Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... Fusion processes in stars have been shown to form nuclei up to 26 protons and 30 neutrons (5626Fe). ...
... Fusion processes in stars have been shown to form nuclei up to 26 protons and 30 neutrons (5626Fe). ...
Unit 5 Notes
... The band of stability can be explained by the relationship between the nuclear force and the electrostatic forces between protons. a) As the number of protons in a nucleus increases, the _____________________ electrostatic force between protons increases faster than the nuclear force. ...
... The band of stability can be explained by the relationship between the nuclear force and the electrostatic forces between protons. a) As the number of protons in a nucleus increases, the _____________________ electrostatic force between protons increases faster than the nuclear force. ...
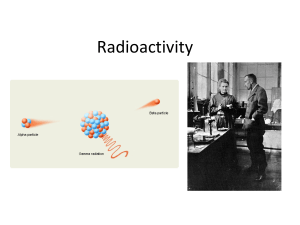
Radioactivity2015
... • The discovery of radioactivity by Becquerel and the Curies showed that one of Dalton’s ideas, that matter is indestructible and indivisible, is not always true. • Certain isotopes, because of their size and/or ratio of protons and neutrons, are not stable. • Radioisotopes have unstable, high energ ...
... • The discovery of radioactivity by Becquerel and the Curies showed that one of Dalton’s ideas, that matter is indestructible and indivisible, is not always true. • Certain isotopes, because of their size and/or ratio of protons and neutrons, are not stable. • Radioisotopes have unstable, high energ ...
atom - sandymessana
... The periodic table is a summary of all ELEMENTS in the universe, which make up MATTER. An ELEMENT is the most basic kind of matter and CAN NOT be broken down into simpler substances. ELEMENTS are pure. ...
... The periodic table is a summary of all ELEMENTS in the universe, which make up MATTER. An ELEMENT is the most basic kind of matter and CAN NOT be broken down into simpler substances. ELEMENTS are pure. ...
Chapter 3: Atom Powerpoint
... Modern Atomic Theory Revised 1. Today we know that atoms are divisible into even smaller particles. (protons, neutrons, electrons) 2. We know that a given element can have atoms with different masses. ...
... Modern Atomic Theory Revised 1. Today we know that atoms are divisible into even smaller particles. (protons, neutrons, electrons) 2. We know that a given element can have atoms with different masses. ...
weighted average - Effingham County Schools
... • Aristotle was wrong. However, his theory persisted for 2000 years. ...
... • Aristotle was wrong. However, his theory persisted for 2000 years. ...
Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... A. Antoine Lavoisier: Law of Conservation of Mass or Matter (1790) _________________________remains _______________during a chemical reaction; or ...
... A. Antoine Lavoisier: Law of Conservation of Mass or Matter (1790) _________________________remains _______________during a chemical reaction; or ...
The Atom
... a new unit was developed to mass atoms . C-12 was chosen as the reference standard. An atom of C-12 was arbitrarily assigned a mass of 12 atomic mass units. The masses of all other atoms are compared with the mass of this type of carbon atom. According to this definition, an atomic mass unit is defi ...
... a new unit was developed to mass atoms . C-12 was chosen as the reference standard. An atom of C-12 was arbitrarily assigned a mass of 12 atomic mass units. The masses of all other atoms are compared with the mass of this type of carbon atom. According to this definition, an atomic mass unit is defi ...
33 Atomic Nucleus and Radioactivity Answers and Solutions for
... 51.Gamma predominates inside the enclosed elevator because the structure of the elevator shields against alpha and beta particles better than against gamma-ray photons. 52. Because of the fact that like charges repel, and that protons have the same sign of charge (positive)as the target atomic nucle ...
... 51.Gamma predominates inside the enclosed elevator because the structure of the elevator shields against alpha and beta particles better than against gamma-ray photons. 52. Because of the fact that like charges repel, and that protons have the same sign of charge (positive)as the target atomic nucle ...
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different masses
... 7. An isotope of xenon has an atomic number of 54 and contains 77 neutrons. What is the mass of this isotope? 8. What is the mass number of uranium-234? 9. How many neutrons are in uranium 234? 10. Silicon is very important to the semiconductor industry. The three naturally occurring isotopes of sil ...
... 7. An isotope of xenon has an atomic number of 54 and contains 77 neutrons. What is the mass of this isotope? 8. What is the mass number of uranium-234? 9. How many neutrons are in uranium 234? 10. Silicon is very important to the semiconductor industry. The three naturally occurring isotopes of sil ...
Name
... Review Chemistry I Unit 2: Atomic Theory and Structure Define each of the following terms: 1. atom: 2. proton: 3. electron: 4. neutron: 5. nucleus: 6. atomic mass: 7. isotope: 8. mass number: 9. atomic number: 10. Avogadro’s number: 11. molar mass: ...
... Review Chemistry I Unit 2: Atomic Theory and Structure Define each of the following terms: 1. atom: 2. proton: 3. electron: 4. neutron: 5. nucleus: 6. atomic mass: 7. isotope: 8. mass number: 9. atomic number: 10. Avogadro’s number: 11. molar mass: ...
Honors Midterm - Stamford High School
... What is the charge on the whole atom of helium? neutral How much does a proton weigh? A neutron weigh? A electron weigh? ...
... What is the charge on the whole atom of helium? neutral How much does a proton weigh? A neutron weigh? A electron weigh? ...
Isotope

Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, although all isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons in each atom. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos (ἴσος ""equal"") and topos (τόπος ""place""), meaning ""the same place""; thus, the meaning behind the name it is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic number identifies a specific element, but not the isotope; an atom of a given element may have a wide range in its number of neutrons. The number of nucleons (both protons and neutrons) in the nucleus is the atom's mass number, and each isotope of a given element has a different mass number.For example, carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are three isotopes of the element carbon with mass numbers 12, 13 and 14 respectively. The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that every carbon atom has 6 protons, so that the neutron numbers of these isotopes are 6, 7 and 8 respectively.