General Physical Chemistry I
... à equivalent to saying that the piston is at equilibrium at all stages of the expansion (forces are balanced: pext S = pS )" A system that remains in mechanical equilibrium with its surroundings at all stages of the expansion performs maximum expansion work" If pext = p, expansion/compression can ...
... à equivalent to saying that the piston is at equilibrium at all stages of the expansion (forces are balanced: pext S = pS )" A system that remains in mechanical equilibrium with its surroundings at all stages of the expansion performs maximum expansion work" If pext = p, expansion/compression can ...
pptx
... DFT is a ground-state theory for electrons But many processes involve exciting electrons: • Transport of electrons, electron energy levels • Excited electrons ...
... DFT is a ground-state theory for electrons But many processes involve exciting electrons: • Transport of electrons, electron energy levels • Excited electrons ...
Unit 1B1 - Uddingston Grammar School
... Atoms P and Q have the same number of protons Atoms Q and R have the same number of electrons Atoms P and S have the same number of neutrons Atoms R and S are isotopes of each other Atoms S and T have different chemical properties. ...
... Atoms P and Q have the same number of protons Atoms Q and R have the same number of electrons Atoms P and S have the same number of neutrons Atoms R and S are isotopes of each other Atoms S and T have different chemical properties. ...
Chapter 7 - Chemical Reactions
... Given the balanced equation above for the reaction of calcium carbide and water, how many grams of calcium carbide, CaC2 will react with 3 moles of water? ...
... Given the balanced equation above for the reaction of calcium carbide and water, how many grams of calcium carbide, CaC2 will react with 3 moles of water? ...
Chapter 2 What Is Matter
... If a mixture contains large particles dispersed in a liquid or a gas that will settle out, it is classified as a suspension. If the particles of a suspension are not stirred constantly, they will settle out. Particles of a suspension can also be filtered out. The particles are large enough to be ca ...
... If a mixture contains large particles dispersed in a liquid or a gas that will settle out, it is classified as a suspension. If the particles of a suspension are not stirred constantly, they will settle out. Particles of a suspension can also be filtered out. The particles are large enough to be ca ...
The Gaseous State - Soegijapranata Catholic University
... Substances that exist as gases • Ionic compounds can’t be present in gas state under normal condition (25oC, 1atm). But they can be converted to gas at high temperature. Ex: NaCl • Molecular compounds such as CO, CO2, HCl, NH3, CH4 are gases. The majority of molecular compounds are solid or liquid ...
... Substances that exist as gases • Ionic compounds can’t be present in gas state under normal condition (25oC, 1atm). But they can be converted to gas at high temperature. Ex: NaCl • Molecular compounds such as CO, CO2, HCl, NH3, CH4 are gases. The majority of molecular compounds are solid or liquid ...
Final Exam Review
... 30. Which of the following electron configurations for neutral atoms in their lowest energy state is not correct? (Ch. 11) a. fluorine 1s22s22px22py22pz1 b. rubidium [Kr] 5s1 c. scandium 1s22s22p63s23p64s24px1 d. zinc [Ar] 4s23d10 e. germanium [Ar] 4s23d104px14py1 31. When a 9.81-gram sample of sulf ...
... 30. Which of the following electron configurations for neutral atoms in their lowest energy state is not correct? (Ch. 11) a. fluorine 1s22s22px22py22pz1 b. rubidium [Kr] 5s1 c. scandium 1s22s22p63s23p64s24px1 d. zinc [Ar] 4s23d10 e. germanium [Ar] 4s23d104px14py1 31. When a 9.81-gram sample of sulf ...
Name:_____________ Chemistry 114 Second Hour Exam
... HF will form intermolecular hydrogen bonds, HCl won’t; this will give HF stronger intermolecular interactions and give it a higher boiling point. I2 has a lower vapor pressure than Cl2 at room temperature. I2 is larger that Cl2, this will make its London force larger to give it stronger intermolecul ...
