Caboxylic acid Derivatives
... Carboxylic acid Derivatives Carboxylic acid derivatives are described as compounds that can be converted to carboxylic acids via simple acidic or basic hydrolysis. The most important acid derivatives are esters, amides and nitriles, although acid halides and anhydrides are also derivatives (really a ...
... Carboxylic acid Derivatives Carboxylic acid derivatives are described as compounds that can be converted to carboxylic acids via simple acidic or basic hydrolysis. The most important acid derivatives are esters, amides and nitriles, although acid halides and anhydrides are also derivatives (really a ...
PREPARATION, STRUCTURAL STUDIES AND CHEMICAL
... 1. The first reported preparation of a hypervalent iodine (III) compound…………..……1 2. Structural types of hypervalent iodine compounds…………………………………….2 3. Common classes of hypervalent iodine(III) and (V) compounds…………………….. 4 4. Known classes of heterocyclic hypervalent iodine compounds………………..………5 5 ...
... 1. The first reported preparation of a hypervalent iodine (III) compound…………..……1 2. Structural types of hypervalent iodine compounds…………………………………….2 3. Common classes of hypervalent iodine(III) and (V) compounds…………………….. 4 4. Known classes of heterocyclic hypervalent iodine compounds………………..………5 5 ...
CHE2060 Lecture 5: Acid-base chemistry CHE2060 Lecture 5: Acid
... Deprotonated dimethyl amine is a powerful base. Its conjugate acid, dimethyl amine, has a pKa of 38! • For bases, the equilibrium is pushed towards the acid with the higher pKa. • The strength of deprotonated dimethyl amine pushes equilibrium towards products by a factor of 2.oE22! • Howeve ...
... Deprotonated dimethyl amine is a powerful base. Its conjugate acid, dimethyl amine, has a pKa of 38! • For bases, the equilibrium is pushed towards the acid with the higher pKa. • The strength of deprotonated dimethyl amine pushes equilibrium towards products by a factor of 2.oE22! • Howeve ...
Chapter 16-18 - Bakersfield College
... – Reduction of a ketone gives a secondary alcohol (-CHOH-). ...
... – Reduction of a ketone gives a secondary alcohol (-CHOH-). ...
15.1 Amines
... •Amino acids-monomers of proteins. Have both amino group and Carboxyl group •Reactions: Amines are weak bases. The lone electron pair attracts H+ (Remember-acids donate H+ and bases accept H+) •Physical properties- smaller ones are polar, but weaker than alcohols (O eneg is 3.5; N is 3.0) ...
... •Amino acids-monomers of proteins. Have both amino group and Carboxyl group •Reactions: Amines are weak bases. The lone electron pair attracts H+ (Remember-acids donate H+ and bases accept H+) •Physical properties- smaller ones are polar, but weaker than alcohols (O eneg is 3.5; N is 3.0) ...
Petrochemicals - MullisChemistry
... LONGEST STRAIGHT chain of carbon atoms. Add the name of the alkyl groups attached to the chain. If more than one group is attached, use the proper numerical prefix to indicate how many groups are attached. (2=di, 3-tri,etc.) Assign numbers to the carbons in the parent chain. Assign so that attached ...
... LONGEST STRAIGHT chain of carbon atoms. Add the name of the alkyl groups attached to the chain. If more than one group is attached, use the proper numerical prefix to indicate how many groups are attached. (2=di, 3-tri,etc.) Assign numbers to the carbons in the parent chain. Assign so that attached ...
PDF carboxylic acids
... Let us discuss them one by one. i) Reactions due to hydroxyl hydrogen – Because of their acidic nature these compounds readily react with base in polar medium to form corresponding ionic salts which are soluble in water. For example RCOOH + NaHCO3 ...
... Let us discuss them one by one. i) Reactions due to hydroxyl hydrogen – Because of their acidic nature these compounds readily react with base in polar medium to form corresponding ionic salts which are soluble in water. For example RCOOH + NaHCO3 ...
REASONING QUESTIONS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... even alcohols of comparable molecular masses. Explain. Ans: Carboxylic acids are higher boiling liquids than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable molecular masses. This is due to more extensive association of carboxylic acid molecules through intermolecular hydrogen bonding. The hydrog ...
... even alcohols of comparable molecular masses. Explain. Ans: Carboxylic acids are higher boiling liquids than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable molecular masses. This is due to more extensive association of carboxylic acid molecules through intermolecular hydrogen bonding. The hydrog ...
REASONING QUESTIONS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY TEXT
... even alcohols of comparable molecular masses. Explain. Ans: Carboxylic acids are higher boiling liquids than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable molecular masses. This is due to more extensive association of carboxylic acid molecules through intermolecular hydrogen bonding. The hydrog ...
... even alcohols of comparable molecular masses. Explain. Ans: Carboxylic acids are higher boiling liquids than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable molecular masses. This is due to more extensive association of carboxylic acid molecules through intermolecular hydrogen bonding. The hydrog ...
