Sensory Disorders
... Results from injury to brain in which the skull is penetrated either by projectiles (gunshots/missile wounds) or other moving objects. ...
... Results from injury to brain in which the skull is penetrated either by projectiles (gunshots/missile wounds) or other moving objects. ...
7-Sheep Brain
... The line here divides the PITUITARY into its two parts NEUROHYPOPHYSIS and ADENOHYPOPHYSIS . ...
... The line here divides the PITUITARY into its two parts NEUROHYPOPHYSIS and ADENOHYPOPHYSIS . ...
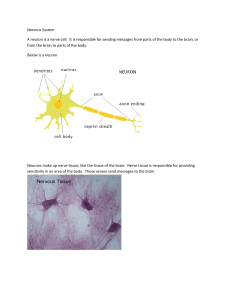
Nervous System A neuron is a nerve cell. It is responsible for
... signals that make the organs of our bodies function properly. The brain is why we blink, breathe and our hearts beat without thinking about it or being able to really stop it for very long. The brain is also responsible for thinking, dreaming, learning and more. ...
... signals that make the organs of our bodies function properly. The brain is why we blink, breathe and our hearts beat without thinking about it or being able to really stop it for very long. The brain is also responsible for thinking, dreaming, learning and more. ...
Central Tendency” - North Dakota State University
... a. axons grow faster than dendrites in order to play a role in shaping dendritic growth b. axons grow faster than dendrites in order to reach a larger maximum size c. dendrite grow faster than axons in order to play a role in shaping axonal growth d. dendrite grow faster than axons in order to reach ...
... a. axons grow faster than dendrites in order to play a role in shaping dendritic growth b. axons grow faster than dendrites in order to reach a larger maximum size c. dendrite grow faster than axons in order to play a role in shaping axonal growth d. dendrite grow faster than axons in order to reach ...
Nervous System Bookwork—KEY
... generates the action potential, which is then self-propagating. This event is quickly followed by a second permeability change that restricts Na + entry but allows K+ to leave the neuron, causing repolarization. One way conduction occurs at synapse because axons (not dendrites) release the neurotran ...
... generates the action potential, which is then self-propagating. This event is quickly followed by a second permeability change that restricts Na + entry but allows K+ to leave the neuron, causing repolarization. One way conduction occurs at synapse because axons (not dendrites) release the neurotran ...
Chapter 12
... determines which of these signals to forward to the cerebral cortex Hypothalamus - regulates the pituitary gland, body T, food intake, emotion, sleep-wake cycle and memory; controls autonomic functions (heart rate, respiration, blood pressure) ...
... determines which of these signals to forward to the cerebral cortex Hypothalamus - regulates the pituitary gland, body T, food intake, emotion, sleep-wake cycle and memory; controls autonomic functions (heart rate, respiration, blood pressure) ...
Language & Brain Lecture 120110
... Most of what we know about the brain comes from brain damage - Damage to specific regions often produces specific deficits - e.g., In the 1800s, Broca observed that damage to the left frontal lobe led to language deficits (aphasia) - This is how it was first discovered that different parts of the br ...
... Most of what we know about the brain comes from brain damage - Damage to specific regions often produces specific deficits - e.g., In the 1800s, Broca observed that damage to the left frontal lobe led to language deficits (aphasia) - This is how it was first discovered that different parts of the br ...
Key Learning Guide - City Vision University
... 5. Neurons have a central body with wispy tendrils called ___________________. ...
... 5. Neurons have a central body with wispy tendrils called ___________________. ...
SNS—brain and spinal cord
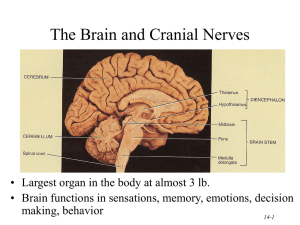
... Brain—control center of the nervous system surrounded by the skull which provides protection and support. Two hemispheres and four major regions. Left and right hemisphere. Four regions: Cerebrum, diencephalons, brain stem, cerebellum. Pg 1470 fig. Tables Each hemisphere: temporal, front ...
... Brain—control center of the nervous system surrounded by the skull which provides protection and support. Two hemispheres and four major regions. Left and right hemisphere. Four regions: Cerebrum, diencephalons, brain stem, cerebellum. Pg 1470 fig. Tables Each hemisphere: temporal, front ...
Brain
... • It is divided into 6 major parts: – The cerebrum – The diencephalon – The mesencephalon – The cerebellum – The pons – The medulla oblongata ...
... • It is divided into 6 major parts: – The cerebrum – The diencephalon – The mesencephalon – The cerebellum – The pons – The medulla oblongata ...
biological persp
... Patterns of behavior can be inherited Cognitions, emotions and behaviors are products of neurotransmitters in the brain and hormones in the body ...
... Patterns of behavior can be inherited Cognitions, emotions and behaviors are products of neurotransmitters in the brain and hormones in the body ...
46 Chapter Review: Fill-in-the
... deficiency of it is associated with Parkinson's disease, and anoversensitivity to it is associated with some cases of schizophrenia. 10. The control voluntary body mo;'ements, speech production, and such functions as thinking, motivation, planning for the future, impulse control, and emotional respo ...