... HF will form intermolecular hydrogen bonds, HCl won’t; this will give HF stronger intermolecular interactions and give it a higher boiling point. I2 has a lower vapor pressure than Cl2 at room temperature. I2 is larger that Cl2, this will make its London force larger to give it stronger intermolecul ...
chapter16StarBirth
... • As contraction packs the molecules and dust particles of a cloud fragment closer together, it becomes harder for infrared and radio photons to escape • Thermal energy then begins to build up inside, increasing the internal pressure ...
... • As contraction packs the molecules and dust particles of a cloud fragment closer together, it becomes harder for infrared and radio photons to escape • Thermal energy then begins to build up inside, increasing the internal pressure ...
Atomic Structure Electrons in Atoms
... • Bohr proposed: – Electrons move around the nucleus in circular orbits (“rings”) with distinct energy levels • smaller orbits have lower energy, larger orbits higher energy – In other words, electrons found closer to the nucleus has less energy than electrons found at greater distances from the nuc ...
... • Bohr proposed: – Electrons move around the nucleus in circular orbits (“rings”) with distinct energy levels • smaller orbits have lower energy, larger orbits higher energy – In other words, electrons found closer to the nucleus has less energy than electrons found at greater distances from the nuc ...
Unit 2: Atoms and Ions Homework Booklet
... 3. Read the following passage and list the raw materials and their products in the form of a table. It’s quite surprising what chemists do! They make useful substances like soaps and bleach from raw materials such as sea water. Crude oil which is a sticky black mixture, can be manufactured into lubr ...
... 3. Read the following passage and list the raw materials and their products in the form of a table. It’s quite surprising what chemists do! They make useful substances like soaps and bleach from raw materials such as sea water. Crude oil which is a sticky black mixture, can be manufactured into lubr ...
A historical perspective on the discovery of neutron stars
... fully ionized and all electrons are free. However electrons are fermions and due to the Pauli exclusion principle (1925), they cannot occupy the same quantum state. Only four months after Dirac published his paper about the statistics of fermions, R.H. Fowler realized that this is the electron degen ...
... fully ionized and all electrons are free. However electrons are fermions and due to the Pauli exclusion principle (1925), they cannot occupy the same quantum state. Only four months after Dirac published his paper about the statistics of fermions, R.H. Fowler realized that this is the electron degen ...
A. Atomic and Nuclear Structure
... with a mass of about 1.007 atomic mass units (1.673 x 10 grams). Neutrons are neutral, or uncharged. Neutrons have a mass slightly larger than the proton, about 1.008 atomic ...
... with a mass of about 1.007 atomic mass units (1.673 x 10 grams). Neutrons are neutral, or uncharged. Neutrons have a mass slightly larger than the proton, about 1.008 atomic ...
powerpoint
... in continuous, random straight line motion 2. Not all particles have same KE, avg KE of particles=temp of gas 3. Elastic collisions between particlestransfer of energy w/ no loss(Total energy stays the same.) 4. Volume of gas particles ignored compared to volume of space in which they contain. 5. G ...
... in continuous, random straight line motion 2. Not all particles have same KE, avg KE of particles=temp of gas 3. Elastic collisions between particlestransfer of energy w/ no loss(Total energy stays the same.) 4. Volume of gas particles ignored compared to volume of space in which they contain. 5. G ...
Chapter 6: Stellar Evolution (part 2)
... The pair production decreases the distance that gamma rays travel in the gas, which leads to an instability: as gamma ray travel distance decreases, the temperature at the core increases, and this increases the generation of the nuclear energy and hence the gamma ray energy and further decreases the ...
... The pair production decreases the distance that gamma rays travel in the gas, which leads to an instability: as gamma ray travel distance decreases, the temperature at the core increases, and this increases the generation of the nuclear energy and hence the gamma ray energy and further decreases the ...
Chapter 16 Star Birth Where do stars form? Star
... • Degeneracy pressure halts the contraction of objects with <0.08MSun before core temperature become hot enough for fusion • Starlike objects not massive enough to start fusion are brown dwarfs ...
... • Degeneracy pressure halts the contraction of objects with <0.08MSun before core temperature become hot enough for fusion • Starlike objects not massive enough to start fusion are brown dwarfs ...
