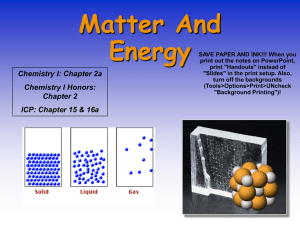
unit-3-atoms-and-nuclear - Waukee Community School District Blogs
... Nuclear Fission ■ Nuclear Fission = a very heavy nucleus splits into more stable nuclei or intermediate mass and releases large amounts of energy – Can occur spontaneously or when nuclei are bombarded with particles. – A chain reaction = a reaction in which the material that starts the reaction is ...
... Nuclear Fission ■ Nuclear Fission = a very heavy nucleus splits into more stable nuclei or intermediate mass and releases large amounts of energy – Can occur spontaneously or when nuclei are bombarded with particles. – A chain reaction = a reaction in which the material that starts the reaction is ...
Chapter 4 Study Guide
... 7. Dalton’s atomic theory stated that atoms of different elements combine in ...
... 7. Dalton’s atomic theory stated that atoms of different elements combine in ...
Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... 17. Alpha particles beamed at thin metal foil may A) pass directly through without changing direction B) be slightly diverted by attraction to electrons C) be reflected by direct contact with nuclei D) A and C E) A, B, and C 18. Which one of the following statements about atomic structure is false? ...
... 17. Alpha particles beamed at thin metal foil may A) pass directly through without changing direction B) be slightly diverted by attraction to electrons C) be reflected by direct contact with nuclei D) A and C E) A, B, and C 18. Which one of the following statements about atomic structure is false? ...
ViewpointAPBiology
... Atomic structure determines behavior of an element Atoms combine by chemical bonding to form ...
... Atomic structure determines behavior of an element Atoms combine by chemical bonding to form ...
Semester I CP Chemistry Review
... for your choice. a. Na or Li - Na because atomic radius increases as you go down the group, plus Na has 3 energy levels and Li only has 2. b. Sr or Mg – Sr. Sr has 5 energy levels and Mg only has 3. c. C or Ge – Ge has 4 energy levels, C has 2 d. Se or O – Se has 4 energy levels, O has 2 ...
... for your choice. a. Na or Li - Na because atomic radius increases as you go down the group, plus Na has 3 energy levels and Li only has 2. b. Sr or Mg – Sr. Sr has 5 energy levels and Mg only has 3. c. C or Ge – Ge has 4 energy levels, C has 2 d. Se or O – Se has 4 energy levels, O has 2 ...
IsotopeGeochemistry Chapter1 - Earth and Atmospheric Sciences
... surprisingly). Other isotopic studies revealed changes in the ocean circulation system as the last ice age ended. Changes in ocean circulation may also be an important feedback mechanism affecting climate. Twenty-five years ago, all this seemed very interesting, but not very relevant. Today, it prov ...
... surprisingly). Other isotopic studies revealed changes in the ocean circulation system as the last ice age ended. Changes in ocean circulation may also be an important feedback mechanism affecting climate. Twenty-five years ago, all this seemed very interesting, but not very relevant. Today, it prov ...
No Slide Title
... The metals in these two groups have similar outer electron configurations, with one electron in the outermost s orbital. Chemical properties are quite different due to difference in the ionization energy. ...
... The metals in these two groups have similar outer electron configurations, with one electron in the outermost s orbital. Chemical properties are quite different due to difference in the ionization energy. ...
In 1869, Russia`s Dmitri Mendeleev and Germany`s Lothar Meyer
... Chemists can change the number of electrons in an atom, but they can NOT change the number of protons in an atom. ...
... Chemists can change the number of electrons in an atom, but they can NOT change the number of protons in an atom. ...
Dalton Model of the Atom - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... • Each compound has a specific ratio of elements • It is a ratio by mass • Water is always 8 grams of oxygen for every one gram of hydrogen ...
... • Each compound has a specific ratio of elements • It is a ratio by mass • Water is always 8 grams of oxygen for every one gram of hydrogen ...
Nuclear Reactions - Manasquan Public Schools
... Because of their large mass and charge, alpha particles do not travel very far and are not very penetrating. • A sheet of paper or the surface of your skin can stop them. – But radioisotopes that emit alpha particles can cause harm when ingested. – Once inside the body, the particles don’t have to t ...
... Because of their large mass and charge, alpha particles do not travel very far and are not very penetrating. • A sheet of paper or the surface of your skin can stop them. – But radioisotopes that emit alpha particles can cause harm when ingested. – Once inside the body, the particles don’t have to t ...
Chemistry- CST Review
... Standard 6- Solutions 1. Define solute and solvent. Salt is dissolved in a glass of water. Which is the solute? Which is the solvent? Solute is the substance being dissolved and it is present in lesser amount. The solvent is usually a liquid and present in the greater amount. Salt is a solute and wa ...
