File
... By 1925, Bohr’s model no longer explained all observations. In Modern theory, it is suggested that e- behave like waves on a vibrating string. ...
... By 1925, Bohr’s model no longer explained all observations. In Modern theory, it is suggested that e- behave like waves on a vibrating string. ...
Half Life
... 22. Gamma rays can be stopped by an aluminum sheet. 23. The change of an atom into a new element is called a chemical change. 24. The first artificial transmutation was performed by Albert Einstein. 25. The rate at which a radioactive element decays is known as the half-life. 26. Devices used in sma ...
... 22. Gamma rays can be stopped by an aluminum sheet. 23. The change of an atom into a new element is called a chemical change. 24. The first artificial transmutation was performed by Albert Einstein. 25. The rate at which a radioactive element decays is known as the half-life. 26. Devices used in sma ...
2_AtomicStructure
... J.J. Thomson: discovery of the electron Henri Becquerel: Discovery of radioactivity 1900's Robert Millikan: Charge and mass of the electron Ernest Rutherford: Existence of the nucleus, and its relative size Meitner & Fermi: Sustained nuclear fission Ernest Lawrence: The cyclotron and tra ...
... J.J. Thomson: discovery of the electron Henri Becquerel: Discovery of radioactivity 1900's Robert Millikan: Charge and mass of the electron Ernest Rutherford: Existence of the nucleus, and its relative size Meitner & Fermi: Sustained nuclear fission Ernest Lawrence: The cyclotron and tra ...
John Dalton William Crookes J.J. Thomson Ernest Rutherford
... apart chemists discovered that ALL matter is made of elements) ...
... apart chemists discovered that ALL matter is made of elements) ...
The History of the Atom and Its Structure
... Protons, Electrons & Neutrons. 4. Which isotope is more common? 5. How do you know # 4 above? 6. About what % of Lithium weighs 7 7. Where is most of an atoms wt. 8. What occupies most of the volume of an atom. ...
... Protons, Electrons & Neutrons. 4. Which isotope is more common? 5. How do you know # 4 above? 6. About what % of Lithium weighs 7 7. Where is most of an atoms wt. 8. What occupies most of the volume of an atom. ...
synthetic elements
... Only minute traces of technetium occur naturally in the Earth's crust—as a spontaneous fission product of uranium-238 or by neutron capture in molybdenum ores—but technetium is present naturally in red giant stars. No element with an atomic number greater than 98, (Californium), has been proven to h ...
... Only minute traces of technetium occur naturally in the Earth's crust—as a spontaneous fission product of uranium-238 or by neutron capture in molybdenum ores—but technetium is present naturally in red giant stars. No element with an atomic number greater than 98, (Californium), has been proven to h ...
Atomic Structure Test Review 2016
... You may need to check your notes for some definitions. Remember, resources are on ItsLearning. ...
... You may need to check your notes for some definitions. Remember, resources are on ItsLearning. ...
1 Chapter 4 Atomic Structure 4.1 Defining the Atom Early Models of
... An _____________ is the smallest particle of an element that retains it identity in a chemical reaction. The Greek philosopher Democritus (460 B.C. - 370 B.C) was among the first to suggest the existence of atoms. Democritus believed that atoms were indivisible and _______________________. Dalton's ...
... An _____________ is the smallest particle of an element that retains it identity in a chemical reaction. The Greek philosopher Democritus (460 B.C. - 370 B.C) was among the first to suggest the existence of atoms. Democritus believed that atoms were indivisible and _______________________. Dalton's ...
Station 1 - The Periodic Table, Molecules and Molecular
... 4. What is the mass in amu of a carbon-12 atom? Why is the atomic weight of carbon reported as 12.011 on the periodic table? 5. Only two isotopes of copper occur naturally, 63Cu (atomic mass = 62.9296 amu; abundance 69.17%) and 65Cu (atomic mass = 64.9278 amu; abundance 30.83%). Calculate the atomic ...
