this PowerPoint - Mr. Hunsaker`s Classes
... within each temporal lobe Responsible for the formation of conscious memories such as the storage of memory for location of objects. ...
... within each temporal lobe Responsible for the formation of conscious memories such as the storage of memory for location of objects. ...
ocular manifestations of impending stroke
... Non Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy Treatment of Stroke: Diagnosis of Stroke: Two major prospective studies: ...
... Non Arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy Treatment of Stroke: Diagnosis of Stroke: Two major prospective studies: ...
File
... Movement of extremities: arms and legs are raised, let fall Eye movement: eyes must remain fixed showing lack of brain-to-motor-nerve reflex Corneal reflex: must be absent Pupil reflex: must be absent Gag reflex: must be absent Respiration (breathing) response: must be absent ...
... Movement of extremities: arms and legs are raised, let fall Eye movement: eyes must remain fixed showing lack of brain-to-motor-nerve reflex Corneal reflex: must be absent Pupil reflex: must be absent Gag reflex: must be absent Respiration (breathing) response: must be absent ...
Download PDF
... metabolism by comparison of oxygen levels in venous and arterial blood. Significantly lower levels of oxygen were found in the tissues than would have been gauged from the measurement of arterial blood gases alone. ...
... metabolism by comparison of oxygen levels in venous and arterial blood. Significantly lower levels of oxygen were found in the tissues than would have been gauged from the measurement of arterial blood gases alone. ...
Chapter5 Respiration
... the internal environment of the body. Changes in the body PCO2, pH and PO2 cause changes in alveolar ventilation designed to restore these variable to their normal values. 1.Carbon dioxide (CO2) The most important factor in the control of breathing under normal conditions Receptors: 1) Central chemo ...
... the internal environment of the body. Changes in the body PCO2, pH and PO2 cause changes in alveolar ventilation designed to restore these variable to their normal values. 1.Carbon dioxide (CO2) The most important factor in the control of breathing under normal conditions Receptors: 1) Central chemo ...
Grant Clay
... 1. Why is the cerebral cortex considered the part of the brain that makes people uniquely human? 2. How do we know what we know about the brain? 3. What are the major processes at work in the developing brain? 4. Is our behavior determined by nature, nurture, or both? 5. Why do studies of identical ...
... 1. Why is the cerebral cortex considered the part of the brain that makes people uniquely human? 2. How do we know what we know about the brain? 3. What are the major processes at work in the developing brain? 4. Is our behavior determined by nature, nurture, or both? 5. Why do studies of identical ...
Methods to Study the Brain
... within the brain are aligned in a strong magnetic field. A brief pulse of radio waves disorients the aligned atoms, and the signals released as the atoms realign are processed to form images. ...
... within the brain are aligned in a strong magnetic field. A brief pulse of radio waves disorients the aligned atoms, and the signals released as the atoms realign are processed to form images. ...
Methods to Study the Brain - Grand Haven Area Public Schools
... within the brain are aligned in a strong magnetic field. A brief pulse of radio waves disorients the aligned atoms, and the signals released as the atoms realign are processed to form images. ...
... within the brain are aligned in a strong magnetic field. A brief pulse of radio waves disorients the aligned atoms, and the signals released as the atoms realign are processed to form images. ...
GUIDELINES FORTHE DIAGNOSIS OF BRAIN DEATH
... with caloric stimulation while the head is 30° above the horizontal. In adults a minimum of 120 ml of ice water should be used. Grimacing or any other motor response to pharyngeal or tracheal suctioning is incompatible with brain death. c) Apnea. Apnea was originally defined as lack of respiration w ...
... with caloric stimulation while the head is 30° above the horizontal. In adults a minimum of 120 ml of ice water should be used. Grimacing or any other motor response to pharyngeal or tracheal suctioning is incompatible with brain death. c) Apnea. Apnea was originally defined as lack of respiration w ...
Chapter 14 - FacultyWeb
... 2. Some portions extend into the cranial cavity as dural folds. 3. It contains dural sinuses. 4. All of these are differences from spinal dura mater. ...
