nuclear properties
... How many neutrons in nucleus many possibilities for each element. Different isotopes of same element have different numbers of neutrons N = neutron number ex: A nucleus with 6 protons and 6 neutrons is different from a nucleus with 6 protons and 7 neutrons They are different isotopes of carbon ...
... How many neutrons in nucleus many possibilities for each element. Different isotopes of same element have different numbers of neutrons N = neutron number ex: A nucleus with 6 protons and 6 neutrons is different from a nucleus with 6 protons and 7 neutrons They are different isotopes of carbon ...
Chapter 2 - Chemistry
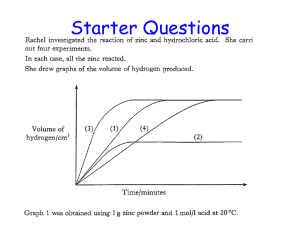
... 2.) Law of Mass Conservation - states that total mass remains constant during a chemical reaction 3.) Law of Definite Proportions - compound is type of matter containing atoms of two or more elements is definite proportions 4.) Law of Multiple Proportions - when two elements form more than one compo ...
... 2.) Law of Mass Conservation - states that total mass remains constant during a chemical reaction 3.) Law of Definite Proportions - compound is type of matter containing atoms of two or more elements is definite proportions 4.) Law of Multiple Proportions - when two elements form more than one compo ...
Module 17
... It is converted into kinetic energy of the ion zV = ½ mv2 ……………….(1) In the magnetic field (B) of the analyzer they are drawn into circular motion by the field. At equilibrium the centrifugal force (mv2/r) and centripetal force (zBv) are equal. mv2/r = zBv ……………..(2) From eqn. (1) and (2) m/z = B2r2 ...
... It is converted into kinetic energy of the ion zV = ½ mv2 ……………….(1) In the magnetic field (B) of the analyzer they are drawn into circular motion by the field. At equilibrium the centrifugal force (mv2/r) and centripetal force (zBv) are equal. mv2/r = zBv ……………..(2) From eqn. (1) and (2) m/z = B2r2 ...
Name Date Class DEFINING THE ATOM Section Review Objectives
... 9. According to Dalton’s atomic theory, atoms are composed of protons, electrons, and neutrons. 10. Atoms of elements are electrically neutral. 11. The mass of an electron is equal to the mass of a neutron. 12. The charge on all protons is the same. ...
... 9. According to Dalton’s atomic theory, atoms are composed of protons, electrons, and neutrons. 10. Atoms of elements are electrically neutral. 11. The mass of an electron is equal to the mass of a neutron. 12. The charge on all protons is the same. ...
PPT_Topic2
... Mass Spectrometer which separates atoms according to their mass. When a sample of an element is analysed the relative proportion of each isotope is given as a percentage, called the % abundance. For example when chlorine gas is analysed it is found to have two isotopes, one with a mass of 35 and one ...
... Mass Spectrometer which separates atoms according to their mass. When a sample of an element is analysed the relative proportion of each isotope is given as a percentage, called the % abundance. For example when chlorine gas is analysed it is found to have two isotopes, one with a mass of 35 and one ...
Chapter 3 STUDY GUIDE True/False Indicate whether the statement
... 24. When someone stirs cocoa powder into hot water or hot milk, the cocoa changes from a ____. a. homogeneous mixture into a compound b. homogeneous mixture into a non-uniform mixture c. compound into a heterogeneous mixture d. heterogeneous mixture into a homogeneous mixture ...
... 24. When someone stirs cocoa powder into hot water or hot milk, the cocoa changes from a ____. a. homogeneous mixture into a compound b. homogeneous mixture into a non-uniform mixture c. compound into a heterogeneous mixture d. heterogeneous mixture into a homogeneous mixture ...
Atomic Theory - Hicksville Public Schools
... Most of the atom consists of empty space (electrons are outside the nucleus) - accounts for the volume of the atom (moves around the nucleus in space) b. The mass of the atom is concentrated almost entirely in the nucleus (protons & neutrons) - nucleus is positively charged (proton) and ...
... Most of the atom consists of empty space (electrons are outside the nucleus) - accounts for the volume of the atom (moves around the nucleus in space) b. The mass of the atom is concentrated almost entirely in the nucleus (protons & neutrons) - nucleus is positively charged (proton) and ...
12_physics_notes_ch13_nuclei
... ∆ = [ Zm + ( A− Z) m ]− m p n • Binding Energy: a) It may be defined as the energy required to break a nucleus into its constituent protons and neutrons and to separate them to such a large distance that they may not interact with each ...
... ∆ = [ Zm + ( A− Z) m ]− m p n • Binding Energy: a) It may be defined as the energy required to break a nucleus into its constituent protons and neutrons and to separate them to such a large distance that they may not interact with each ...
+ The ATOM - cloudfront.net
... have different numbers of electrons. • Atoms of the same element with different numbers of electrons are called ions. • When the number of protons and electrons is different, the atom becomes charged. ...
... have different numbers of electrons. • Atoms of the same element with different numbers of electrons are called ions. • When the number of protons and electrons is different, the atom becomes charged. ...
