HOCl → CH3COOH + HCl), whereas the ammonium ion can ...
... The decomposition of the monochloro derivative is first order with a half–life of 46 min at 25°C over the pH range 5–9. The apparent activation energy is 26.6 Kcal. The acetaldehyde formed will be oxidized by free chlorine to acetic acid (CH3CHO + HOCl → CH3COOH + HCl), whereas the ammonium ion can ...
FREE Sample Here
... B) the two atoms sharing electrons are equally electronegative. C) oxygen is one of the two atoms sharing electrons. D) one of the atoms has absorbed more energy than the other atom. E) the two atoms sharing electrons are different elements. Answer: A Topic: Concept 2.3 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehensio ...
... B) the two atoms sharing electrons are equally electronegative. C) oxygen is one of the two atoms sharing electrons. D) one of the atoms has absorbed more energy than the other atom. E) the two atoms sharing electrons are different elements. Answer: A Topic: Concept 2.3 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehensio ...
Monodisperse Samarium and Cerium Orthovanadate Nanocrystals
... area, thermal stability, and oxygen storage/release capacity (OSC).1-3 These materials have been used as oxygen ion conductors in solid oxide fuel cells, as three way catalysts (TWCs), and as high-activity catalysts in oxidative dehydrogenation of propane to propene and selective oxidation of hydrog ...
... area, thermal stability, and oxygen storage/release capacity (OSC).1-3 These materials have been used as oxygen ion conductors in solid oxide fuel cells, as three way catalysts (TWCs), and as high-activity catalysts in oxidative dehydrogenation of propane to propene and selective oxidation of hydrog ...
FREE Sample Here
... B) the two atoms sharing electrons are equally electronegative. C) oxygen is one of the two atoms sharing electrons. D) one of the atoms has absorbed more energy than the other atom. E) the two atoms sharing electrons are different elements. Answer: A Topic: Concept 2.3 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehensio ...
... B) the two atoms sharing electrons are equally electronegative. C) oxygen is one of the two atoms sharing electrons. D) one of the atoms has absorbed more energy than the other atom. E) the two atoms sharing electrons are different elements. Answer: A Topic: Concept 2.3 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehensio ...
Kinetic investigation of low-pH Fe(II) oxidation and development of a
... mainly from the group Acidithiobacillus Ferrooxidans. However, this method suffers from two major drawbacks: (1) the dependence of the process on the sensitive autotrophic biomass and (2) the relatively rapid precipitation of Fe(III) solids, mostly of the jarosite group. The current work investigate ...
... mainly from the group Acidithiobacillus Ferrooxidans. However, this method suffers from two major drawbacks: (1) the dependence of the process on the sensitive autotrophic biomass and (2) the relatively rapid precipitation of Fe(III) solids, mostly of the jarosite group. The current work investigate ...
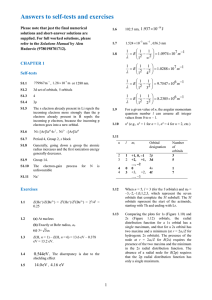
Answers to Self-Tests and Exercises
... As a consequence of these two trends, the valence electrons are held tighter and closer to the atomic nucleus. This means that, as we move from left to right, the distance between two non-metallic atoms has to decrease in order for the covalent bond to be formed. This results in a shorter internucle ...
... As a consequence of these two trends, the valence electrons are held tighter and closer to the atomic nucleus. This means that, as we move from left to right, the distance between two non-metallic atoms has to decrease in order for the covalent bond to be formed. This results in a shorter internucle ...
4 Molecular Symmetry - Beck-Shop
... 4.14 Elemental sulfur, S8 , has the “crown” structure shown below (left). Viewed from the “top”, this structure becomes an octagon. This octagon is also shown below (right), where the “+” sign denotes atoms that are above the paper plane and the “−” sign indicates atoms below. All eight atoms are la ...
... 4.14 Elemental sulfur, S8 , has the “crown” structure shown below (left). Viewed from the “top”, this structure becomes an octagon. This octagon is also shown below (right), where the “+” sign denotes atoms that are above the paper plane and the “−” sign indicates atoms below. All eight atoms are la ...
Density Functional Theory Study of the Interaction of 2
... configuration of gold atom Au(0) is described as [Xe]4f145d106s1 [63] the last orbital 6s1 is occupied by one electron, so this atom can donate and accept one electron to become more stable as shown in the following configuration[Xe]4f145d10s2. Furthermore, the donate electron is given to sulfur ato ...
... configuration of gold atom Au(0) is described as [Xe]4f145d106s1 [63] the last orbital 6s1 is occupied by one electron, so this atom can donate and accept one electron to become more stable as shown in the following configuration[Xe]4f145d10s2. Furthermore, the donate electron is given to sulfur ato ...