... 2. Some portions extend into the cranial cavity as dural folds. 3. It contains dural sinuses. 4. All of these are differences from spinal dura mater. ...
The human brain contains approximately - Lake
... Brain Facts, a book on the brain and nervous system published by the Society for Neuroscience. To find out how to get an updated version of this book, go to www.nepaahec.org and click on Brain Bee Book. For complete information -Rules-Driving Directions-Snow IssuesGo to http://academic.scranton.edu/ ...
... Brain Facts, a book on the brain and nervous system published by the Society for Neuroscience. To find out how to get an updated version of this book, go to www.nepaahec.org and click on Brain Bee Book. For complete information -Rules-Driving Directions-Snow IssuesGo to http://academic.scranton.edu/ ...
Nervous System
... injury or compression of the spinal cord or spinal nerves. Brain Tumor- an abnormal growth that involves the brain itself or its surroundings structures. Two general classes: 1. Intra- axial tumors- tumors which grow with in the substance of the brain. 2. Extraaxial tumors- tumors that originate out ...
... injury or compression of the spinal cord or spinal nerves. Brain Tumor- an abnormal growth that involves the brain itself or its surroundings structures. Two general classes: 1. Intra- axial tumors- tumors which grow with in the substance of the brain. 2. Extraaxial tumors- tumors that originate out ...
Chapter 15 - Austin Community College
... • Cavities within the cerebrum and brain stem where cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is manufactured and circulated. • Two lateral ventricles over thalamus and roll out into temporal lobes, medial third and fourth ventricles joined by cerebral aqueduct. • Lateral ventricles look like a “Rocky Mountain” she ...
... • Cavities within the cerebrum and brain stem where cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is manufactured and circulated. • Two lateral ventricles over thalamus and roll out into temporal lobes, medial third and fourth ventricles joined by cerebral aqueduct. • Lateral ventricles look like a “Rocky Mountain” she ...
Introduction to Neurophysiology
... pressure autoregulation or severe hypotension), the brain can initially protect itself from ischemia and maintain metabolic supply by increasing extraction of the required oxygen from the flow. Clinically this results in an increase AVDO2. ...
... pressure autoregulation or severe hypotension), the brain can initially protect itself from ischemia and maintain metabolic supply by increasing extraction of the required oxygen from the flow. Clinically this results in an increase AVDO2. ...
THE DOGMA OF AN AGING BRAIN
... IMPORTANT WARNING Please note that this PowerPoint Presentation contains animations. In order to view the content properly, an add-in function must be installed into the PowerPoint software. The add-in function is downloadable from the following hyperlink. Swiff Point Player ...
... IMPORTANT WARNING Please note that this PowerPoint Presentation contains animations. In order to view the content properly, an add-in function must be installed into the PowerPoint software. The add-in function is downloadable from the following hyperlink. Swiff Point Player ...
Chapter 45 Central Nervous System BRain
... • The brain is the human body's most mysterious organ. It learns. It changes. It adapts. It tells us what we see. What we hear. It lets us feel love. I think it holds our soul. But no matter how much research we do, no one can really say how all that delicate gray matter inside our skull works. And ...
... • The brain is the human body's most mysterious organ. It learns. It changes. It adapts. It tells us what we see. What we hear. It lets us feel love. I think it holds our soul. But no matter how much research we do, no one can really say how all that delicate gray matter inside our skull works. And ...
Nervous System Graphics - Beacon Learning Center
... from all the parts to the spinal cord and brain. 4. What is the spinal cord made of? Neurons make nerve tissue and the spinal cord is nerve tissue, so neurons make the spinal cord. ...
... from all the parts to the spinal cord and brain. 4. What is the spinal cord made of? Neurons make nerve tissue and the spinal cord is nerve tissue, so neurons make the spinal cord. ...
Nervous System - cloudfront.net
... Works by increasing heart rate and blood pressure, and slows down unnecessary systems Often animals will soil themselves when fighting or ...