View Transcript
... Okay, so why magic numbers? Why are these numbers appearing over and over again? For instance, a lot of these have more isotopes than they might have expected. In other words, calcium has a lot of isotopes and it’s because there’s special stability associated with 20 protons. Now why? Well, just as ...
... Okay, so why magic numbers? Why are these numbers appearing over and over again? For instance, a lot of these have more isotopes than they might have expected. In other words, calcium has a lot of isotopes and it’s because there’s special stability associated with 20 protons. Now why? Well, just as ...
Chapter 4 The structure of the atom
... Scientists were convinced this cathode ray was really a stream of charged particles -> electrons! ...
... Scientists were convinced this cathode ray was really a stream of charged particles -> electrons! ...
Ch-03 Notes
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1) Matter is made of tiny particles called atoms 2) All atoms of an element are: identical in size, mass and other properties different from those of the other elements 3) Atoms cannot be subdivided, created or destroyed 4) Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1) Matter is made of tiny particles called atoms 2) All atoms of an element are: identical in size, mass and other properties different from those of the other elements 3) Atoms cannot be subdivided, created or destroyed 4) Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other ...
ATOMS - Mr. Deets
... mass of an element from isotopic abundance, given the mass of each contributor ...
... mass of an element from isotopic abundance, given the mass of each contributor ...
Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... A. Antoine Lavoisier: Law of Conservation of Mass or Matter (1790) _________________________remains _______________during a chemical reaction; or ...
... A. Antoine Lavoisier: Law of Conservation of Mass or Matter (1790) _________________________remains _______________during a chemical reaction; or ...
Review Key
... toward the positive field. The ray bent away from the negative field. From this data, and knowing that likes repel and opposites attract, Thomson decided that since the ray is attracted to the positive field, and repelled by the negative field, it must be negative. Thus, he determined that the catho ...
... toward the positive field. The ray bent away from the negative field. From this data, and knowing that likes repel and opposites attract, Thomson decided that since the ray is attracted to the positive field, and repelled by the negative field, it must be negative. Thus, he determined that the catho ...
The Atom - Fairfield Public Schools
... What happens if the number of protons and electrons is not equal? Atoms can lose or gain electrons! If the number of protons and electrons in an atom are not equal it is called an ION. Negatively charged ion- If there are MORE electrons than protons Positively charged ion- if there are FEWER electr ...
... What happens if the number of protons and electrons is not equal? Atoms can lose or gain electrons! If the number of protons and electrons in an atom are not equal it is called an ION. Negatively charged ion- If there are MORE electrons than protons Positively charged ion- if there are FEWER electr ...
The Periodic Table HL Page 1 of 3 G. Galvin Name: Periodic Table
... -arrange elements in order of relative atomic mass and note differences with modern periodic table -define atomic number (Z) and mass number (A) -define relative atomic mass (Ar) using 12C scale -define isotope -describe the composition of isotopes using hydrogen and carbon as an example -ca ...
... -arrange elements in order of relative atomic mass and note differences with modern periodic table -define atomic number (Z) and mass number (A) -define relative atomic mass (Ar) using 12C scale -define isotope -describe the composition of isotopes using hydrogen and carbon as an example -ca ...
The Structure of the Atom
... •The laser beam consisted of positively charged alpha particles. •Hypothesized that if the Plum Pudding model of the atom was correct then the + charged alpha particles should deflect or bend slightly when in contact with the gold foil atoms. •His experimental results revealed something different. M ...
... •The laser beam consisted of positively charged alpha particles. •Hypothesized that if the Plum Pudding model of the atom was correct then the + charged alpha particles should deflect or bend slightly when in contact with the gold foil atoms. •His experimental results revealed something different. M ...
Lesson 5 Atomic Theory File
... - unlike charges (i.e. “+” and “-“ or p+ and e- ) attract each other - like charges (i.e. “+” and “+” or “-“ and “-“) repel each other ...
... - unlike charges (i.e. “+” and “-“ or p+ and e- ) attract each other - like charges (i.e. “+” and “+” or “-“ and “-“) repel each other ...
Document
... ______ b (halogen) 15) The Noble Gases are a very reactive group of mostly nonmetals whose atoms gain or share one electron in chemical reactions. a) True b) False ______ b (metals) 16) Nonmetals are good conductors of heat and electricity. a) True b) False ______ b (increasing) 17) From left to rig ...
... ______ b (halogen) 15) The Noble Gases are a very reactive group of mostly nonmetals whose atoms gain or share one electron in chemical reactions. a) True b) False ______ b (metals) 16) Nonmetals are good conductors of heat and electricity. a) True b) False ______ b (increasing) 17) From left to rig ...
Isotope

Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, although all isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons in each atom. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos (ἴσος ""equal"") and topos (τόπος ""place""), meaning ""the same place""; thus, the meaning behind the name it is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic number identifies a specific element, but not the isotope; an atom of a given element may have a wide range in its number of neutrons. The number of nucleons (both protons and neutrons) in the nucleus is the atom's mass number, and each isotope of a given element has a different mass number.For example, carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are three isotopes of the element carbon with mass numbers 12, 13 and 14 respectively. The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that every carbon atom has 6 protons, so that the neutron numbers of these isotopes are 6, 7 and 8 respectively.