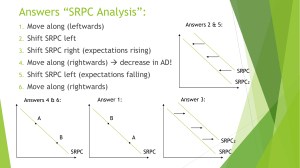
doc Test 3 (Midterm) 2013
... The following equations describe the commodity and money markets of an open economy for which the central bank uses the interest rate as its operating monetary policy instrument. ...
... The following equations describe the commodity and money markets of an open economy for which the central bank uses the interest rate as its operating monetary policy instrument. ...
Monetary Economics Lecture 1. October 30, 2007
... • Either because public has less money (monetarist view) or because interest rate increase reduces demand for equity (Keynesian) ...
... • Either because public has less money (monetarist view) or because interest rate increase reduces demand for equity (Keynesian) ...
The Demand for Base Money in Turkey: Implications for
... these measures partially restored the confidence in Turkish lira, which were severely deteriorating before 1994. The following section introduces the model. Section 4 and 5 estimate the model by using two alternative opportunity cost measures for holding money, the inflation rate and the depreciatio ...
... these measures partially restored the confidence in Turkish lira, which were severely deteriorating before 1994. The following section introduces the model. Section 4 and 5 estimate the model by using two alternative opportunity cost measures for holding money, the inflation rate and the depreciatio ...
money - theevanthompson
... setup a marketplace for these goods in your classroom. ► There is no money in this economy. ► Draw pictures of these items onto the paper sheets provided. ► Then use them for the activity. ...
... setup a marketplace for these goods in your classroom. ► There is no money in this economy. ► Draw pictures of these items onto the paper sheets provided. ► Then use them for the activity. ...
SOTU and the Contemporary Macroeconomic Consensus
... FED policy to steadily increase the money supply to steadily increase GDP regardless of business cycle Take all decision-making away from politicians & avoid the lag that comes with discretionary fiscal policy In fact, discretionary fiscal policy only prolongs recession Very little contempor ...
... FED policy to steadily increase the money supply to steadily increase GDP regardless of business cycle Take all decision-making away from politicians & avoid the lag that comes with discretionary fiscal policy In fact, discretionary fiscal policy only prolongs recession Very little contempor ...
Session 1: Micro-Economics
... – How Banks developed – the Goldsmith Story – Modern Fractional-Reserve Banking – Legal Reserve requirement ...
... – How Banks developed – the Goldsmith Story – Modern Fractional-Reserve Banking – Legal Reserve requirement ...
MACROECONOMICS. FALL 2010. EXAM 1.
... b. What does the assumption of constant velocity of money imply? a. The quantity equation is an identity that expresses the link between the number of transactions that people make and how much money they hold. We write it as Money × Velocity = Price × Transactions M × V = P × T. The right-hand side ...
... b. What does the assumption of constant velocity of money imply? a. The quantity equation is an identity that expresses the link between the number of transactions that people make and how much money they hold. We write it as Money × Velocity = Price × Transactions M × V = P × T. The right-hand side ...
Chapter 4 -- The IS/LM Model
... Considering Additional Behavior (Curve #2) Extra behavior -- decisions to hold money and financial assets. The Demand for Money -- The decision of how much of total wealth should be held as money (I.e. currency and checkable deposits). ...
... Considering Additional Behavior (Curve #2) Extra behavior -- decisions to hold money and financial assets. The Demand for Money -- The decision of how much of total wealth should be held as money (I.e. currency and checkable deposits). ...
Spring Exam Study Guide
... Prices are determined by supply and demand 88. Which question addresses the most fundamental issue for an economic system? What goods will be produced? 89. Which factor is most fundamental in determining what a market economy will produce? Price 90. _____ are accounts that require the deposit to rem ...
... Prices are determined by supply and demand 88. Which question addresses the most fundamental issue for an economic system? What goods will be produced? 89. Which factor is most fundamental in determining what a market economy will produce? Price 90. _____ are accounts that require the deposit to rem ...
WORLD
... responsibility, but it is a frank admission of the limits of monetary policy. If printing money were the solution to unemployment and sluggish growth, Bernanke could just drop dollars like manna from heaven. What the United States needs is not another dose of monetary stimulus but a more certain pol ...
... responsibility, but it is a frank admission of the limits of monetary policy. If printing money were the solution to unemployment and sluggish growth, Bernanke could just drop dollars like manna from heaven. What the United States needs is not another dose of monetary stimulus but a more certain pol ...
Spring 2007
... 23) One line of the US Balance of Payments is called: “Private sales and purchases of assets.” One possible cause of a net increase in this line would be a) the Fed buying Chinese Treasury bonds. b) the Chinese central bank buying US Treasury bonds. c) Europeans increasing their holdings of American ...
... 23) One line of the US Balance of Payments is called: “Private sales and purchases of assets.” One possible cause of a net increase in this line would be a) the Fed buying Chinese Treasury bonds. b) the Chinese central bank buying US Treasury bonds. c) Europeans increasing their holdings of American ...
Ch 17 Economic Policy
... Senate but the Fed acts fairly independently – The Fed manages the government run central bank ...
... Senate but the Fed acts fairly independently – The Fed manages the government run central bank ...
APS7 - Cornell
... attempt to rid the economy of inflation. Ultimately, the economy went into a deep recession, but before it did, interest rates went to record levels. a. Explain how this policy mix led to very high interest rates. b. Show graphically the effect of the high interest rates on the foreign exchange mark ...
... attempt to rid the economy of inflation. Ultimately, the economy went into a deep recession, but before it did, interest rates went to record levels. a. Explain how this policy mix led to very high interest rates. b. Show graphically the effect of the high interest rates on the foreign exchange mark ...
Name - Instructure
... The mainstream view of macroeconomic instability is Keynesian-based and focuses on aggregate spending and its components. Particularly significant are changes in investment spending, which change aggregate demand and, occasionally, adverse supply shocks which change aggregate supply. Investment spen ...
... The mainstream view of macroeconomic instability is Keynesian-based and focuses on aggregate spending and its components. Particularly significant are changes in investment spending, which change aggregate demand and, occasionally, adverse supply shocks which change aggregate supply. Investment spen ...
Word Document
... Keynes: interest rates should be in a narrow band: when interest high, people expect it to fall. Keynes: If interest rates rise, then the price of a bond falls. So if ie↑, expect a capital loss from bonds. Baumol & Tobin showed transactions and precautionary demand are also sensitive to the in ...
... Keynes: interest rates should be in a narrow band: when interest high, people expect it to fall. Keynes: If interest rates rise, then the price of a bond falls. So if ie↑, expect a capital loss from bonds. Baumol & Tobin showed transactions and precautionary demand are also sensitive to the in ...
Causes of the Great Depression
... they began to fall because they had a little people a large supply of panicked and sold product but no out of fear demand for it ...
... they began to fall because they had a little people a large supply of panicked and sold product but no out of fear demand for it ...