Atomic Number
... How to Read the Periodic Table -Each element is designated by its _____________________________ -Some symbols do not match actual element name because they were named under their ________________________________, -The first letter of an atomic symbol is ____________________ and the second letter is ...
... How to Read the Periodic Table -Each element is designated by its _____________________________ -Some symbols do not match actual element name because they were named under their ________________________________, -The first letter of an atomic symbol is ____________________ and the second letter is ...
Jeopardy
... • Q What subatomic particle was discovered by inference to account for the discrepancy between particle mass and atomic mass? • A Neutron ...
... • Q What subatomic particle was discovered by inference to account for the discrepancy between particle mass and atomic mass? • A Neutron ...
Ch 3: Atoms
... isotopes of an element – is a number with a decimal – is always the larger number on the periodic table. mass number (A) - sum of the protons and neutrons in a nucleus this number is rounded from atomic mass due to the fact that there are isotopes # neutrons = A - Z example - # of neutrons in Li = 6 ...
... isotopes of an element – is a number with a decimal – is always the larger number on the periodic table. mass number (A) - sum of the protons and neutrons in a nucleus this number is rounded from atomic mass due to the fact that there are isotopes # neutrons = A - Z example - # of neutrons in Li = 6 ...
Power point on the Periodic Table
... These metals have properties that you normally associate with the metals you encounter in everyday ...
... These metals have properties that you normally associate with the metals you encounter in everyday ...
Nuclear Decay
... can ionize, or strip the electrons from, atoms. Types of radiation that can ionize atoms are known as ionization radiation. When this makes contact with living tissue, it can result in burns, tumours and other harmful effects. It is important to protect tissues from exposure to ionizing radiation. A ...
... can ionize, or strip the electrons from, atoms. Types of radiation that can ionize atoms are known as ionization radiation. When this makes contact with living tissue, it can result in burns, tumours and other harmful effects. It is important to protect tissues from exposure to ionizing radiation. A ...
Unit 2 - Chapter 3 Elements, Atoms, Ions The elements Can we
... • #of neutrons = Mass number - Atomic number =A-Z ...
... • #of neutrons = Mass number - Atomic number =A-Z ...
are made up of
... that grouped elements accordingto their properties. They found that these properties repeated in a regular or periodic manner. This fact was used to predict properties of undiscovered elements. Reviewelectron arrangement from your textbook.In Table I, write.the maximum number of electrons that can f ...
... that grouped elements accordingto their properties. They found that these properties repeated in a regular or periodic manner. This fact was used to predict properties of undiscovered elements. Reviewelectron arrangement from your textbook.In Table I, write.the maximum number of electrons that can f ...
and View
... atom. * Number never changes* b. Isotopes—atoms of same element that have different numbers of neutrons. Ex: carbon-12, carbon-13, carbon-14 c. Mass number—number of neutrons plus protons in an atom. i. Neutron number is found by--Mass number - Atomic number _______________ Number of neutrons ...
... atom. * Number never changes* b. Isotopes—atoms of same element that have different numbers of neutrons. Ex: carbon-12, carbon-13, carbon-14 c. Mass number—number of neutrons plus protons in an atom. i. Neutron number is found by--Mass number - Atomic number _______________ Number of neutrons ...
Scientists` Consensus Ideas Atomic Structure and Nuclear Interactions
... 16. Radioactive decay occurs when unstable atoms break apart. Some isotopes of elements are not stable. The nucleus of an unstable atom eventually decays (breaks apart), sometimes forming atoms with a different number of protons or neutrons, and always emitting (releasing) fast-moving particles and ...
... 16. Radioactive decay occurs when unstable atoms break apart. Some isotopes of elements are not stable. The nucleus of an unstable atom eventually decays (breaks apart), sometimes forming atoms with a different number of protons or neutrons, and always emitting (releasing) fast-moving particles and ...
History - E. R. Greenman
... Used electric charge to show cathode rays were particles with negative charge Used varying electric currents to determine charge to mass ratio ...
... Used electric charge to show cathode rays were particles with negative charge Used varying electric currents to determine charge to mass ratio ...
NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY PACKET - Student
... Spontaneous decay can involve the release of alpha particles, beta particles, positrons and/or gamma radiation from the nucleus of an unstable isotope. These emissions differ in mass, charge, and ionizing power, and penetrating power. (3.1p) Nuclear reactions include natural and artificial transmuta ...
... Spontaneous decay can involve the release of alpha particles, beta particles, positrons and/or gamma radiation from the nucleus of an unstable isotope. These emissions differ in mass, charge, and ionizing power, and penetrating power. (3.1p) Nuclear reactions include natural and artificial transmuta ...