CHM238-01 EXAM 2 October 14, 2002 103
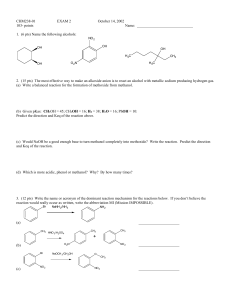
... 5. (12 pts) Preparation of alcohols by Grignard reagents reacted with C=O compounds is very important. (a) If the Grignard reagent were phenyl Grignard, PhMgBr, what C=O compound would be the best one to use in order to make the following alcohols. If it doesn’t work, write NR. (b) If the Grignard ...
... 5. (12 pts) Preparation of alcohols by Grignard reagents reacted with C=O compounds is very important. (a) If the Grignard reagent were phenyl Grignard, PhMgBr, what C=O compound would be the best one to use in order to make the following alcohols. If it doesn’t work, write NR. (b) If the Grignard ...
chm238f02.exam2
... (c) Which reagent(s) would you use if you wanted to substitute the alcohol with bromide in the same position and with inversion of configuration, without any rearrangement. ...
... (c) Which reagent(s) would you use if you wanted to substitute the alcohol with bromide in the same position and with inversion of configuration, without any rearrangement. ...
CHEM 121 Chapter 14. Name: Date: ______ 1. The simplest alcohol
... 23. The solubility of alcohols in water A) decreases as the carbon chain length increases. B) decreases as the number of –OH groups present increases. C) increases with increasing molecular mass. D) more than one correct response E) no correct response 24. In a secondary alcohol, the hydroxyl-bearin ...
... 23. The solubility of alcohols in water A) decreases as the carbon chain length increases. B) decreases as the number of –OH groups present increases. C) increases with increasing molecular mass. D) more than one correct response E) no correct response 24. In a secondary alcohol, the hydroxyl-bearin ...
4-Dimethylaminopyridine - Sigma
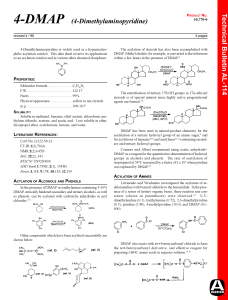
... DMAP has been used in natural-product chemistry for the acetylation of a tertiary hydroxyl group of an amino sugar,9 and for acylations of terpenes4,10 and acetylenes11,12 containing secondary and tertiary hydroxyl groups. Connors and Albert recommend using acetic anhydride/DMAP as a reagent for the ...
... DMAP has been used in natural-product chemistry for the acetylation of a tertiary hydroxyl group of an amino sugar,9 and for acylations of terpenes4,10 and acetylenes11,12 containing secondary and tertiary hydroxyl groups. Connors and Albert recommend using acetic anhydride/DMAP as a reagent for the ...
Developments in Synthetic Application of Selenium(IV) Oxide and
... Owing to the synthetic utility of the oxofunctionalization of a broad spectrum of organic substrates, oxidation is one of the fundamental processes, very often applied in contemporary organic synthesis in both research and industry. Among various oxidants selenium compounds, mainly selenium(IV) oxid ...
... Owing to the synthetic utility of the oxofunctionalization of a broad spectrum of organic substrates, oxidation is one of the fundamental processes, very often applied in contemporary organic synthesis in both research and industry. Among various oxidants selenium compounds, mainly selenium(IV) oxid ...
Forward
... and water at 100°C, distillation of the fermentation broth can be used to give “distilled spirits” of increased ethanol content. Whiskey is the aged distillate of fermented grain and contains slightly less than 50% ethanol. Brandy and cognac are made by aging the distilled spirits from fermented gra ...
... and water at 100°C, distillation of the fermentation broth can be used to give “distilled spirits” of increased ethanol content. Whiskey is the aged distillate of fermented grain and contains slightly less than 50% ethanol. Brandy and cognac are made by aging the distilled spirits from fermented gra ...
Chem341_outcomes
... thiols, including primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols, diols, and poliols Understand the presence of hydroxyl as a major factor determining specific physical and chemical properties of alcohols, including their high boiling points, their acidity and basicity Understand nucleophilic aliphatic s ...
... thiols, including primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols, diols, and poliols Understand the presence of hydroxyl as a major factor determining specific physical and chemical properties of alcohols, including their high boiling points, their acidity and basicity Understand nucleophilic aliphatic s ...
12_chemistry_impq_CH10_haloalkanes_and_haloarenes_02
... density at ortho and para position as follows Since phenol has higher electron density due to electron releasing nature of -OH group , compared to benzene , therefore nitration is easy in phenol than benzene. Q5. How will you account for the following? Ethers possess a net dipole moment even if they ...