... Standard 6- Solutions 1. Define solute and solvent. Salt is dissolved in a glass of water. Which is the solute? Which is the solvent? Solute is the substance being dissolved and it is present in lesser amount. The solvent is usually a liquid and present in the greater amount. Salt is a solute and wa ...
Chapter 11 Evidence for Strong and Weak Forces in Nuclei
... 11.5 1st Proof that Neutrons and Weak Force Do Not Exist in Nuclei Consider the natural decay of Tritium 3H1 with a half-life of 12.33 years into 3He2 and an escaping electron which then is captured as an orbiting electron of the Helium nucleus. This situation is clearly one where the exact same am ...
... 11.5 1st Proof that Neutrons and Weak Force Do Not Exist in Nuclei Consider the natural decay of Tritium 3H1 with a half-life of 12.33 years into 3He2 and an escaping electron which then is captured as an orbiting electron of the Helium nucleus. This situation is clearly one where the exact same am ...
Help us improve Wikipedia by supporting it financially
... The lightest elements are hydrogen and helium, both theoretically created by Big Bang nucleosynthesis during the first 20 minutes of the universe[10] in a ratio of around 3:1 by mass (approximately 12:1 by number of atoms). Almost all other elements found in nature, including some further hydrogen a ...
... The lightest elements are hydrogen and helium, both theoretically created by Big Bang nucleosynthesis during the first 20 minutes of the universe[10] in a ratio of around 3:1 by mass (approximately 12:1 by number of atoms). Almost all other elements found in nature, including some further hydrogen a ...
Radiometric Dating - Tulane University
... Prior to 1905 the best and most accepted age of the Earth was that proposed by Lord Kelvin based on the amount of time necessary for the Earth to cool to its present temperature from a completely liquid state. Although we now recognize lots of problems with that calculation, the age of 25 my was acc ...
... Prior to 1905 the best and most accepted age of the Earth was that proposed by Lord Kelvin based on the amount of time necessary for the Earth to cool to its present temperature from a completely liquid state. Although we now recognize lots of problems with that calculation, the age of 25 my was acc ...
February Homework Packet
... naturally occurring isotopes (2) masses and the half-lives of each of its isotopes (3) atomic number and half-lives of each of its isotopes (4) masses and the ratios of its naturally occurring isotopes 22. Which of these terms refers to matter that could be heterogeneous? ...
... naturally occurring isotopes (2) masses and the half-lives of each of its isotopes (3) atomic number and half-lives of each of its isotopes (4) masses and the ratios of its naturally occurring isotopes 22. Which of these terms refers to matter that could be heterogeneous? ...
Chapter 4 The Liquid Drop Model
... Nuclear masses are nowadays usually quoted in MeV/c2 but are still sometimes quoted in atomic mass units, defined to be 1/12 of the atomic mass of 12 6 C (Carbon). The conversion factor is 1 a.u. = 931.5 MeV/c2 Since different isotopes have different atomic mass numbers they will have different bin ...
... Nuclear masses are nowadays usually quoted in MeV/c2 but are still sometimes quoted in atomic mass units, defined to be 1/12 of the atomic mass of 12 6 C (Carbon). The conversion factor is 1 a.u. = 931.5 MeV/c2 Since different isotopes have different atomic mass numbers they will have different bin ...
APS Science Curriculum Unit Planner
... The smallest unique particle of matter is an atom and atoms can combine physically and chemically. Correlations Unifying Understanding ...
... The smallest unique particle of matter is an atom and atoms can combine physically and chemically. Correlations Unifying Understanding ...
for free - Livewire Learning
... The diagram shows two atoms of the element hydrogen, chemically combining with an atom of the element oxygen, to produce a molecule of the chemical compound water. 1. In 1808, John Dalton, the English Chemist, proposed that an element is made up of atoms and that every element has its own kind of at ...
... The diagram shows two atoms of the element hydrogen, chemically combining with an atom of the element oxygen, to produce a molecule of the chemical compound water. 1. In 1808, John Dalton, the English Chemist, proposed that an element is made up of atoms and that every element has its own kind of at ...
Chapter 2 BIO 100 Chemistry
... •If electrons in a covalent bond are shared equally, it’s a nonpolar covalent bond. • Covalent bond between two atoms of the same element is always nonpolar. •A covalent bond between atoms that have similar electronegativities is also nonpolar. •Because carbon and hydrogen do not differ greatly in e ...
... •If electrons in a covalent bond are shared equally, it’s a nonpolar covalent bond. • Covalent bond between two atoms of the same element is always nonpolar. •A covalent bond between atoms that have similar electronegativities is also nonpolar. •Because carbon and hydrogen do not differ greatly in e ...
Elements and Atoms
... atoms. While the atoms may have different weights and organization, they are all built in the same way. ...
... atoms. While the atoms may have different weights and organization, they are all built in the same way. ...
Chemistry 1st Semester Practice Exam
... 94. Water can be formed from the stoichiometric reaction of hydrogen with oxygen: ...
... 94. Water can be formed from the stoichiometric reaction of hydrogen with oxygen: ...