... 4. What is the mass in amu of a carbon-12 atom? Why is the atomic weight of carbon reported as 12.011 on the periodic table? 5. Only two isotopes of copper occur naturally, 63Cu (atomic mass = 62.9296 amu; abundance 69.17%) and 65Cu (atomic mass = 64.9278 amu; abundance 30.83%). Calculate the atomic ...
PowerPoint_Atomic Structure
... suggested that all matter was made up of tiny spheres that were able to bounce around with perfect elasticity and called them ...
... suggested that all matter was made up of tiny spheres that were able to bounce around with perfect elasticity and called them ...
Chapter 4 Notes - DunlapChemistry
... Elements combine in a certain proportion or ratio (by mass) to form a compound. Example: H2O is always 11% hydrogen and 89% oxygen ...
... Elements combine in a certain proportion or ratio (by mass) to form a compound. Example: H2O is always 11% hydrogen and 89% oxygen ...
atoms - My CCSD
... contain different numbers of PROTONS The “atomic number” of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus ...
... contain different numbers of PROTONS The “atomic number” of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus ...
Matter - Moodle
... • The chemical composition ______________________ A chemical property describes how a substance ________________ into a new substance Either by: • __________________ with other elements • _________________ __________________ into new substances ...
... • The chemical composition ______________________ A chemical property describes how a substance ________________ into a new substance Either by: • __________________ with other elements • _________________ __________________ into new substances ...
Document
... Chemical Changes and Properties of Matter • Chemical change or chemical reaction: • Making a NEW compound • The transformation of one or more atoms or molecules into one or more different molecules ...
... Chemical Changes and Properties of Matter • Chemical change or chemical reaction: • Making a NEW compound • The transformation of one or more atoms or molecules into one or more different molecules ...
A quick summary about atoms: Atomic masses and/or hydrogen
... molecules shoving particles around). This later won the Nobel Prize for Jean Perrin in 1926. ...
... molecules shoving particles around). This later won the Nobel Prize for Jean Perrin in 1926. ...
Chemistry - Spokane Public Schools
... 1. Atom – All matter is made of small particles called atoms. Atoms are the building blocks of matter. Anything that takes up space and has mass is matter. As we have learned matter consists of any solid, liquid, or gas. Forms of energy such as heat, light, and electricity are not forms of matter an ...
... 1. Atom – All matter is made of small particles called atoms. Atoms are the building blocks of matter. Anything that takes up space and has mass is matter. As we have learned matter consists of any solid, liquid, or gas. Forms of energy such as heat, light, and electricity are not forms of matter an ...
Independent Study: Nuclear Chemistry
... 22. Gamma rays can be stopped by an aluminum sheet. 23. The change of an atom into a new element is called a chemical change. 24. The first artificial transmutation was performed by Albert Einstein. 25. The rate at which a radioactive element decays is known as the half-life. 26. Devices used in sma ...
... 22. Gamma rays can be stopped by an aluminum sheet. 23. The change of an atom into a new element is called a chemical change. 24. The first artificial transmutation was performed by Albert Einstein. 25. The rate at which a radioactive element decays is known as the half-life. 26. Devices used in sma ...
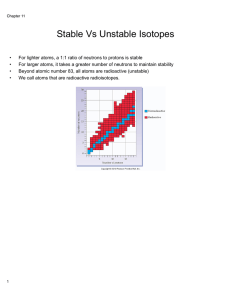
Isotope

Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, although all isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons in each atom. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos (ἴσος ""equal"") and topos (τόπος ""place""), meaning ""the same place""; thus, the meaning behind the name it is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic number identifies a specific element, but not the isotope; an atom of a given element may have a wide range in its number of neutrons. The number of nucleons (both protons and neutrons) in the nucleus is the atom's mass number, and each isotope of a given element has a different mass number.For example, carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are three isotopes of the element carbon with mass numbers 12, 13 and 14 respectively. The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that every carbon atom has 6 protons, so that the neutron numbers of these isotopes are 6, 7 and 8 respectively.