... density at ortho and para position as follows Since phenol has higher electron density due to electron releasing nature of -OH group , compared to benzene , therefore nitration is easy in phenol than benzene. Q5. How will you account for the following? Ethers possess a net dipole moment even if they ...
Lecture - Ch 21
... • Conversion of acid chlorides into alcohols: Reduction and Grignard reaction – LiAlH4 reduces acid chlorides to yield aldehydes and then primary alcohols in a ...
... • Conversion of acid chlorides into alcohols: Reduction and Grignard reaction – LiAlH4 reduces acid chlorides to yield aldehydes and then primary alcohols in a ...
NOTES ON THE INTERPRETATION OF NMR SPECTRA The nuclei
... bonding affects the frequency much less than for the O-H absorptions. N-H peaks are usually sharper but weaker in intensity than O-H peaks. It is possible to distinguish between primary and secondary amines and amides on the basis of these N-H absorptions. Ths -NH- group (secondary) gives rise to a ...
... bonding affects the frequency much less than for the O-H absorptions. N-H peaks are usually sharper but weaker in intensity than O-H peaks. It is possible to distinguish between primary and secondary amines and amides on the basis of these N-H absorptions. Ths -NH- group (secondary) gives rise to a ...
Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers
... hydroxyl (—OH) group is attached. The name for this chain is obtained by dropping the final -e from the name of the hydrocarbon parent name and adding the ending -ol. • Step 2. Number the longest chain to give the lowest possible number to the carbon bearing the hydroxyl ...
... hydroxyl (—OH) group is attached. The name for this chain is obtained by dropping the final -e from the name of the hydrocarbon parent name and adding the ending -ol. • Step 2. Number the longest chain to give the lowest possible number to the carbon bearing the hydroxyl ...
Redox reactions_organic - Welcome to SALEM
... it does not react with water the reduction reactions using NaBH4 can be carried out in water or alcohols ...
... it does not react with water the reduction reactions using NaBH4 can be carried out in water or alcohols ...
The Effects of Ozone on Compounds in Epicuticular Waxes in Plant
... productivity of the plants by predisposing them to pest attack and decrease their efficacy of water use. Ozone can also be a phytotoxic substance at certain concentrations, which can stunt plant growth and development. As ozone enters the plant tissues through the stomata, reactive oxygen species (R ...
... productivity of the plants by predisposing them to pest attack and decrease their efficacy of water use. Ozone can also be a phytotoxic substance at certain concentrations, which can stunt plant growth and development. As ozone enters the plant tissues through the stomata, reactive oxygen species (R ...
Name Reactions in Heterocyclic Chemistry-II
... remained undetected and were thrown away, although in some cases they were probably the major reaction products. In 1931, H. Hopff working for I. G. Farbenindustrie in Germany had published results concerning the reaction of carbon monoxide at high pressure (around 100 atm.) with alkanes and cycloal ...
... remained undetected and were thrown away, although in some cases they were probably the major reaction products. In 1931, H. Hopff working for I. G. Farbenindustrie in Germany had published results concerning the reaction of carbon monoxide at high pressure (around 100 atm.) with alkanes and cycloal ...
carboxylic acid
... Chemistry of Acid Halides Conversion of Acid Halides into Anhydrides • Nucleophilic acyl substitution of an acid chloride with a carboxylate anion gives an acid anhydride • Both symmetrical and unsymmetrical anhydrides ...
... Chemistry of Acid Halides Conversion of Acid Halides into Anhydrides • Nucleophilic acyl substitution of an acid chloride with a carboxylate anion gives an acid anhydride • Both symmetrical and unsymmetrical anhydrides ...
Phenols

In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest of the class is phenol, which is also called carbolic acid C6H5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule.Synonyms are arenols or aryl alcohols.Phenolic compounds are synthesized industrially; they also are produced by plants and microorganisms, with variation between and within species.Although similar to alcohols, phenols have unique properties and are not classified as alcohols (since the hydroxyl group is not bonded to a saturated carbon atom). They have higher acidities due to the aromatic ring's tight coupling with the oxygen and a relatively loose bond between the oxygen and hydrogen. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids (their pKa is usually between 10 and 12).Loss of a positive hydrogen ion (H+) from the hydroxyl group of a phenol forms a corresponding negative phenolate ion or phenoxide ion, and the corresponding salts are called phenolates or phenoxides, although the term aryloxides is preferred according to the IUPAC Gold Book. Phenols can have two or more hydroxy groups bonded to the aromatic ring(s) in the same molecule. The simplest examples are the three benzenediols, each having two hydroxy groups on a benzene ring.Organisms that synthesize phenolic compounds do so in response to ecological pressures such as pathogen and insect attack, UV radiation and wounding. As they are present in food consumed in human diets and in plants used in traditional medicine of several cultures, their role in human health and disease is a subject of research.ref name=Klepacka Some phenols are germicidal and are used in formulating disinfectants. Others possess estrogenic or endocrine disrupting activity.