... deficiency of it is associated with Parkinson's disease, and anoversensitivity to it is associated with some cases of schizophrenia. 10. The control voluntary body mo;'ements, speech production, and such functions as thinking, motivation, planning for the future, impulse control, and emotional respo ...
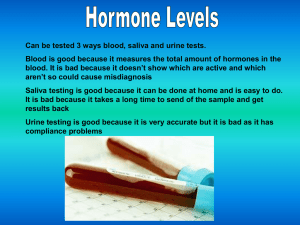
Hormone Levels and EEG (Ashanti)
... EEG is useful because the time resolution is very high. As other methods for researching brain activity have time resolution between seconds and minutes, the EEG has a resolution down to sub-millisecond. It is also good because other methods for exploring functions in the brain rely on blood flow or ...
... EEG is useful because the time resolution is very high. As other methods for researching brain activity have time resolution between seconds and minutes, the EEG has a resolution down to sub-millisecond. It is also good because other methods for exploring functions in the brain rely on blood flow or ...
14-1
... Functions of Hypothalamus • Controls and integrates activities of the ANS which regulates smooth, cardiac muscle and glands • Synthesizes regulatory hormones that control the ...
... Functions of Hypothalamus • Controls and integrates activities of the ANS which regulates smooth, cardiac muscle and glands • Synthesizes regulatory hormones that control the ...
Structure of the Nervous System
... At the center of everything… but separated by layers of membranes ...
... At the center of everything… but separated by layers of membranes ...
Document
... Not really part but… The brain is well protected Bony skull 3 protective sheets of tissue • Space in the brain is filled with fluid: – Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) – Acts as a shock absorber ...
... Not really part but… The brain is well protected Bony skull 3 protective sheets of tissue • Space in the brain is filled with fluid: – Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) – Acts as a shock absorber ...
Neurological Diseases ppt
... viral infections Symptoms – severe headache and stiff neck with pain Need to seek immediate medical attention ...
... viral infections Symptoms – severe headache and stiff neck with pain Need to seek immediate medical attention ...
Chapter 18: Neurologic Emergencies
... must be recognized and EMS dispatched quickly, and the patient must be transported rapidly to an appropriate facility, such as a stroke center. Transient ischemic attacks are episodes of cerebral ischemia that resolve within 24 hours, leaving no permanent damage. They may, however, signal an underly ...
... must be recognized and EMS dispatched quickly, and the patient must be transported rapidly to an appropriate facility, such as a stroke center. Transient ischemic attacks are episodes of cerebral ischemia that resolve within 24 hours, leaving no permanent damage. They may, however, signal an underly ...
Chapter 51 Disorders of Brain Function
... – Caused by an interruption of blood flow in a cerebral vessel and are the most common type of stroke, accounting for 70–80% of all strokes. • Hemorrhagic strokes – Caused by bleeding into brain tissue, usually from a blood vessel rupture caused by hypertension, aneurysms, arteriovenous malformation ...
... – Caused by an interruption of blood flow in a cerebral vessel and are the most common type of stroke, accounting for 70–80% of all strokes. • Hemorrhagic strokes – Caused by bleeding into brain tissue, usually from a blood vessel rupture caused by hypertension, aneurysms, arteriovenous malformation ...
can - Austin Community College
... Compliance less effective & increase risk for IICP Any small increase in volume causes great increase in ICP, loss of autoregulation & Cushing's triad Herniation ...
... Compliance less effective & increase risk for IICP Any small increase in volume causes great increase in ICP, loss of autoregulation & Cushing's triad Herniation ...
can - Austin Community College
... Compliance less effective & increase risk for IICP Any small increase in volume causes great increase in ICP, loss of autoregulation & Cushing's triad Herniation ...
... Compliance less effective & increase risk for IICP Any small increase in volume causes great increase in ICP, loss of autoregulation & Cushing's triad Herniation ...
The Circulatory System - Heart and Blood
... • Take a section of healthy artery or vein from another part of body • Used to create a new pathway for blood around the blockage ...
... • Take a section of healthy artery or vein from another part of body • Used to create a new pathway for blood around the blockage ...
Intracranial pressure

Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the pressure inside the skull and thus in the brain tissue and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The body has various mechanisms by which it keeps the ICP stable, with CSF pressures varying by about 1 mmHg in normal adults through shifts in production and absorption of CSF. CSF pressure has been shown to be influenced by abrupt changes in intrathoracic pressure during coughing (intraabdominal pressure), valsalva maneuver, and communication with the vasculature (venous and arterial systems). ICP is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and, at rest, is normally 7–15 mmHg for a supine adult. Changes in ICP are attributed to volume changes in one or more of the constituents contained in the cranium. Intracranial hypertension, commonly abbreviated IH, IICP or raised ICP, is elevation of the pressure in the cranium. ICP is normally 7–15 mm Hg; at 20–25 mm Hg, the upper limit of normal, treatment to reduce ICP may be needed.