... Works by increasing heart rate and blood pressure, and slows down unnecessary systems Often animals will soil themselves when fighting or ...
Nervous-System
... cerebral hemispheres and contains auditory and visual reflex centers Pons - Involved in Breathing Medulla Oblangata - Controls heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, swallowing ...
... cerebral hemispheres and contains auditory and visual reflex centers Pons - Involved in Breathing Medulla Oblangata - Controls heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, swallowing ...
Your Brain and What It Does
... body’s hormonal system interact, the hypothalamus maintains the body’s status quo. It monitors numerous bodily functions such as blood pressure and body temperature, as well as controlling body weight and appetite. ...
... body’s hormonal system interact, the hypothalamus maintains the body’s status quo. It monitors numerous bodily functions such as blood pressure and body temperature, as well as controlling body weight and appetite. ...
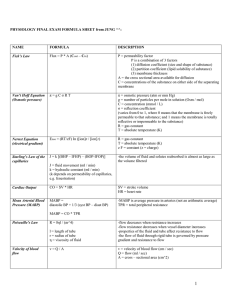
Cumulative Formula Sheet
... -flow decreases when resistance increases -flow resistance decreases when vessel diameter increases -properties of the fluid and tube affect resistance to flow -the flow of fluid through rigid tube is governed by pressure gradient and resistance to flow v = velocity of blood flow (cm / sec) Q = flow ...
... -flow decreases when resistance increases -flow resistance decreases when vessel diameter increases -properties of the fluid and tube affect resistance to flow -the flow of fluid through rigid tube is governed by pressure gradient and resistance to flow v = velocity of blood flow (cm / sec) Q = flow ...
Circulation Angina Hypertension Arrhythmias
... blood is thickened it moves more slowly than when it is very fluid and the pressure increases to push it around. * Irregularities in the surface of the blood vessels tend to slow down the flow, which increases the pressure. (Guyton 1982) There are two types of hypertension; primary and secondary. Ki ...
... blood is thickened it moves more slowly than when it is very fluid and the pressure increases to push it around. * Irregularities in the surface of the blood vessels tend to slow down the flow, which increases the pressure. (Guyton 1982) There are two types of hypertension; primary and secondary. Ki ...
Introduction to the Brain
... movement of the brain within the skull and so protects it from damage. Bleeding below this layer can result in a subdural haematoma. Bleeding above the dura can result in an extradural haematoma. The middle layer of the meninges is called the arachnoid. A bleed that occurs in the space between this ...
... movement of the brain within the skull and so protects it from damage. Bleeding below this layer can result in a subdural haematoma. Bleeding above the dura can result in an extradural haematoma. The middle layer of the meninges is called the arachnoid. A bleed that occurs in the space between this ...
Introduction to the Brain
... movement of the brain within the skull and so protects it from damage. Bleeding below this layer can result in a subdural haematoma. Bleeding above the dura can result in an extradural haematoma. The middle layer of the meninges is called the arachnoid. A bleed that occurs in the space between this ...
... movement of the brain within the skull and so protects it from damage. Bleeding below this layer can result in a subdural haematoma. Bleeding above the dura can result in an extradural haematoma. The middle layer of the meninges is called the arachnoid. A bleed that occurs in the space between this ...
Intracranial pressure

Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the pressure inside the skull and thus in the brain tissue and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The body has various mechanisms by which it keeps the ICP stable, with CSF pressures varying by about 1 mmHg in normal adults through shifts in production and absorption of CSF. CSF pressure has been shown to be influenced by abrupt changes in intrathoracic pressure during coughing (intraabdominal pressure), valsalva maneuver, and communication with the vasculature (venous and arterial systems). ICP is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and, at rest, is normally 7–15 mmHg for a supine adult. Changes in ICP are attributed to volume changes in one or more of the constituents contained in the cranium. Intracranial hypertension, commonly abbreviated IH, IICP or raised ICP, is elevation of the pressure in the cranium. ICP is normally 7–15 mm Hg; at 20–25 mm Hg, the upper limit of normal, treatment to reduce ICP may be needed.