Chapter 5 The Structure of the Atom
... 2. A particle of matter smaller than the atom had to exist. 3. The atom was divisible. 4. Called the negatively particles “corpuscles” (now called electrons) 5. Since the gas was known to be neutral, there had to be positive charged particles in the gas. ...
... 2. A particle of matter smaller than the atom had to exist. 3. The atom was divisible. 4. Called the negatively particles “corpuscles” (now called electrons) 5. Since the gas was known to be neutral, there had to be positive charged particles in the gas. ...
9April2012 Notes
... the size of protons and neutrons (6) protons & neutrons are each 1 atomic mass unit (abbreviated “amu”) (7) the atomic number on the periodic table is equal to the # of protons for that element (8) the mass listed on the periodic table is the weighted average mass, thought of in terms of either atom ...
... the size of protons and neutrons (6) protons & neutrons are each 1 atomic mass unit (abbreviated “amu”) (7) the atomic number on the periodic table is equal to the # of protons for that element (8) the mass listed on the periodic table is the weighted average mass, thought of in terms of either atom ...
Atomic Timeline - Ms Brown`s Chemistry Page
... • John Dalton formulated the Atomic Theory which states that: atoms of an element are different than atoms of other elements; atoms of one element are the same; that atoms of different elements can be combined; that atoms cannot be divided or separated; and that elements are made of tiny particles c ...
... • John Dalton formulated the Atomic Theory which states that: atoms of an element are different than atoms of other elements; atoms of one element are the same; that atoms of different elements can be combined; that atoms cannot be divided or separated; and that elements are made of tiny particles c ...
Atoms and their Structure
... century BC – world made up of empty space and tiny particles called atoms (atomos)‘indivisible’ – Hypothesized without using experiments ...
... century BC – world made up of empty space and tiny particles called atoms (atomos)‘indivisible’ – Hypothesized without using experiments ...
Atomic Information
... number of protons equals the number of electrons. • If electrons are added or taken away, the ratio between protons and electrons becomes imbalanced and the atom will have a charge. ...
... number of protons equals the number of electrons. • If electrons are added or taken away, the ratio between protons and electrons becomes imbalanced and the atom will have a charge. ...
Standard 5 Notes
... Dalton studied many ideas about atoms and developed the first atomic theory ...
... Dalton studied many ideas about atoms and developed the first atomic theory ...
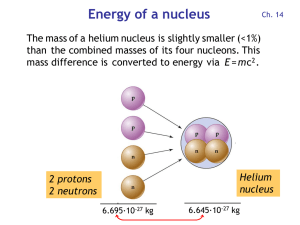
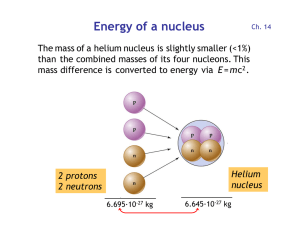
Energy per nucleon
... a black hole (> 3 solar masses) or a neutron star (between 1.4 and 3 solar masses), where the atoms collapse into a single huge nucleus. Lighter stars become white dwarfs . ...
... a black hole (> 3 solar masses) or a neutron star (between 1.4 and 3 solar masses), where the atoms collapse into a single huge nucleus. Lighter stars become white dwarfs . ...
ATOMS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE chapter three
... – This makes the mass of different atoms of the same element different. – The average mass is a weighted number so that more common isotopes have a greater affect on the average than rare isotopes. ...
... – This makes the mass of different atoms of the same element different. – The average mass is a weighted number so that more common isotopes have a greater affect on the average than rare isotopes. ...
Isotope

Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, although all isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons in each atom. The term isotope is formed from the Greek roots isos (ἴσος ""equal"") and topos (τόπος ""place""), meaning ""the same place""; thus, the meaning behind the name it is that different isotopes of a single element occupy the same position on the periodic table. The number of protons within the atom's nucleus is called atomic number and is equal to the number of electrons in the neutral (non-ionized) atom. Each atomic number identifies a specific element, but not the isotope; an atom of a given element may have a wide range in its number of neutrons. The number of nucleons (both protons and neutrons) in the nucleus is the atom's mass number, and each isotope of a given element has a different mass number.For example, carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14 are three isotopes of the element carbon with mass numbers 12, 13 and 14 respectively. The atomic number of carbon is 6, which means that every carbon atom has 6 protons, so that the neutron numbers of these isotopes are 6, 7 and 8 respectively.