Chapter 16 Star Birth
... • As contraction packs the molecules and dust particles of a cloud fragment closer together, it becomes harder for infrared and radio photons to escape • Thermal energy then begins to build up inside, increasing the internal pressure • Contraction slows down, and the center of the cloud fragment bec ...
... • As contraction packs the molecules and dust particles of a cloud fragment closer together, it becomes harder for infrared and radio photons to escape • Thermal energy then begins to build up inside, increasing the internal pressure • Contraction slows down, and the center of the cloud fragment bec ...
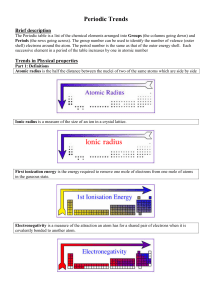
Topic 3 Periodicity notes SL - Chemical Minds
... Going down a group, the atomic radius and ionic radius increase due to an increase in the number of electron shells surrounding the nucleus. The ionisation energy and electronegativity decrease because i) there is a decrease in the electrostatic attraction between the positive protons in the nucleus ...
... Going down a group, the atomic radius and ionic radius increase due to an increase in the number of electron shells surrounding the nucleus. The ionisation energy and electronegativity decrease because i) there is a decrease in the electrostatic attraction between the positive protons in the nucleus ...
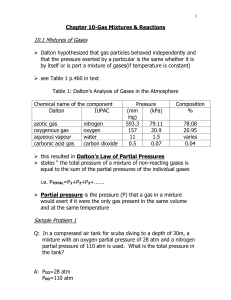
Chapter 10 Notes
... react with 125L of carbon monoxide produced during a 100km trip? A: 2CO(g) + O2(g)-----2CO2(g) 125L V=? VO2=125L CO x 1mol/2mol =62.5L ,therefore the volume of O2 required is 62.5L Answer questions 1, 3-5 on pages 468 & 469. ...
... react with 125L of carbon monoxide produced during a 100km trip? A: 2CO(g) + O2(g)-----2CO2(g) 125L V=? VO2=125L CO x 1mol/2mol =62.5L ,therefore the volume of O2 required is 62.5L Answer questions 1, 3-5 on pages 468 & 469. ...
Structure of atoms and solids
... The high electrical and thermal conductivities of metals follows from the ability of these free electrons to freely move throughout their crystal structure. This is not the case in covalent or ionic bonding where electrons are tightly bound to single or groups of atoms. Unlike other crystals, metals ...
... The high electrical and thermal conductivities of metals follows from the ability of these free electrons to freely move throughout their crystal structure. This is not the case in covalent or ionic bonding where electrons are tightly bound to single or groups of atoms. Unlike other crystals, metals ...
Here
... • Sirius B has a mass roughly equal to the Sun’s mass, but it is about 10,000 times fainter than the Sun while being having a surface temperature about 10 times higher than the Sun’s. • To be so faint while being hot, the radius of Sirius B must be 1% of the Sun’s radius! • The density is roughly 1. ...
... • Sirius B has a mass roughly equal to the Sun’s mass, but it is about 10,000 times fainter than the Sun while being having a surface temperature about 10 times higher than the Sun’s. • To be so faint while being hot, the radius of Sirius B must be 1% of the Sun’s radius! • The density is roughly 1. ...
S90 Notes U2 Topic 6 Chemical Compounds
... S90 Notes U2 Topic 6 Chemical Compounds Chemical compounds are formed by 2 or more elements. There are 2 types of compounds – ionic compounds and molecular compounds ...
... S90 Notes U2 Topic 6 Chemical Compounds Chemical compounds are formed by 2 or more elements. There are 2 types of compounds – ionic compounds and molecular compounds ...
AP Review – Life and Chemistry Name: Date: ___B_ 1. The atomic
... Calcium’s electrons in orbitals are shown to the left. Notice how the two electrons in the valence shell (outermost shell) are paired? This is done sometimes when only two electrons are in the valence shell – it helps to make sure you don’t “lose them” in the diagram by separating them. To draw ...
... Calcium’s electrons in orbitals are shown to the left. Notice how the two electrons in the valence shell (outermost shell) are paired? This is done sometimes when only two electrons are in the valence shell – it helps to make sure you don’t “lose them” in the diagram by separating them. To draw ...